Business
Column: Bowing to business and the right wing, the SEC issues a pathetically watered-down climate disclosure rule

Corporate managements nationwide undoubtedly breathed sighs of relief Wednesday, when the Securities and Exchange Commission approved a rule mandating their disclosures of greenhouse gas emissions and risks from global warming.
That’s because the rule is much weaker than its original version, which was first published in March 2022. The final version removed provisions requiring disclosure of some emissions produced by a company’s entire business chain and expanded exemptions for smaller companies.
But if managements think they’ll be able to avoid making more complete disclosures than the SEC is requiring, they have another think coming.
Far more investors are making investment decisions that are informed by climate risk, and far more companies are making disclosures about climate risk.
— SEC Chairman Gary Gensler
Shareholders are demanding more. So is the European Union, which has enacted rules requiring all companies with EU branches employing more than 250 workers, more than $42 million in European revenues or more than $21 million in capital assets to make the very disclosures that the SEC dropped from its mandate, starting in 2025.
More than 3,200 U.S. corporations are expected to become subject to the EU mandate.
Then there’s California, which last year enacted two laws requiring companies with annual revenues of more than $500 million and business activities in the state to disclose their climate-related economic risks; companies with revenues of more than $1 billion face more stringent requirements to report the full range of their emissions, similar to the EU mandate.
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce and several other business lobbying groups have already filed a federal lawsuit to overturn the California law, in which they estimate that the laws will cover 10,000 companies. (Rule of thumb: If the Chamber of Commerce is on one side of a lawsuit, you can rarely go wrong in assuming the public interest is on the other side.)
In any event, the laws have the support of numerous corporations with headquarters or sizable business interests in California, including Microsoft and Apple.
“We know that consistent, comparable, and reliable emissions data at scale is necessary to fully assess the global economy’s risk exposure and to navigate the path to a net-zero future,” Microsoft and 14 other businesses wrote in an Aug. 14 letter to state legislative leaders.
The state’s legislation, they wrote, “would break new ground on ambitious climate policy and would allow the largest economic actors to fully understand and mitigate their harmful greenhouse gas emissions.”
Meanwhile, 10 states with Republican political leaderships have signaled that they will sue to invalidate the SEC initiative, on the claim that the rule “exceeds the agency’s statutory authority.”
All this does more than hint at the headwinds the SEC faced in crafting its final disclosure rule. These included objections from many in the business community and conservative politicians pursuing their fatuous campaigns against ESG policies — environmental, social and governance — of corporations and investment firms.
The SEC’s Democratic majority, led by its chairman, Gary Gensler, also plainly harbored concerns about how its more expansive rule proposal might fare with a conservative federal judiciary, including a Supreme Court that seems to be searching for grounds to pare back the reach of federal regulatory agencies, if not invalidate their authority altogether.
Gensler observed after the commission vote that its goal was to provide for consistency in how companies report information that most are already compiling.
“Far more investors are making investment decisions that are informed by climate risk, and far more companies are making disclosures about climate risk,” he said. He didn’t specifically defend the SEC’s weakening of its initial proposal, except to say that the plan was revised “based upon public feedback.”
Let’s take a closer look at the issues and the political context.
First, here’s what the SEC’s rule encompasses.
At its core are disclosures about emissions of greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide — emissions that trap heat within the Earth’s atmosphere, driving global temperatures higher. Global warming produces major changes in climatological manifestations — more storms of greater severity, droughts, melting ice producing a rise in sea levels, and so on.
Emissions fall into three general categories. Scope 1 emissions are those a company produces directly, say from its delivery trucks, boilers, refineries, manufacturing plants. Scope 2 emissions are those it produces indirectly, for example, from the power plants from which it purchases its electricity.
Scope 3 emissions are the most contentious. They’re produced by a company’s vendors when it orders supplies and consumers when they use its products. In general this is the largest category, accounting for 70% of total emissions for many businesses and as much as 90% for some. But they can be hard to define, calculate and manage.
The SEC originally contemplated requiring disclosures of all three categories. The final rule removed the Scope 3 reporting requirement entirely, and mandates reporting of Scope 1 and 2 emissions only when they have or are likely to have “a material impact on the registrant’s business strategy, results of operations, or financial condition.”
Those changes gratified some business organizations and their henchpersons in Congress, but disturbed environmental groups. Removing Scope 3 disclosures, said Danielle Fugere, president of the Berkeley-based environmental organization As You Sow, “creates a significant hole in shareholders’ understanding of climate risk.”
The fact is that full disclosure of these risks is something that regulators around the world, as well as shareholders and investors, have been demanding for years. Who’s against it? Head-in-the-sand Republicans and right-wing culture warriors, that’s who.
Hester Peirce, one of the two Republicans on the SEC, carried their ball into its meeting room. Weak as the final rule is, she wasn’t satisfied. As enacted, she groused in a statement Wednesday, the rule “still promises to spam investors with details about the Commission’s pet topic of the day — climate.”
