Science
'I don't want him to go': An autistic teen and his family face stark choices
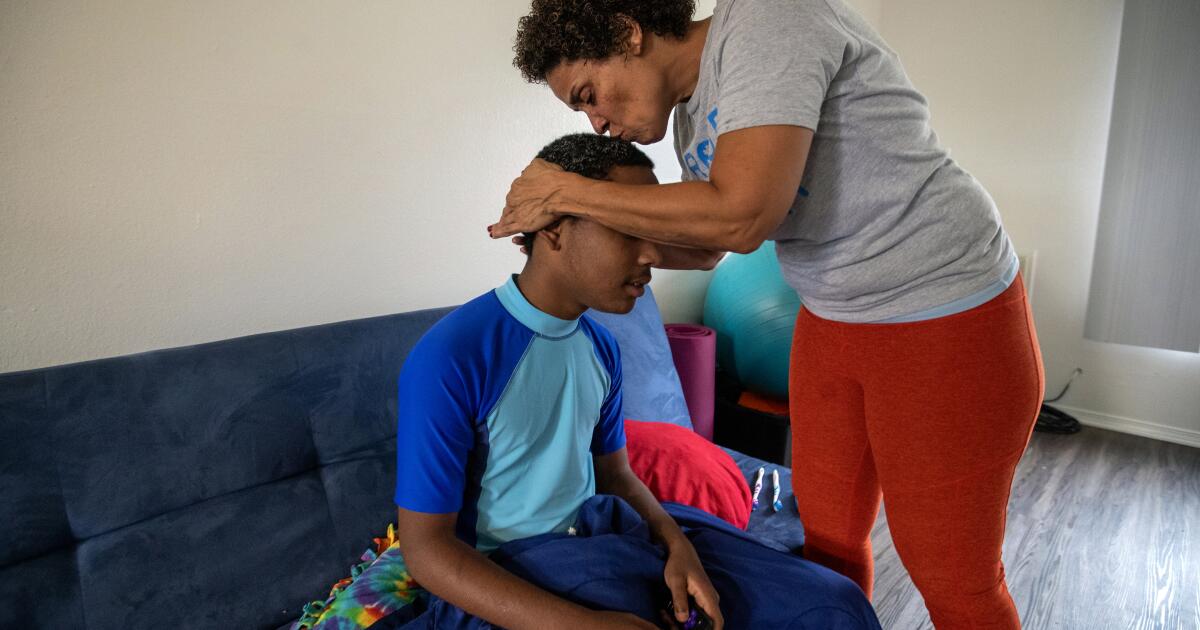

Christine LyBurtus was aching and fearful of what might happen when her 13-year-old son returned home.
Noah had been sent to Children’s Hospital of Orange County for a psychiatric hold lasting up to 72 hours after he punched at walls, flipped over a table, ripped out a chunk of his mother’s hair and tried to break a car window.
“There’s nothing else to call it except a psychotic episode,” LyBurtus said.
The clock was ticking on that August day in 2022. The single mother wanted help to prevent such an episode from happening again, maybe with a different medication. Hospital staff were waiting for a psychiatric bed, possibly at another hospital with a dedicated unit for patients with autism or other developmental disabilities.
But as the hours ran out on the hold, it became clear that wasn’t happening. LyBurtus brought Noah home to their Fullerton apartment.
“When he came back home, it kind of broke my heart,” said his sister, Karissa, who is two years older. “He looked like, ‘What the heck did you guys put me into?’”
Christine LyBurtus makes a snack for Noah.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
The next night, Noah was back in the ER after smashing a television and attacking his mother. This time, he was transferred to a different hospital for three weeks, prescribed medications for psychosis, and then sent to a residential facility in Garden Grove.
LyBurtus said she was told it would be a stopgap measure — just for three weeks — until she could line up more help at home. But when she phoned to ask about visiting her son, LyBurtus said she was told she couldn’t see him for a month.
“He lives here now,” someone told her, she said, and the staff needed time to “break him in.”
LyBurtus felt like she was being pushed to give up her son, instead of getting the help her family needed. She insisted on bringing him home.
::
Autism is a developmental condition that can shape how people think, communicate, move and process sensory information. When Noah was 3, a doctor noted he was a “very cute little boy” who played alone, rocked back and forth, and sometimes bit himself. Noah’s eye contact was “fleeting.” He could speak about 20 words, but often cried or pulled his mother’s hand to communicate.
The physician summed up his behavior as “characteristic of a DSM-IV diagnosis of autistic disorder.”
When he was in elementary school, LyBurtus stopped working full time outside the home and enrolled in a state program that paid her as his caregiver. She relies on Medi-Cal for his medical care, and much of his schooling has been in Orange County-run programs for children with moderate to severe disabilities.
Noah does not speak but sometimes uses pictures, an app on a tablet, or some sign language to communicate. When a reporter visited their home last year, Noah bobbed his head and shoulders as he listened to music on his iPad. He flapped his hands as LyBurtus made him a peanut-butter-and-banana smoothie, and then dutifully followed her instructions to chuck the peel and put the almond milk away. It was a good day, LyBurtus said with relief.
But on other days, LyBurtus said her son could be rigid; his demands, unpredictable. “Some days he’s fixated on having three pairs of pants on … Some days he wants to take seven showers. The next day, I can’t get him to take showers.”

Christine LyBurtus greets Noah as he arrives home from school.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
When frustrated, Noah might erupt, banging his head against walls and trying to jump out the windows of their apartment. He had kicked and bitten his mother when she tried to redirect him. In the worst instances, LyBurtus had resorted to hiding in the bathroom — her “safe room” — and urged Karissa to lock herself in the bedroom.
As Noah grew taller and stronger, LyBurtus stripped bare the walls of her apartment to try to make it safe, installed shatterproof windows and removed a knob from a closet door to prevent Noah from using it as a foothold to scale over the top of the closet door. She made sure to flag her address for the Fullerton Police Department so it knew her son was developmentally disabled.
“I’m just so grateful that my son never got shot,” LyBurtus said.
Each of the 911 calls was the start of a Sisyphean routine. Noah “has been challenging to place in [a] mental health facility due to behavioral care needs with severe autism,” a doctor wrote when he was back at Children’s Hospital of Orange County yet again.
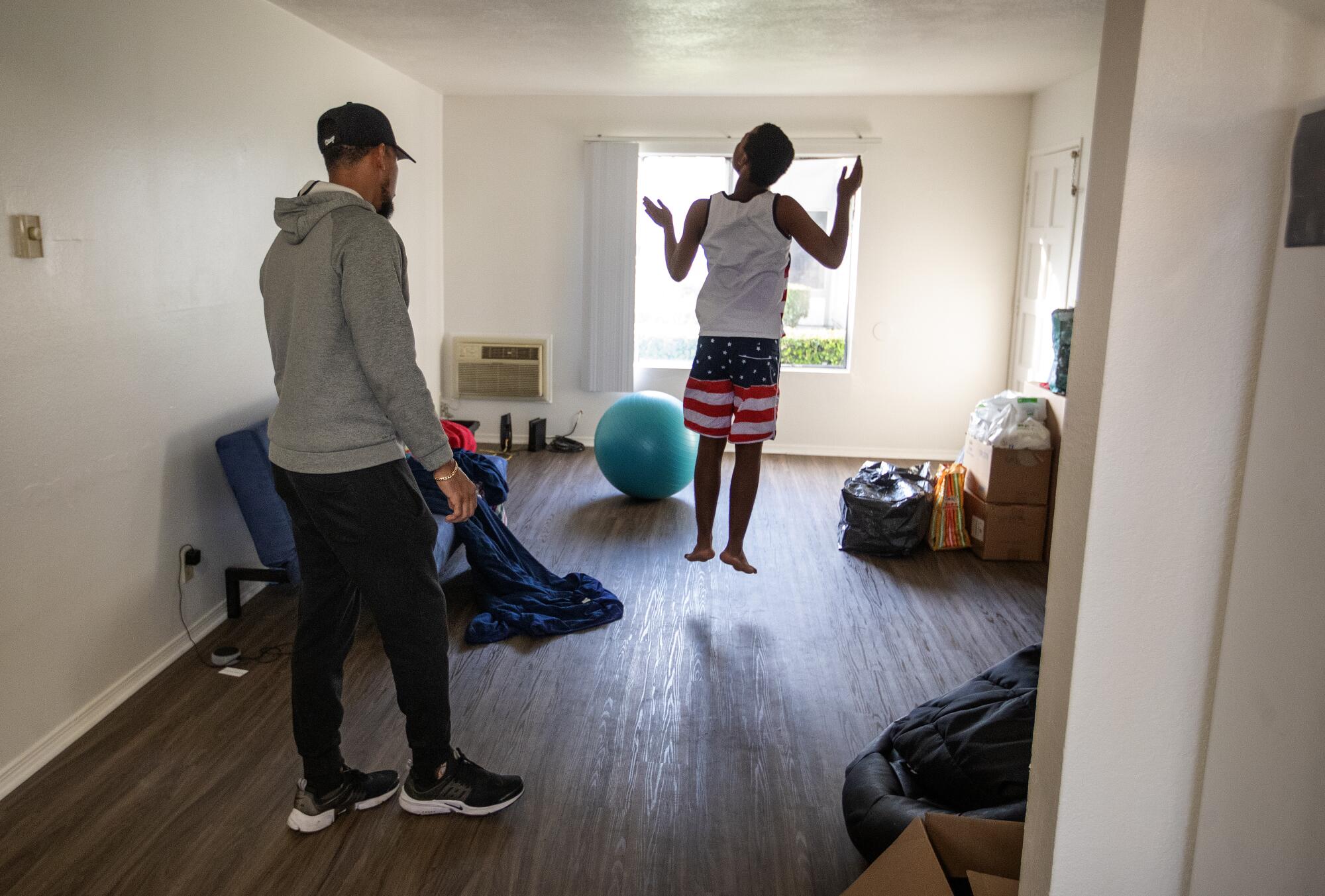

Noah leaps into the air inside his Fullerton home. At left is Terrence Morris, one of Noah’s caregivers.
(Mel Melcon / Los Angeles Times)
As the family tried to get through each crisis, LyBurtus was also facing a common struggle among parents of California children with disabilities: not getting the help they were supposed to receive from the state.
LyBurtus was getting assistance through a local regional center, one of the nonprofit agencies contracted by the California Department of Developmental Services. She said she’d been authorized to receive 40 hours weekly of respite care — meant to relieve families of children with disabilities for short periods — but was sometimes receiving only 12 to 16 hours.
She was also supposed to have two workers at a time, LyBurtus said, but caregivers were so scarce that she was scheduling one at a time in order to cover as many hours as she could.
In the meantime, Noah wasn’t sleeping and she was going through so much laundry detergent and quarters that her grocery budget was drained. At one point, she wanted to go to a food bank, but there would be no one to watch him.
“I could not be anymore tired and frustrated!!!!” she wrote to her regional center coordinator. “Is the only way Noah is going to get help [is] if I abandoned him and surrender him to the State!?!?”
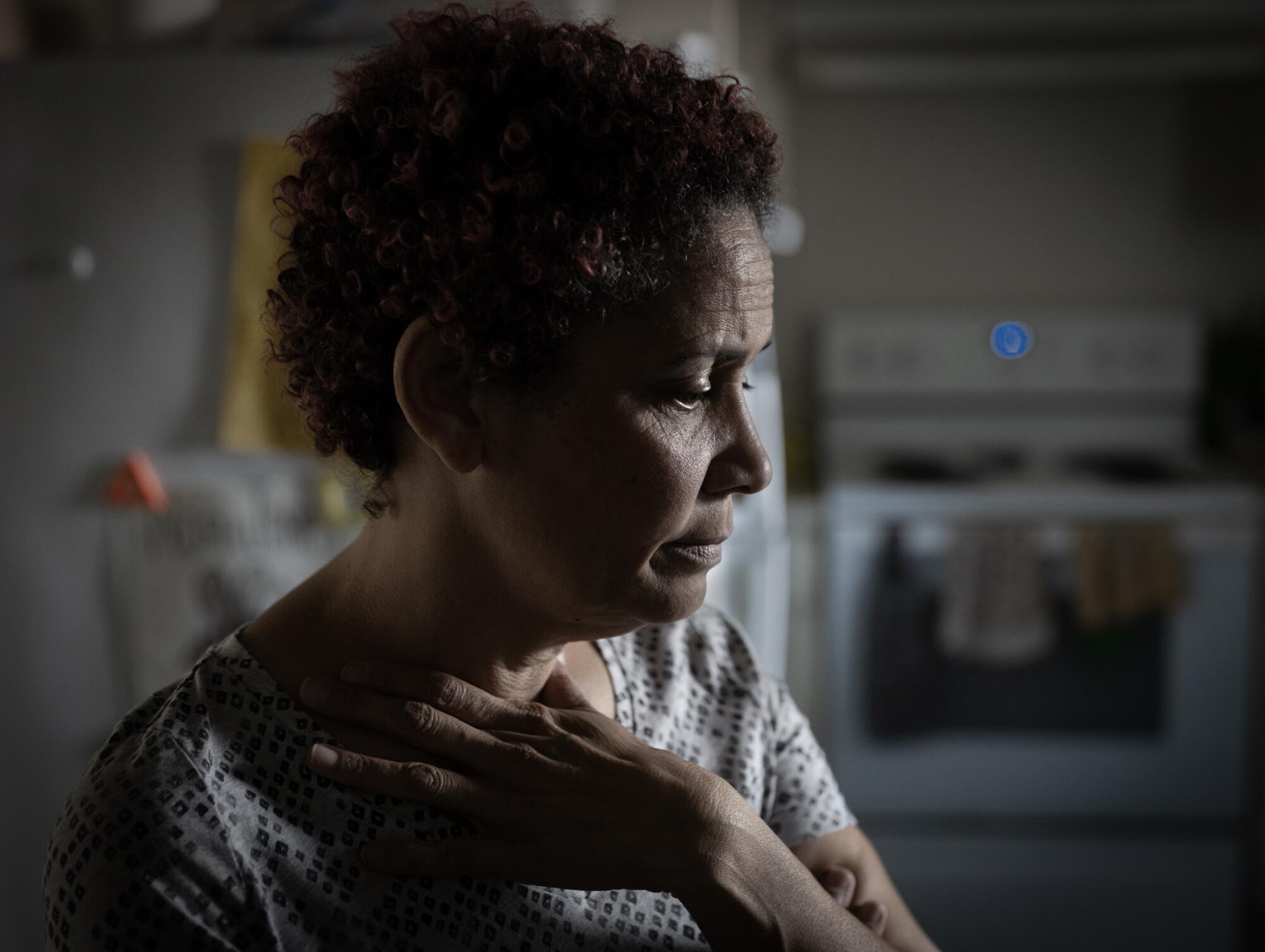

Christine LyBurtus said she’s struggled to find the right care for Noah.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
::
Across the country, surging numbers of young people have landed in emergency rooms in the throes of a mental health crisis amid a shortage of needed care. Children in need of psychiatric care are routinely held in emergency departments for hours or even days. Even amid COVID, as people tried to avoid emergency rooms, mental health-related visits continued to rise among teens in 2021 and 2022.
Among those hit hardest by the crisis are autistic youth, who turn up in emergency rooms at higher rates than other kids — and are much more likely to do so for psychiatric issues. Many have overlapping conditions such as anxiety, and researchers have also found they face a higher risk of abuse and trauma.
“We’re a misunderstood, marginalized population of people” at higher risk of suicide, Lisa Morgan, founder of the Autism and Suicide Prevention Workgroup, said at a national meeting.
Yet the available assistance is “not designed for us.”
According to the National Autism Indicators Report, more than half of parents of autistic youth who were surveyed had trouble getting the mental health services their autistic kids needed, with 22% saying it was “very difficult” or “impossible.” A report commissioned by L.A. County found autistic youth were especially likely to languish in ERs amid few options for ongoing psychiatric treatment.
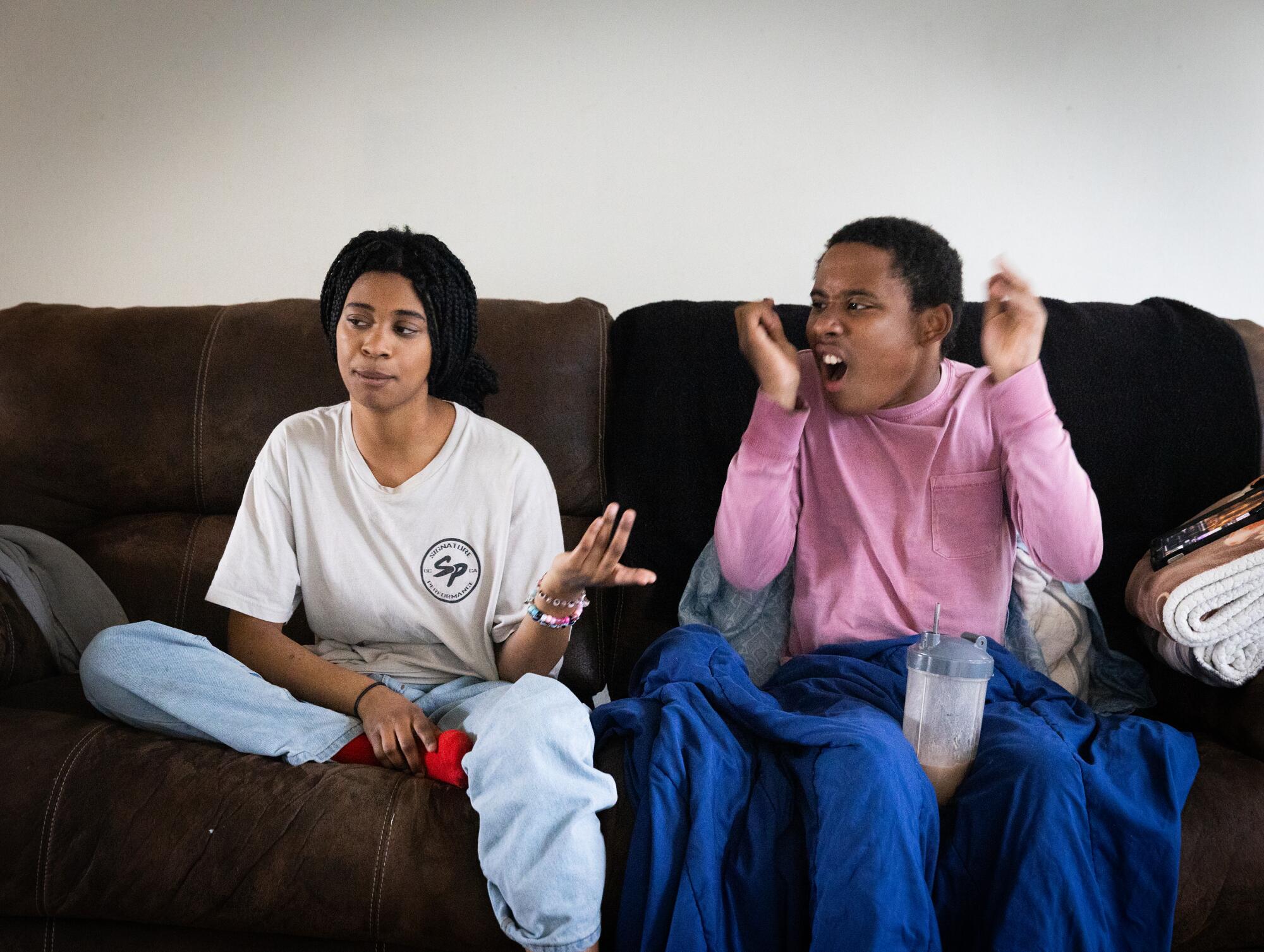