That dismissal of global warming, an elemental threat to life on Earth, as a “pet topic” should tell you how fundamentally unserious GOP policymakers are about their responsibilities.
The anti-ESG cabal among state-level Republicans appears determined to undermine the interests of their own constituents, all for the sake of “owning the libs.”
Consider three states that have been among the leaders in banning investment firms from doing business with their governments because of the firms’ support for environmental policies: Texas, Florida and Louisiana.
Those are the three states that have led the nation in cumulative damage costs due to climate-related disasters from 1980 through 2022 — racking up expenses of $380 billion, $370 billion and $290 billion, respectively.
The general approach of disclosure critics has two threads. One is to pretend that the effects of global warming are irrelevant to the operations and the future of most businesses. The other is to assert that they’re too nebulous to calculate or, alternatively, that performing the calculations is just too burdensome.
Neither argument holds water.
I reported in 2021 that shareholders were already asking for more disclosures from managements about how their activities contribute to climate change, and more about how climate change will affect their destinies.
Fossil fuel companies weren’t the only targets of shareholder resolutions on these topics — they also appeared on the agendas of annual meetings of manufacturers, retailers, banks and many others.
In 2023, shareholder resolutions demanding climate and environmental disclosures dominated the proxy season with 146 filed, according to the Interfaith Center on Corporate Responsibility, which tracks ESG issues. Many won plurality support, but more than half dealing with climate were withdrawn after managements made commitments to their sponsors to meet their disclosure goals.
Investment watchdogs are on the case. Fitch Ratings, which analyzes corporate creditworthiness, says that as many as 20% of the 1,650 corporations it studied might face ratings downgrades due to their “climate vulnerabilities if such risks are not mitigated” by 2035. BlackRock, the world’s largest asset management firm, has said it’s not backing off from pushing corporations to disclose how they address climate-related risks.
The U.S. government’s National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration identified 28 weather- and climate-related disasters costing $1 billion or more in 2023, including a drought, four floods, 22 severe storms and a wildfire.
2023 brought a record number of weather- and climate-related disasters costing more than $1 billion each to the U.S., with a toll of 492 deaths and damage of more than $90 billion.
(NOAA)
That was the highest number recorded since NOAA began taking count in 1980 and the ninth consecutive year in which 10 or more billion-dollar weather or climate disasters struck the U.S.
NOAA’s initial estimate is that the 2023 disasters cost more than $90 billion, but it’s certain to rise, since the ultimate price tag of the 18 disasters reported in 2022 came to more than $165 billion. The disasters took 492 lives.
To put it another way, any management of a large business in the U.S. that thinks it can evade the costs of global warming is living in a dream world.
Global warming deniers in business and politics persist in treating the climate crisis as merely a ginned-up topic of debate. That’s the gist of the business lobby’s lawsuit over the California laws.
The lawsuit treats the laws, bizarrely, as infringements on companies’ 1st Amendment rights. The state, the plaintiffs assert, is forcing “thousands of companies to engage in controversial speech that they do not wish to make” — speech they say is “political, and thus controversial.”
This is absurd on its face — tantamount to Donald Trump’s claim that by urging his followers to march to the Capitol on Jan. 6, 2021, he was just exercising his right to free speech.
This would allow any mandated disclosure to be reduced to a free-speech violation — after all, any such disclosure must be expressed as a series of words.
The courts, including the Supreme Court, have generally rejected assertions that mandated disclosures violate the 1st Amendment when the disclosures serve a legitimate government interest, such as protecting investors from fraudulent claims, or providing investors with important information — for example, the level of emissions by a public corporation or its potential exposure to global warming.
In this case, the business lobbies stretch to the breaking point their description of the state’s mandated emission disclosures as mere speech. They also assert that the state’s purpose is merely to “fuel pressure campaigns against business.”
They can’t make that claim stick with a straight face, so they misrepresent the laws. Here’s how they quote a state Senate analysis of one of the statutes: “‘For companies, the knowledge’ that their compelled statements ‘will be publicly available might encourage them to take meaningful steps’ to support the policy goals of the state.”
That’s a flagrant misquotation. Here’s what the analysis actually said: “For companies, the knowledge that their emissions will be publicly available might encourage them to take meaningful steps to reduce GHG emissions.” The words and phrases that the plaintiffs replaced with their own tendentious language are in italics.
It’s not the “compelled statements” that will be publicly available, but the actual level of their emissions. If the result is “pressure campaigns” aimed at prompting the companies to be cleaner, what’s wrong with that?
As for the state’s “policy goals,” the laws aren’t aimed at supporting a goal cherished by the liberal legislators of California, as the plaintiffs want you to think, but the national and international goal of reducing greenhouse gases.
None of this is to say that the Chamber of Commerce and its fellow lobbies won’t prevail in court. But it’s proper to note that when the best arguments they muster are based on lies and misrepresentations, they might not have many other arrows in their quiver.