Karissa interacts with her brother, Noah, as he watches a video after school.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
In decades past, many psychiatrists were unwilling to diagnose mental health disorders in autistic people, believing “it was either part of the autism or for other reasons it was undiagnosable,” said Jessica Rast, an assistant research professor affiliated with the A.J. Drexel Autism Institute. Much more is now known about both autism and mental health treatment, but experts say the two fields aren’t consistently linked in practice.
Mental health providers may focus on an autism diagnosis for a prospective patient and say, “‘Well, that’s not in our wheelhouse. We’re treating things like depression or anxiety,’” said Brenna Maddox, assistant professor of psychiatry at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine.
Yet patients or their families “weren’t asking for autism treatment. They were asking for depression or anxiety or other mental health treatment,” Maddox said.
In the meantime, the system that serves children with developmental disabilities has faltered.
“Never have I seen that we can’t staff the needed things on so many cases,” Larry Landauer, executive director of the Regional Center of Orange County, said last year. Statewide, “there’s thousands and thousands of cases that are struggling.”
“If I’m a respite worker and I get called on to provide help to families … who am I going to select?” Landauer asked. “The [person] that watches TV and plays on his iPad and I just sit and monitor him? Or do I take someone that is significantly behaviorally challenged — that pulls my hair, that scares me all the time, that tries to run out the door? … Those are the ones getting left out.”
::
The fall and winter of 2022 were so trying that LyBurtus eventually took matters into her own hands. Noah bit his mother and smashed a bathroom window and tried to climb out before the Fullerton Fire Department arrived. Weeks later, LyBurtus had to dial 911 again after he bit his sister’s finger badly enough to draw blood.
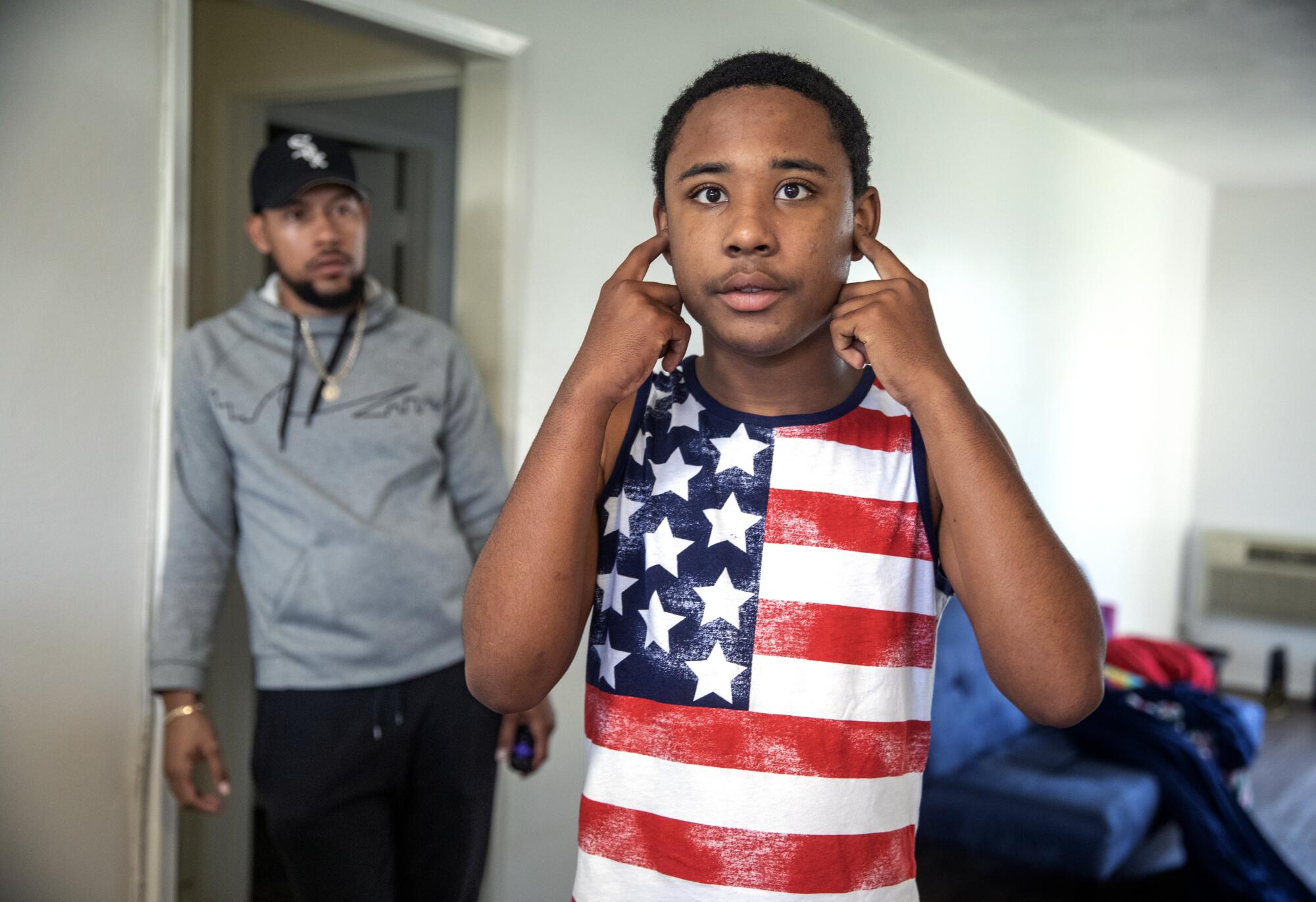

Caregiver Terrence Morris, left, keeps a watchful eye on Noah.
(Mel Melcon / Los Angeles Times)
He ended up in a hold at Children’s Hospital of Orange County, which searched for another facility that might help him, but “all placement options declined patient placement,” according to his medical records.
Noah was again sent home with his mother, but the next day, he was back at Children’s Hospital of Orange County after slamming his head against a tile floor.
LyBurtus, frantic and bruised, made call after call and finally used her credit card to pay for an ambulance to take him to UCLA Resnick Neuropsychiatric Hospital, where he was admitted.
Week by week, psychiatrists there said Noah seemed to be making some strides as they adjusted his alphabet soup of medications. But hospital staff struggled to understand what would set him off.
Once, while playing cards, Noah suddenly started knocking the cards off the table and struck another patient in the face. Another day, he appeared suddenly to be frightened after using the bathroom, and then charged at a computer plugged in nearby.
But there were also days when he danced to a Michael Jackson song, or played Giant Jenga outside on the deck. One day, a doctor wrote, “He made eye contact for a few seconds. I waved to him, and he looked at his hand, as though he was wondering what to do with it in return.”
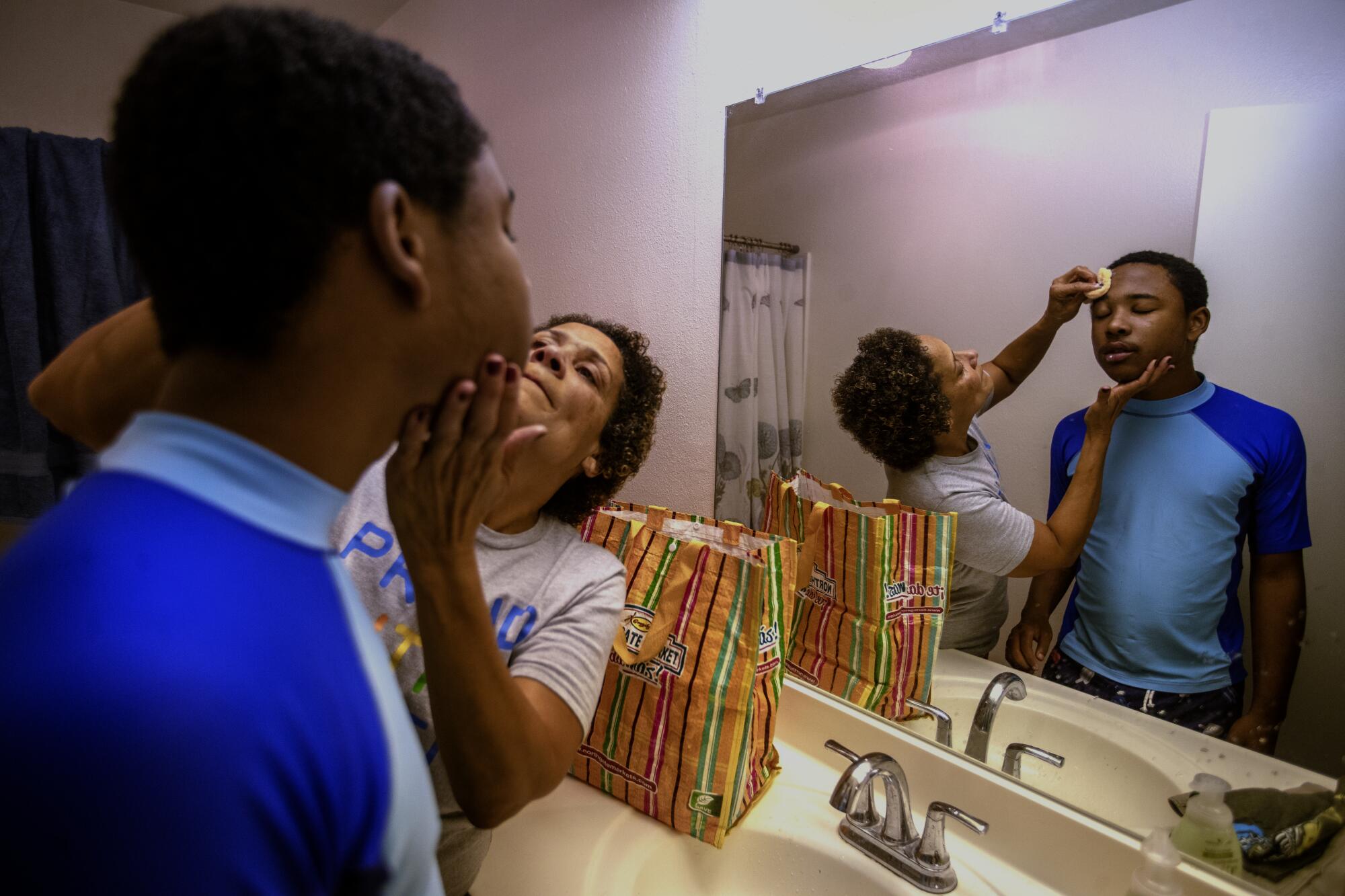

Christine LyBurtus washes her son’s face. When Noah was 3, a doctor noted he was a “very cute little boy” who played alone, rocked back and forth, and sometimes bit himself.
(Mel Melcon / Los Angeles Times)
LyBurtus was straining to find more help at home so UCLA held off on discharging him, but at the end of January 2023 Noah was sent home. With no changes in medication planned, “and the strong possibility that Noah grew tired of the inpatient setting, the ward no longer was deemed therapeutic or necessary,” a doctor wrote.
Less than a month later, he was back in the emergency room at Children’s Hospital of Orange County after biting and attacking his mother.
A psychiatrist at the pediatric hospital wrote that because he had limited ability to communicate, another round of psychiatric hospitalization would do little unless it was specialized for “individuals with neurodevelopmental needs.” When the 72-hour hold at children’s hospital ran out, LyBurtus asked for an ambulance to take Noah home, fearful of driving him herself.
In May, the month Noah turned 14, LyBurtus heard the regional center had found a place for Noah: a four-bed facility in Rio Linda, a tiny town near Sacramento that she’d never heard of. He could live there for more than a year, she was told, and then hopefully return home with the right support.
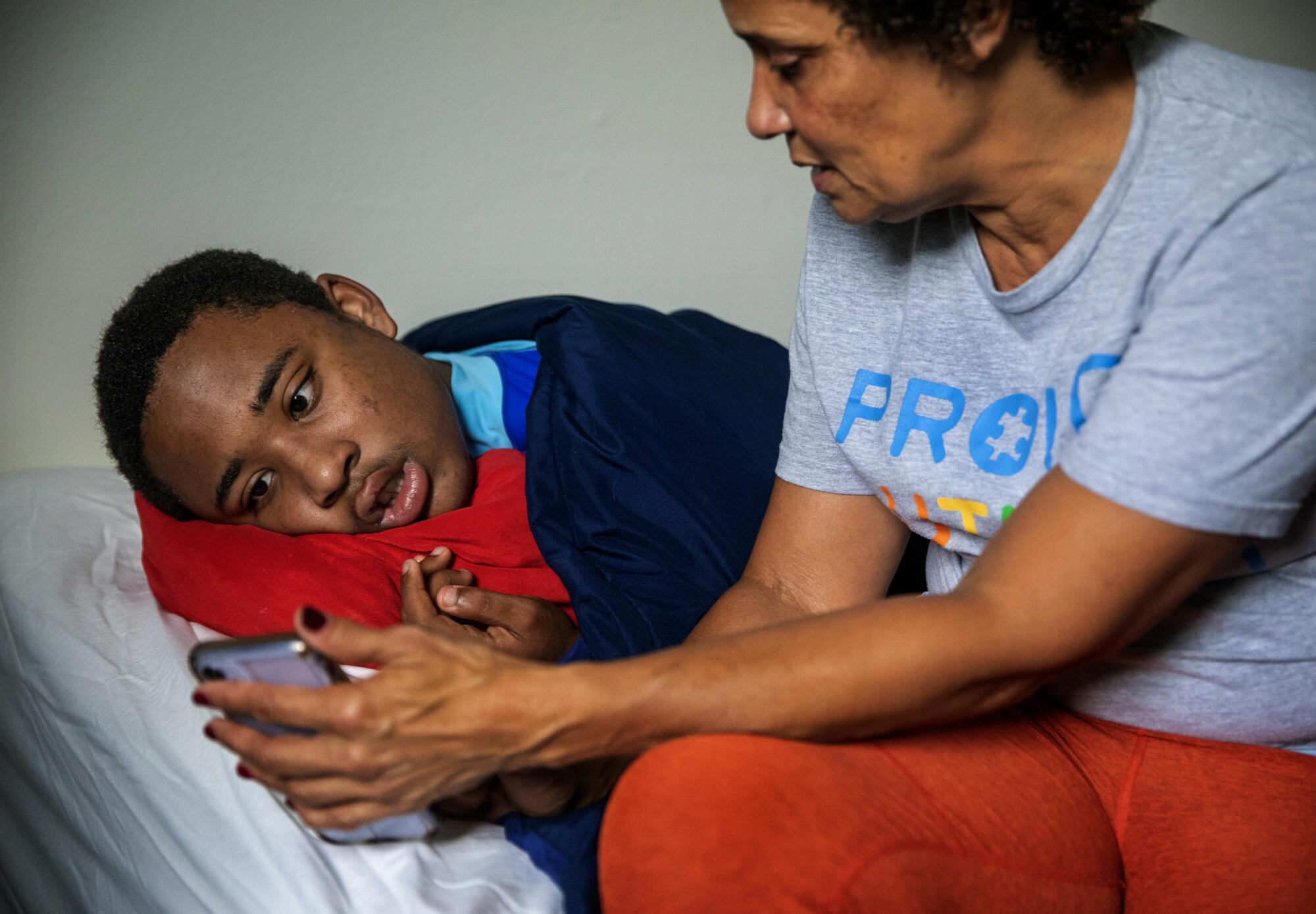