Business
Trump orders federal agencies to stop using Anthropic’s AI after clash with Pentagon

President Trump on Friday directed federal agencies to stop using technology from San Francisco artificial intelligence company Anthropic, escalating a high-profile clash between the AI startup and the Pentagon over safety.
In a Friday post on the social media site Truth Social, Trump described the company as “radical left” and “woke.”
“We don’t need it, we don’t want it, and will not do business with them again!” Trump said.
The president’s harsh words mark a major escalation in the ongoing battle between some in the Trump administration and several technology companies over the use of artificial intelligence in defense tech.
Anthropic has been sparring with the Pentagon, which had threatened to end its $200-million contract with the company on Friday if it didn’t loosen restrictions on its AI model so it could be used for more military purposes. Anthropic had been asking for more guarantees that its tech wouldn’t be used for surveillance of Americans or autonomous weapons.
The tussle could hobble Anthropic’s business with the government. The Trump administration said the company was added to a sweeping national security blacklist, ordering federal agencies to immediately discontinue use of its products and barring any government contractors from maintaining ties with it.
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth, who met with Anthropic’s Chief Executive Dario Amodei this week, criticized the tech company after Trump’s Truth Social post.
“Anthropic delivered a master class in arrogance and betrayal as well as a textbook case of how not to do business with the United States Government or the Pentagon,” he wrote Friday on social media site X.
Anthropic didn’t immediately respond to a request for comment.
Anthropic announced a two-year agreement with the Department of Defense in July to “prototype frontier AI capabilities that advance U.S. national security.”
The company has an AI chatbot called Claude, but it also built a custom AI system for U.S. national security customers.
On Thursday, Amodei signaled the company wouldn’t cave to the Department of Defense’s demands to loosen safety restrictions on its AI models.
The government has emphasized in negotiations that it wants to use Anthropic’s technology only for legal purposes, and the safeguards Anthropic wants are already covered by the law.
Still, Amodei was worried about Washington’s commitment.
“We have never raised objections to particular military operations nor attempted to limit use of our technology in an ad hoc manner,” he said in a blog post. “However, in a narrow set of cases, we believe AI can undermine, rather than defend, democratic values.”
Tech workers have backed Anthropic’s stance.
Unions and worker groups representing 700,000 employees at Amazon, Google and Microsoft said this week in a joint statement that they’re urging their employers to reject these demands as well if they have additional contracts with the Pentagon.
“Our employers are already complicit in providing their technologies to power mass atrocities and war crimes; capitulating to the Pentagon’s intimidation will only further implicate our labor in violence and repression,” the statement said.
Anthropic’s standoff with the U.S. government could benefit its competitors, such as Elon Musk’s xAI or OpenAI.
Sam Altman, chief executive of OpenAI, the company behind ChatGPT and one of Anthropic’s biggest competitors, told CNBC in an interview that he trusts Anthropic.
“I think they really do care about safety, and I’ve been happy that they’ve been supporting our war fighters,” he said. “I’m not sure where this is going to go.”
Anthropic has distinguished itself from its rivals by touting its concern about AI safety.
The company, valued at roughly $380 billion, is legally required to balance making money with advancing the company’s public benefit of “responsible development and maintenance of advanced AI for the long-term benefit of humanity.”
Developers, businesses, government agencies and other organizations use Anthropic’s tools. Its chatbot can generate code, write text and perform other tasks. Anthropic also offers an AI assistant for consumers and makes money from paid subscriptions as well as contracts. Unlike OpenAI, which is testing ads in ChatGPT, Anthropic has pledged not to show ads in its chatbot Claude.
The company has roughly 2,000 employees and has revenue equivalent to about $14 billion a year.
Business
Video: The Web of Companies Owned by Elon Musk