Christine LyBurtus shows photographs to Noah.
(Mel Melcon / Los Angeles Times)
But LyBurtus fretted about what she would do if something happened to him so far away. She felt, she said, like she had failed her child. Months passed as they waited for a spot there; LyBurtus said she was told they were trying to hire the needed staff.
“I don’t want him to go,” she said, “but I don’t want to continue going on the way that we’re going on.”
Then in August, LyBurtus was told the regional center had found a spot at a facility much closer to home: the state-run South STAR facility in Costa Mesa, about 20 miles from their apartment. Noah would occupy one of only 15 STAR beds across the state for developmentally disabled adolescents in “acute crisis.”
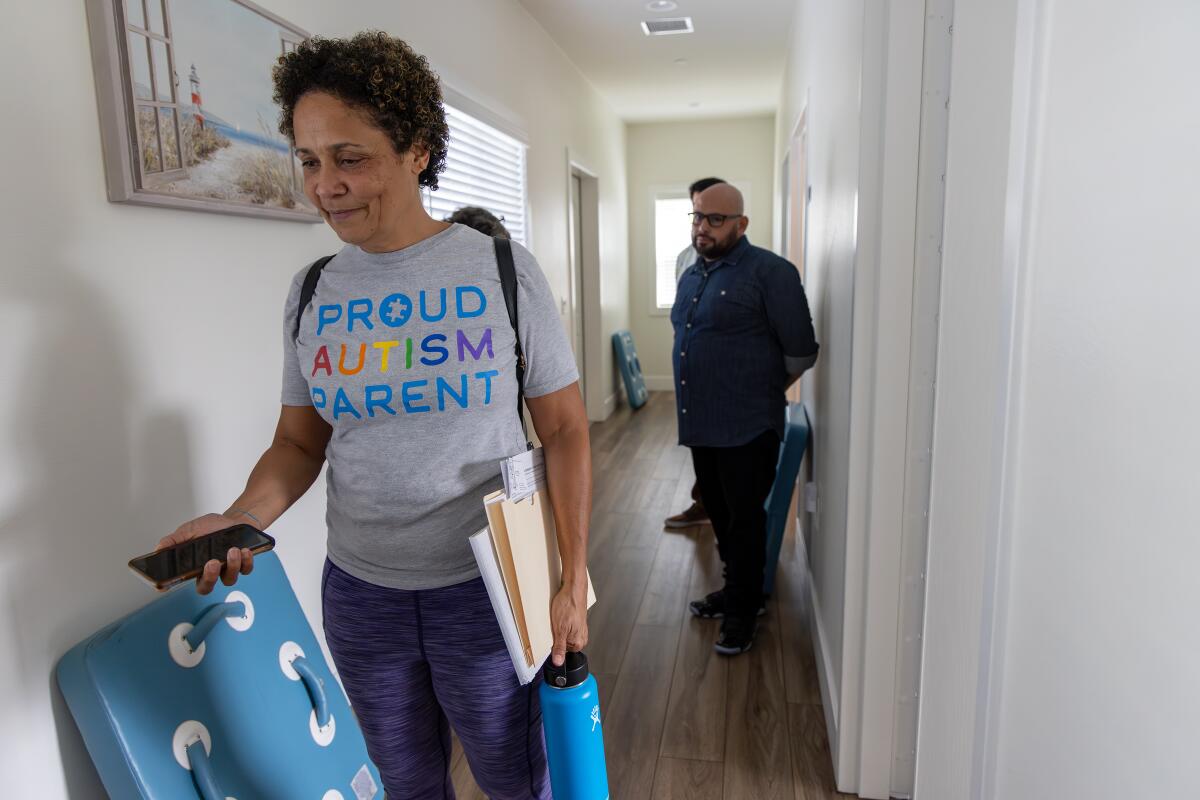
On a bright September morning, LyBurtus pulled up at an unassuming gray house with a “Home Sweet Home” sign by the door. The three teens living there were gone for the morning while an administrator and South STAR program director Kim Hamilton-Royse showed LyBurtus around the house.
Minutes into the tour, LyBurtus found herself crying. Hamilton-Royse stopped her explanation of the daily schedule. “I know this is super hard for you,” she said gently.
But LyBurtus brightened at the sight of the sensory room outfitted with crash pads and a mesmerizing, colorful cylinder of bubbling water. Hamilton-Royse pointed out a vibrating chair and added that they had a projector that would fill the room with illuminated stars.
LyBurtus took photos on her smartphone to show Noah. “You’re not going to be able to get him out of here,” she said.
As they rounded the rest of the house — bedrooms with dressers secured to the wall, a living room with paintings of sailboats, a fish tank — Hamilton-Royse asked if LyBurtus felt any better.
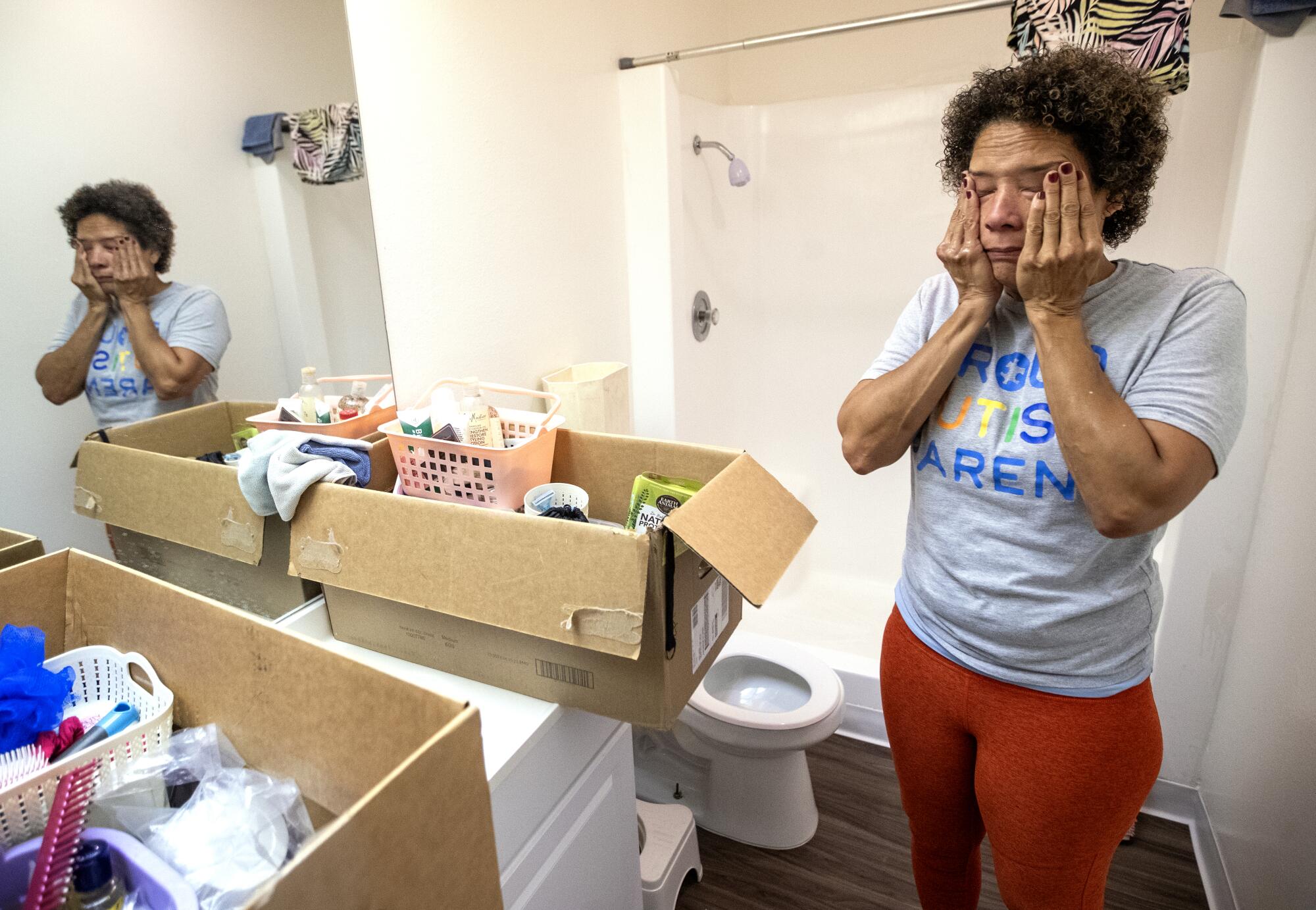

Christine LyBurtus reacts while boxing up items for Noah’s move.
(Mel Melcon / Los Angeles Times)
“I do,” she said. “I just hope that he can behave.”
Hamilton-Royse reassured her that South STAR had never kicked anyone out. “And we’ve had some really challenging folks,” she said.
“I promise you we’ll take very good care of him.”
As she returned to her car, LyBurtus took a deep breath. “It’s hard not to feel like I’m betraying him,” she said, her voice shaking. “But I can’t keep living like this, you know?”
1
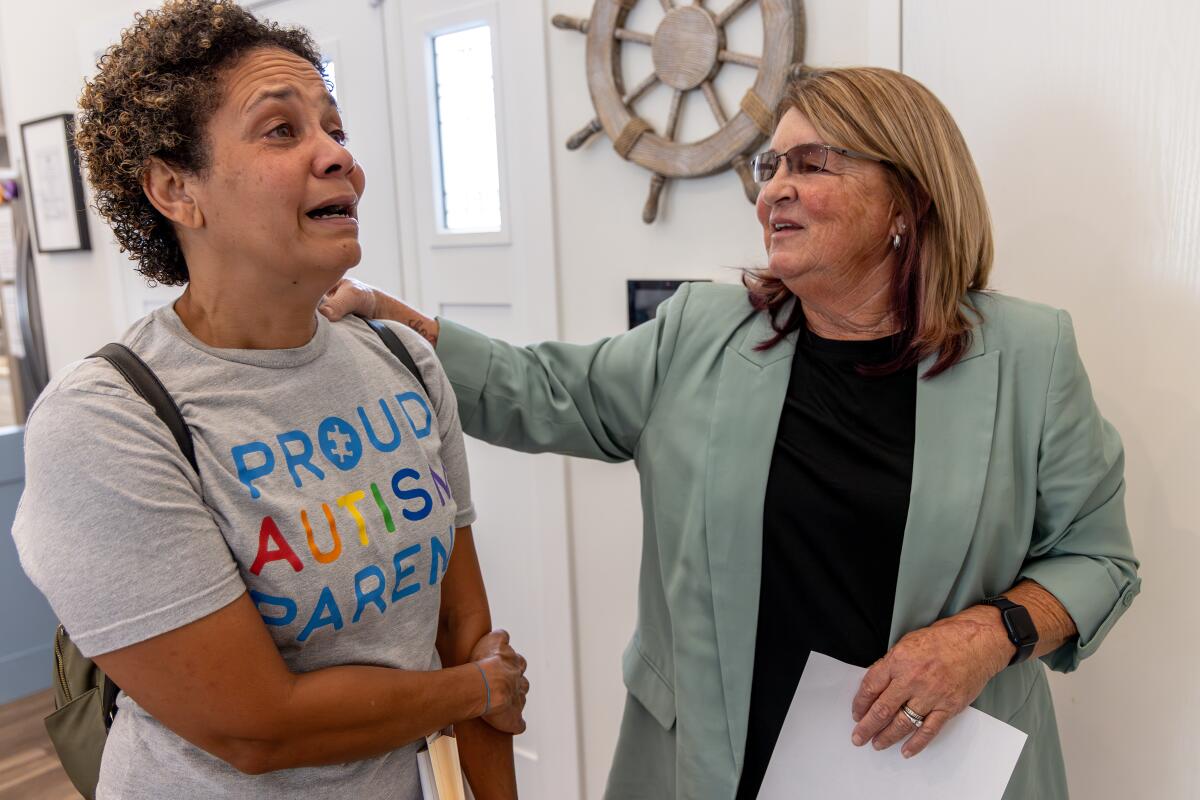
2

3
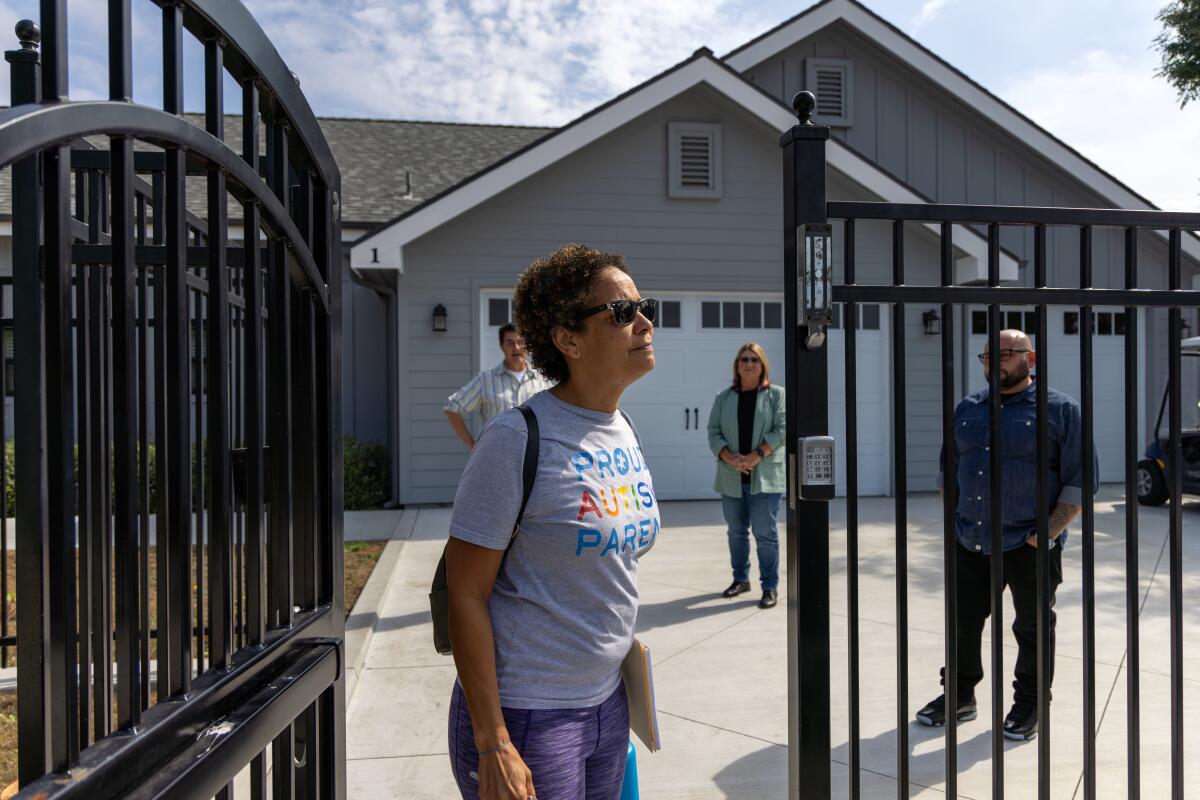

1. Christine Lyburtus tours a residential care facility in Costa Mesa, about 20 minutes from her home. (Irfan Khan / Los Angeles Times) 2. At the South STAR facility, LyBurtus was told, Noah would occupy one of only 15 STAR beds across the state for developmentally disabled adolescents in “acute crisis.” (Irfan Khan / Los Angeles Times) 3. “I just hope that he can behave,” LyBurtus said of son Noah. (Irfan Khan / Los Angeles Times)
Three days later, Noah went back to the Children’s Hospital of Orange County on another psychiatric hold. He came home, then was back in the emergency department a week and a half later.
::
The October night before Noah left home, LyBurtus had brought home sushi for him, one of his favorite foods. He fell asleep around 6:30 p.m, and woke up again at 1 a.m. LyBurtus gave him his medication and as he drifted back to sleep, his mother held him, enjoying the peace.
When he woke up in the morning, she could tell he knew something was up. His clothes had been packed. She’d already shown him photos of the Costa Mesa home and told him, “This is where you’re going. I’m still your mom. I’m still going to go and see you.”
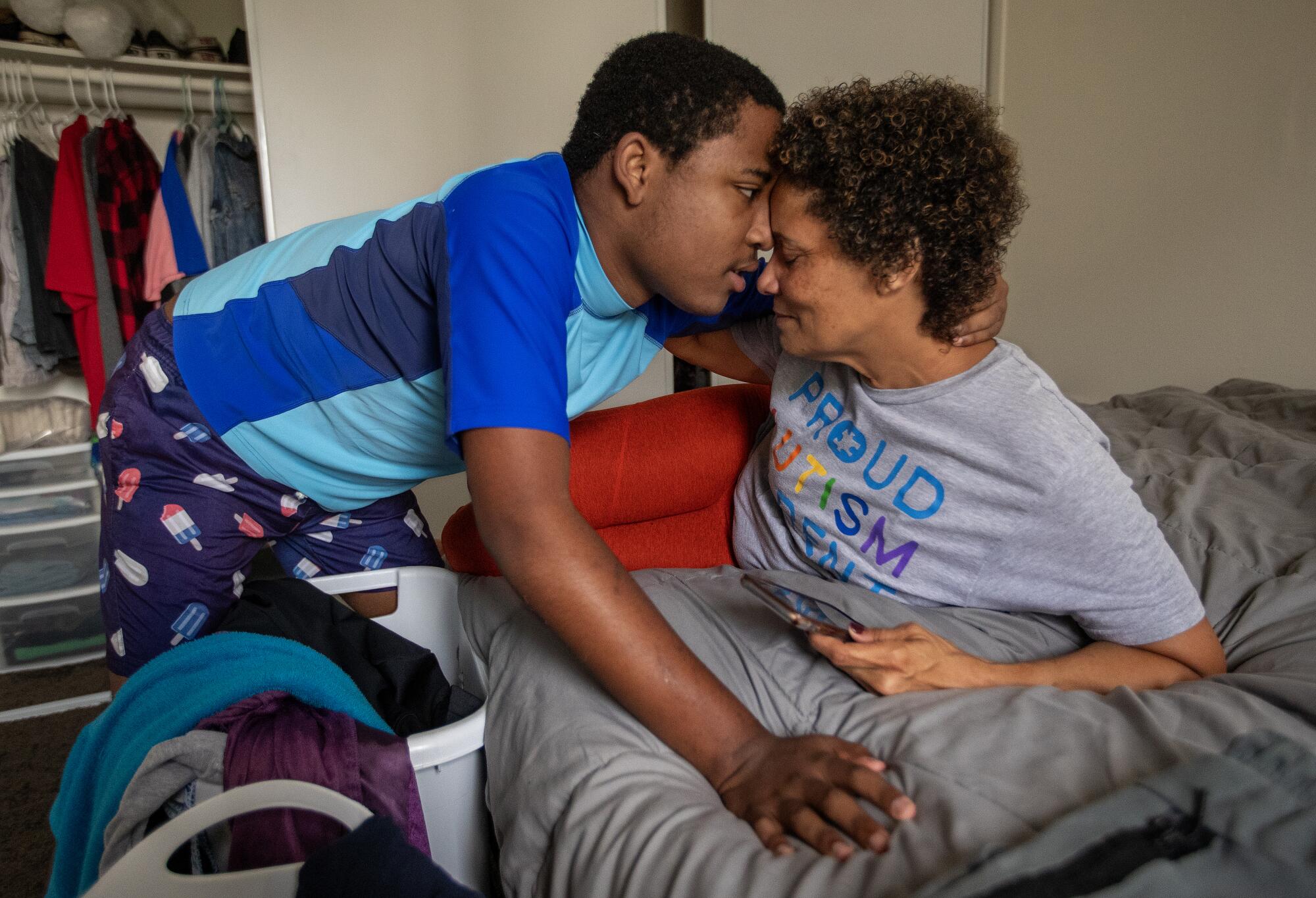