new video loaded: The Web of Companies Owned by Elon Musk

By Kirsten Grind, Melanie Bencosme, James Surdam and Sean Havey
February 27, 2026
Business
Commentary: How Trump helped foreign markets outperform U.S. stocks during his first year in office
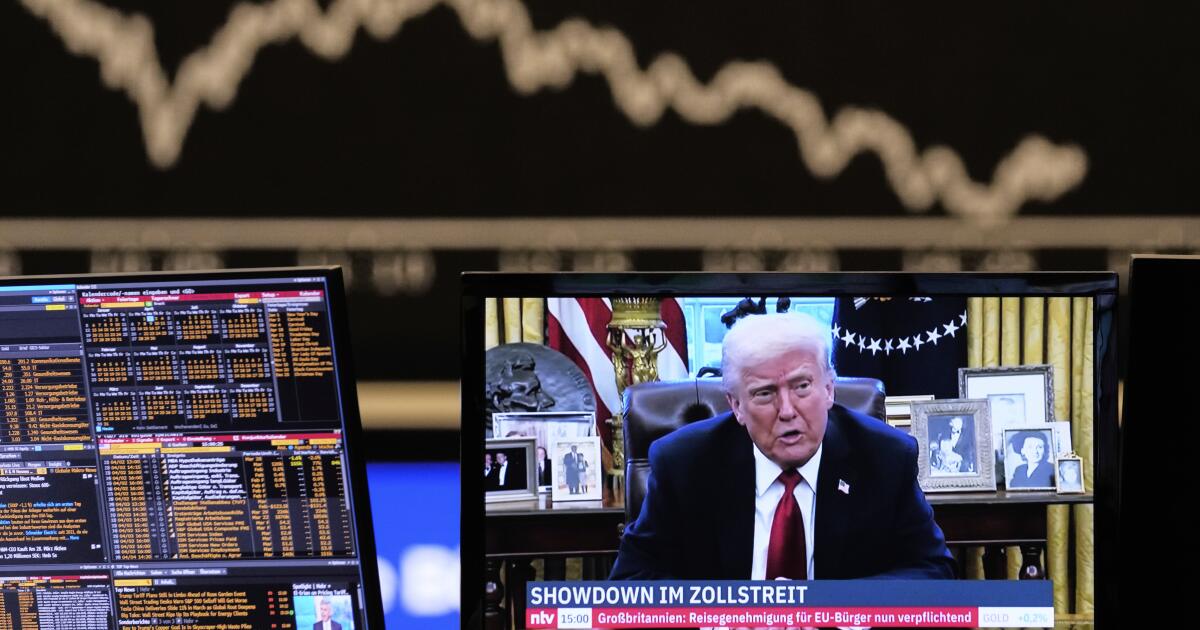
Trump has crowed about the gains in the U.S. stock market during his term, but in 2025 investors saw more opportunity in the rest of the world.
If you’re a stock market investor you might be feeling pretty good about how your portfolio of U.S. equities fared in the first year of President Trump’s term.
All the major market indices seemed to be firing on all cylinders, with the Standard & Poor’s 500 index gaining 17.9% through the full year.
But if you’re the type of investor who looks for things to regret, pay no attention to the rest of the world’s stock markets. That’s because overseas markets did better than the U.S. market in 2025 — a lot better. The MSCI World ex-USA index — that is, all the stock markets except the U.S. — gained more than 32% last year, nearly double the percentage gains of U.S. markets.
That’s a major departure from recent trends. Since 2013, the MSCI US index had bested the non-U.S. index every year except 2017 and 2022, sometimes by a wide margin — in 2024, for instance, the U.S. index gained 24.6%, while non-U.S. markets gained only 4.7%.
The Trump trade is dead. Long live the anti-Trump trade.
— Katie Martin, Financial Times
Broken down into individual country markets (also by MSCI indices), in 2025 the U.S. ranked 21st out of 23 developed markets, with only New Zealand and Denmark doing worse. Leading the pack were Austria and Spain, with 86% gains, but superior records were turned in by Finland, Ireland and Hong Kong, with gains of 50% or more; and the Netherlands, Norway, Britain and Japan, with gains of 40% or more.
Investment analysts cite several factors to explain this trend. Judging by traditional metrics such as price/earnings multiples, the U.S. markets have been much more expensive than those in the rest of the world. Indeed, they’re historically expensive. The Standard & Poor’s 500 index traded in 2025 at about 23 times expected corporate earnings; the historical average is 18 times earnings.
Investment managers also have become nervous about the concentration of market gains within the U.S. technology sector, especially in companies associated with artificial intelligence R&D. Fears that AI is an investment bubble that could take down the S&P’s highest fliers have investors looking elsewhere for returns.
But one factor recurs in almost all the market analyses tracking relative performance by U.S. and non-U.S. markets: Donald Trump.
Investors started 2025 with optimism about Trump’s influence on trading opportunities, given his apparent commitment to deregulation and his braggadocio about America’s dominant position in the world and his determination to preserve, even increase it.