Noah embraces his mother shortly before he was picked up and driven to a residential care facility in Costa Mesa.
(Mel Melcon / Los Angeles Times)
When the black SUV arrived, LyBurtus offered Oreos to coax him into the unfamiliar car. She followed the SUV in her car, staying far enough behind to avoid having Noah see her when he arrived. LyBurtus had been told it would ease the transition.
Back at home, she sank into the bathtub, utterly spent. “I’m going to have to just go with trusting this process as much as I can,” she said, “because I don’t have another choice right now.”
The next day, she met with the South STAR staff to tell them more about Noah. What he likes to eat. What triggers him. His favorite things to do. The Costa Mesa home called whenever staff had physically restrained Noah, but when a weekend passed without a call, she felt some relief.
Lyburtus smiled at the photos and videos sent home: putting together an elaborate stacking toy, washing dishes. It felt like things were going well, LyBurtus said. The staff had scaled back the amount of psychiatric medication he was taking.
But more than a month later, when she first went to visit Noah, he excitedly took her to the front door, as if to say, “Let’s go,” she recalled. She gently told him she was just visiting.
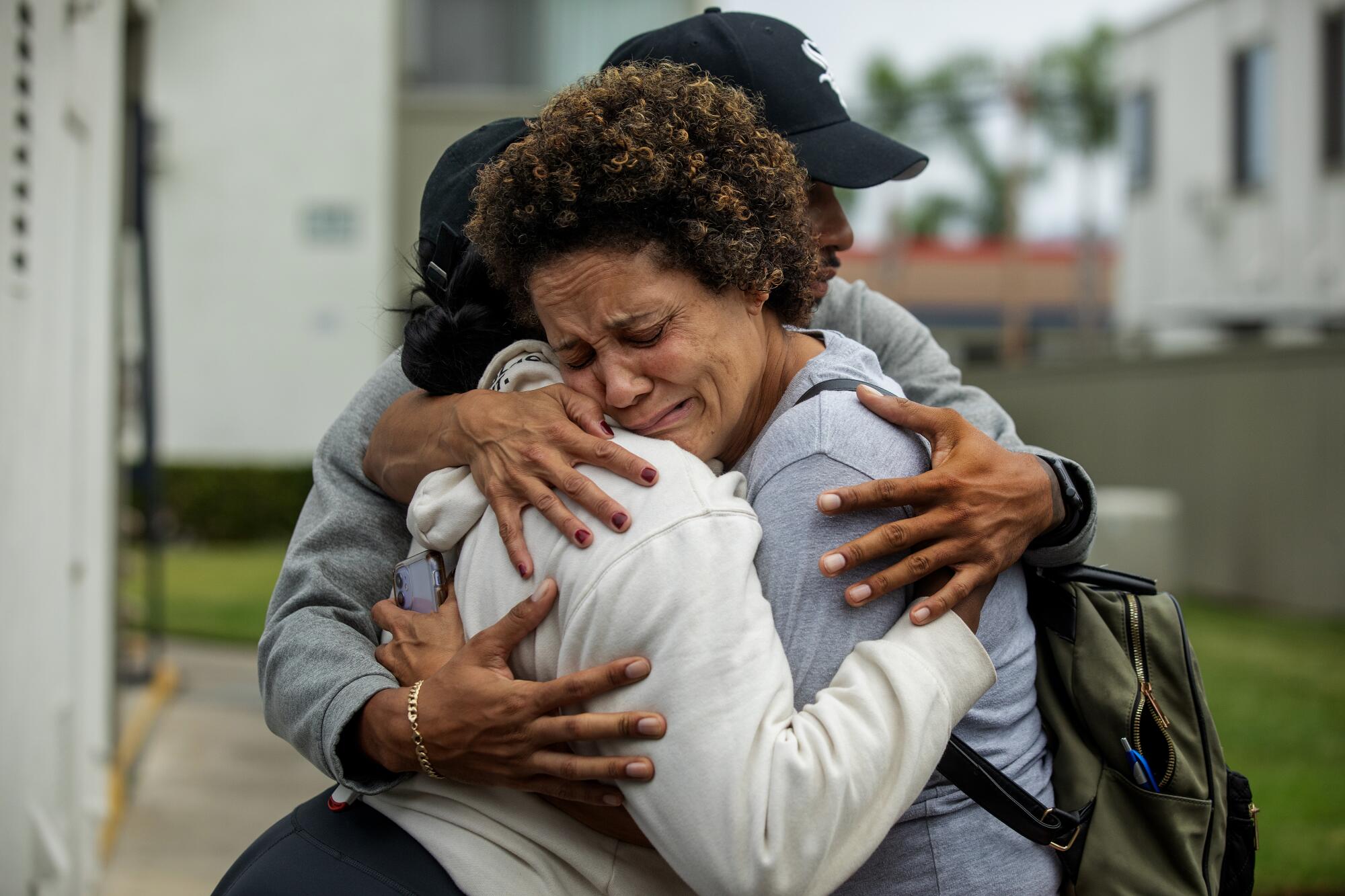

Christine LyBurtus is comforted by caregivers Schahara Zad, left, and Terrence Morris after Noah moved into his residential care facility.
(Mel Melcon / Los Angeles Times)
He led her to the side door instead. She steered him away again. They stepped into the courtyard, and Noah immediately went to the gate to exit.
LyBurtus fell into a funk. As she worried about Noah, she was also figuring out how to make ends meet. With Noah in the Costa Mesa home, Lyburtus was no longer being paid more than $4,000 a month as his caregiver, her sole source of income for years. She tried a number of jobs but ultimately found the work that suited her: caregiving for an elderly woman and children with disabilities.
Her second and third visits with Noah were easier. She snapped photos — Mother and son nestled together on the couch. Noah touching her forehead.
The STAR program runs up to 13 months. As time passed, the regional center had started talking to her about where Noah would go next. LyBurtus was startled.
Wasn’t the plan for him to come home, she asked?
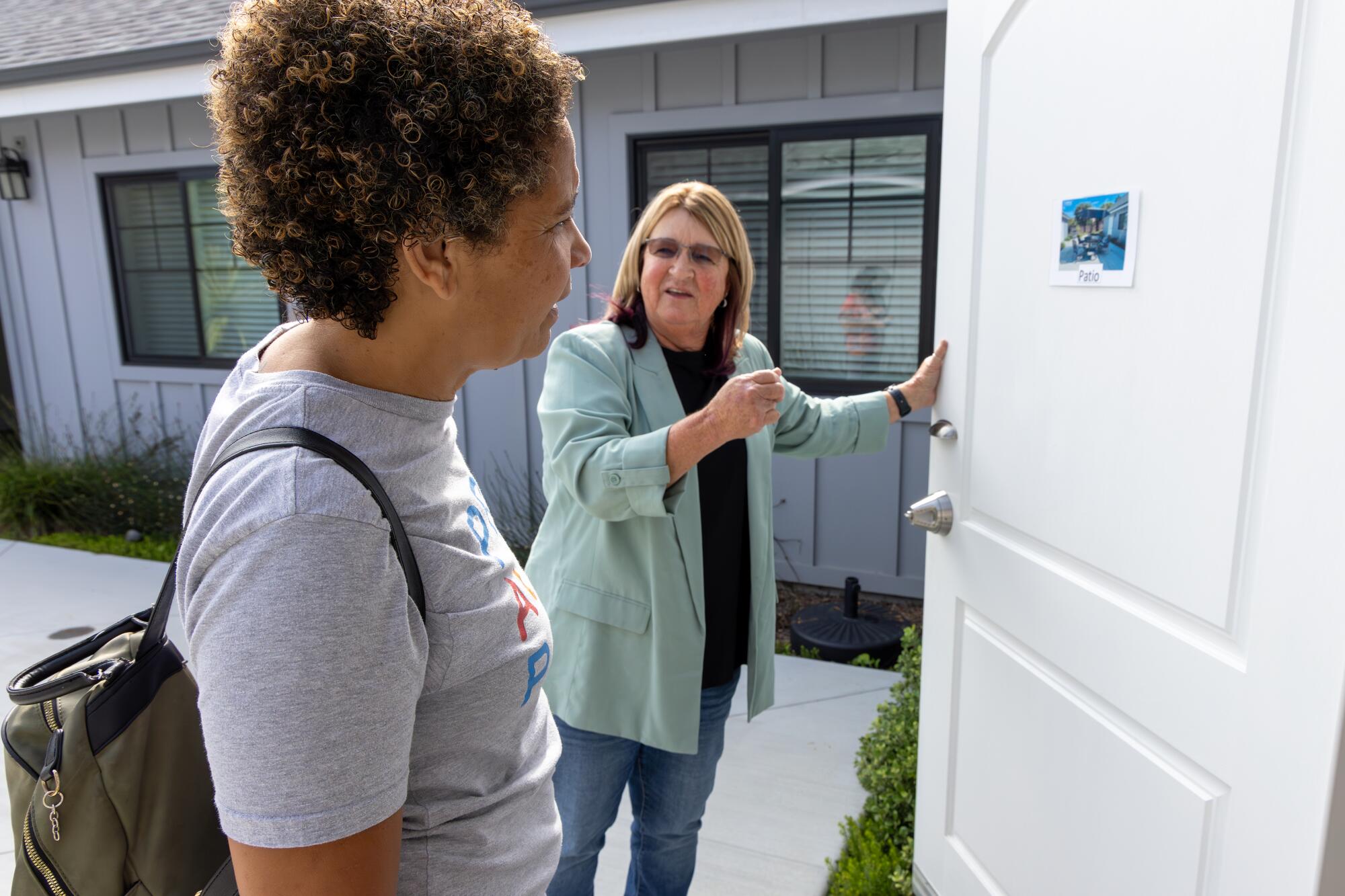

Christine LyBurtus, left, is briefed by Kim Hamilton-Royse while touring a residential care facility for her son.
(Irfan Khan/Los Angeles Times)
That was still on the table, LyBurtus said she was told. But if he wasn’t ready, they didn’t want to wait until the last minute to find somewhere else for Noah, who turned 15 in May.
LyBurtus wanted to block out the idea of him going to another facility.
“I never want to live the way we were living again,” she said.
“But is that worse than him being hours away? I don’t know.”