That hasn’t been the case for months.
”The Trump trade is dead. Long live the anti-Trump trade,” Katie Martin of the Financial Times wrote this week. “Wherever you look in financial markets, you see signs that global investors are going out of their way to avoid Donald Trump’s America.”
Two Trump policy initiatives are commonly cited by wary investment experts. One, of course, is Trump’s on-and-off tariffs, which have left investors with little ability to assess international trade flows. The Supreme Court’s invalidation of most Trump tariffs and the bellicosity of his response, which included the immediate imposition of new 10% tariffs across the board and the threat to increase them to 15%, have done nothing to settle investors’ nerves.
Then there’s Trump’s driving down the value of the dollar through his agitation for lower interest rates, among other policies. For overseas investors, a weaker dollar makes U.S. assets more expensive relative to the outside world.
It would be one thing if trade flows and the dollar’s value reflected economic conditions that investors could themselves parse in creating a picture of investment opportunities. That’s not the case just now. “The current uncertainty is entirely man-made (largely by one orange-hued man in particular) but could well continue at least until the US mid-term elections in November,” Sam Burns of Mill Street Research wrote on Dec. 29.
Trump hasn’t been shy about trumpeting U.S. stock market gains as emblems of his policy wisdom. “The stock market has set 53 all-time record highs since the election,” he said in his State of the Union address Tuesday. “Think of that, one year, boosting pensions, 401(k)s and retirement accounts for the millions and the millions of Americans.”
Trump asserted: “Since I took office, the typical 401(k) balance is up by at least $30,000. That’s a lot of money. … Because the stock market has done so well, setting all those records, your 401(k)s are way up.”
Trump’s figure doesn’t conform to findings by retirement professionals such as the 401(k) overseers at Bank of America. They reported that the average account balance grew by only about $13,000 in 2025. I asked the White House for the source of Trump’s claim, but haven’t heard back.
Interpreting stock market returns as snapshots of the economy is a mug’s game. Despite that, at her recent appearance before a House committee, Atty. Gen. Pam Bondi tried to deflect questions about her handling of the Jeffrey Epstein records by crowing about it.
“The Dow is over 50,000 right now, she declared. “Americans’ 401(k)s and retirement savings are booming. That’s what we should be talking about.”
I predicted that the administration would use the Dow industrial average’s break above 50,000 to assert that “the overall economy is firing on all cylinders, thanks to his policies.” The Dow reached that mark on Feb. 6. But Feb. 11, the day of Bondi’s testimony, was the last day the index closed above 50,000. On Thursday, it closed at 49,499.50, or about 1.4% below its Feb. 10 peak close of 50,188.14.
To use a metric suggested by economist Justin Wolfers of the University of Michigan, if you invested $48,488 in the Dow on the day Trump took office last year, when the Dow closed at 48,448 points, you would have had $50,000 on Feb. 6. That’s a gain of about 3.2%. But if you had invested the same amount in the global stock market not including the U.S. (based on the MSCI World ex-USA index), on that same day you would have had nearly $60,000. That’s a gain of nearly 24%.
Broader market indices tell essentially the same story. From Jan. 17, 2025, the last day before Trump’s inauguration, through Thursday’s close, the MSCI US stock index gained a cumulative 16.3%. But the world index minus the U.S. gained nearly 42%.
The gulf between U.S. and non-U.S. performance has continued into the current year. The S&P 500 has gained about 0.74% this year through Wednesday, while the MSCI World ex-USA index has gained about 8.9%. That’s “the best start for a calendar year for global stocks relative to the S&P 500 going back to at least 1996,” Morningstar reports.
It wouldn’t be unusual for the discrepancy between the U.S. and global markets to shrink or even reverse itself over the course of this year.
That’s what happened in 2017, when overseas markets as tracked by MSCI beat the U.S. by more than three percentage points, and 2022, when global markets lost money but U.S. markets underperformed the rest of the world by more than five percentage points.
Economic conditions change, and often the stock markets march to their own drummers. The one thing less likely to change is that Trump is set to remain president until Jan. 20, 2029. Make your investment bets accordingly.
-

 World2 days ago
World2 days agoExclusive: DeepSeek withholds latest AI model from US chipmakers including Nvidia, sources say
-

 Massachusetts2 days ago
Massachusetts2 days agoMother and daughter injured in Taunton house explosion
-

 Montana1 week ago
Montana1 week ago2026 MHSA Montana Wrestling State Championship Brackets And Results – FloWrestling
-

 Louisiana5 days ago
Louisiana5 days agoWildfire near Gum Swamp Road in Livingston Parish now under control; more than 200 acres burned
-

 Oklahoma1 week ago
Oklahoma1 week agoWildfires rage in Oklahoma as thousands urged to evacuate a small city
-

 Denver, CO2 days ago
Denver, CO2 days ago10 acres charred, 5 injured in Thornton grass fire, evacuation orders lifted
-

 Technology7 days ago
Technology7 days agoYouTube TV billing scam emails are hitting inboxes
-

 Technology7 days ago
Technology7 days agoStellantis is in a crisis of its own making



