Science
The neuro disease rat lungworm has reached California

A disease that can cause neurological illness and meningitis in people, rat lungworm, has been found in wild opposums, rats and a zoo animal in San Diego County, indicating its establishment in California for the first time.
Researchers reported their findings in the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases, published by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors, who include veterinarians, researchers and wildlife biologists, urged physicians and other healthcare workers in the region to consider lungworm infection when patients come in with nervous system disorders.
The discovery highlights “a notable expansion of the range of this parasite in North America,” they said.
The CDC website says the risk to the general public of getting this infection is low, but it can be deadly.
If ingested, the worms can cause severe headaches, stiff neck, the sensation of tingling or painful skin, low-grade fever, nausea, vomiting, coma and sometimes death. People who eat freshwater crab, prawns, frogs, snails and slugs are at greatest risk. However, people can also get the disease by eating un-rinsed produce that’s been slimed by a snail or slug, or eating a slug or snail that was chopped up in produce. The worms need moisture, however; if the produce is dry, the worms will die.
Domestic animals, including dogs and cats, are also at risk.
Officials with the California Department of Public Health were not ready to call the disease endemic, or established, in the state.
“Additional surveillance and testing will be necessary to determine whether the detections of rat lungworm in the animals evaluated in San Diego County represent an isolated introduction of the parasite or ongoing local transmission,” spokeswoman Elizabeth Manzo wrote in a statement to The Times.
The department said it is not aware of rat lungworm outside San Diego County, and has seen no human cases.
“However, the San Diego study affirms that the parasite can be introduced to California through movement of infected animals from endemic areas,” the statement said. “Because some species of snails and slugs present in California are capable of serving as hosts for rat lungworm, and the presence of the parasite in other parts of the state is unknown, it is advised to take certain food safety precautions. Persons should not consume any raw or undercooked wild snails or slugs, and should thoroughly wash all produce before consuming.”
The worms that cause the disease, Angiostrongylus cantonensis, are native to Southeast Asia. They’ve been found in the U.S. since the 1960s — including in isolated human and zoo animal cases in California — and are established in Hawaii as well as in much of the southeastern U.S.
It is believed they came overseas via rats on boats.
The worms favored environment is the moist, warm bed of a rat’s lung. When a rat is infected, the worms cause respiratory distress, priming the rodent to cough. Worm-filled sputum is then ejected into the rat’s mouth, and swallowed. The rat then poops the worms out, and animals such as slugs and snails eat the poop. When a rat eats an infected invertebrate, the cycle begins again.
Occasionally, another animal, such as a raccoon or dog, or a person, will accidentally eat an infected animal, or the slime of one, and contract the disease.
The discovery of the worm in San Diego County rodents and opossums was made by staff at the San Diego Zoo and a local wildlife rehabilitation center, Project Wildlife, which is run by the San Diego Humane Society.
In December 2024, a 7-year-old male parma wallaby, born and raised at the zoo, began showing concerning neurological behaviors: incessant head shaking, blindness, a lack of muscle coordination and paralysis in his hind legs. He was euthanized after 11 days in the zoo infirmary.
When zoo staff examined the body, they found six rat lungworms in the marsupial’s brain, along with a lot of damage.
Because the diagnosis was so unusual, zoo staff examined the bodies of 64 free-ranging roof rats that had either been euthanized in the course of regular pest control or found dead on the property. Two, a little more than 3%, had lungworms. Their feces had them too: “numerous live … larvae with coiled posterior ends.” The larvae, roughly 300 in each poop sample, were each about the size of a grain of sand.
Officials at the San Diego Zoo did not respond to requests for comment.
Curiously, at the same time the zoo investigation was underway, staff from Project Wildlife had been dealing with sick opossums brought to them from around the county. Tests of 10 dead animals showed seven carried the lungworms.
Many people and animals remain asymptomatic when they’re infected. Symptoms typically appear within hours or days after ingestion and can last up to eight weeks. The worms will eventually die.
Because the disease has so many varied symptoms, health officials say it can go undiagnosed and untreated. Health officials from Hawaii, where the disease is endemic, say if lungworms are suspected, it’s best to be treated as soon as possible — even before lab results come back.
The CDC too notes that treatment works best when the disease is caught early, and can consist of high doses of corticosteroids, lumbar punctures for symptomatic relief of headaches, and antiparasitic medications, such as albendazole.
Science
Owners of fire-destroyed Palisades mobile home park seek to displace residents for development deal
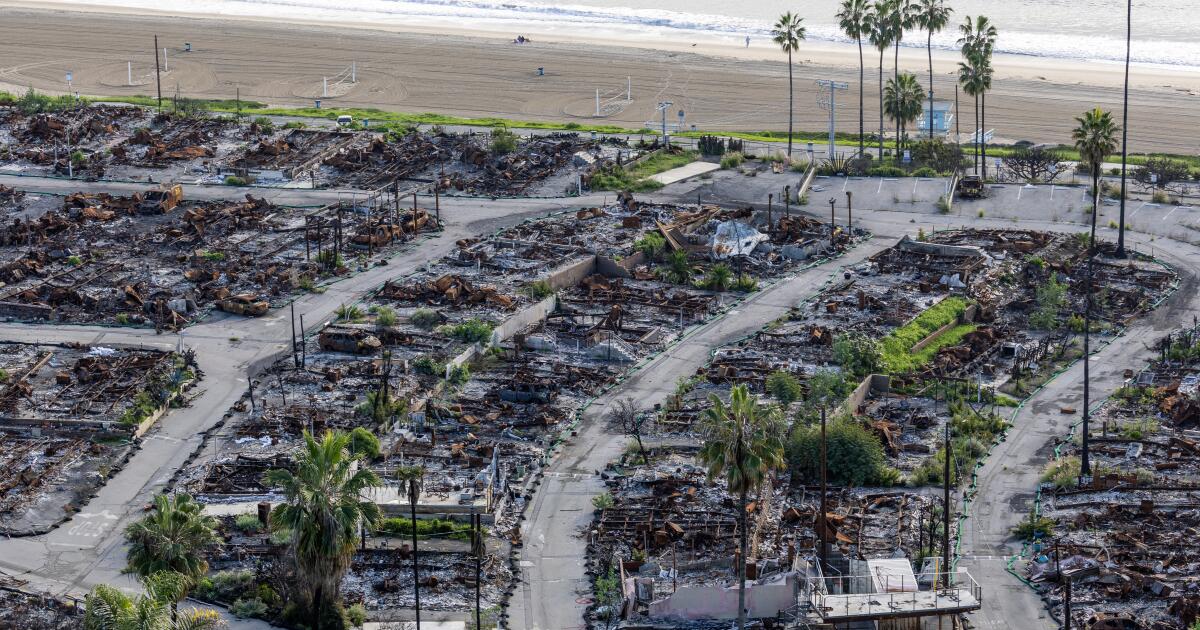

For months, former residents of the Pacific Palisades Bowl Mobile Estates have feared the uncommunicative owners of the property would seek to displace them in favor of a more lucrative development deal after the Palisades fire destroyed the rent-controlled, roughly 170-unit mobile home park.
A confidential memorandum listing the Bowl for sale indicates the owners intend to do exactly that.
The memorandum, quietly posted on a website associated with the global commercial real estate company CBRE, says that the Palisades fire created a “blank canvas for redevelopment” at a site “ideally positioned for a transformative residential or mixed-use project.”
“I just thought, oh my god, this is so much propaganda and false advertising,” said Lisa Ross, a 33-year resident of the Bowl and a Realtor. “How can they even get away with printing this?”
Neither the current owners of the Bowl nor the real estate companies listed on the memorandum responded to requests for comment.
The memorandum describes the current single-family residential zoning as “favorable” for developers; however, the city and mobile housing law experts have painted a different picture.
Fire debris at Pacific Palisades Bowl in January 2026.
(Myung J. Chun / Los Angeles Times)
“Multifamily and mixed-use development on this site is not allowed by existing zoning and land use regulations,” Mayor Karen Bass’s office said in a statement Wednesday, adding only low density single-family housing or reconstructing the mobile home park are currently allowed. “Mayor Bass will continue taking action and [work] with residents to restore the Palisades community.”
City Councilmember Traci Park also reiterated her focus on getting the mobile home park rebuilt and allowing residents to return, with a spokesperson noting she is not entertaining the potential for any rezoning efforts from a developer.
Zoning changes typically require a city council vote and are subject to the mayor’s approval or veto.
Beyond the zoning laws, the site is also currently governed by a state law requiring cities to preserve affordable housing along the coast and a city ordinance protecting mobile home residents against sudden displacement.
Spencer Pratt, a resident of the Palisades and an outspoken supporter of the neighborhood’s mobile home community, criticized the mayor and the owners in a statement to The Times. “It’s unfortunate that Karen Bass has not advocated for mobile home residents impacted by the fire,” he said, “and that the current owner of the Bowl is ignoring good faith offers from residents to buy the property.”
The mayor’s office disputed this, noting Bass recently led a delegation of Palisadians, including mobile home owners, to Sacramento to advocate for recovery. “Mayor Bass’ priority is getting every Palisadian home — single-family homeowners, town home owners, renters, mobile home owners.”

Los Angeles Mayor Karen Bass speaks during a private ceremony outside City Hall with faith leaders, LAPD officers and city officials to commemorate the one-year anniversary of the Eaton and Palisades fires on Jan. 7, 2026.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
Bass also advocated for the federal government to include the Bowl in its debris cleanup efforts; however, the Federal Emergency Management Agency ultimately refused to include it, unlike other mobile home parks impacted by the Palisades fire. Its reasoning: It could not trust the owners to rebuild the park as affordable housing.
Court rulings over the years found the owners routinely failed to maintain the infrastructure and worked to replace the park with an “upscale resort community.” Residents also accused the owners of attempting to circumvent rent control regulations.
After the fire, it ultimately took more than 13 months to begin cleaning up the debris.
Ross said she approached the owners with independent mobile home park developers who were interested in buying the fire-destroyed lot and letting residents rebuild within months. She also approached the owners with a proposition that the former residents band together to buy the park. She heard nothing back.
“They don’t communicate,” Ross said. “It’s a feuding family. That’s also why we had so many problems with maintenance and with upgrades in the park.”
Pratt, who is running for mayor against Bass, also called on private developers like Rick Caruso to step in and save the Bowl. (Caruso’s team noted his rebuilding nonprofit is looking into how to help residents of the Bowl.)
Ross is a fan of Pratt’s proposition. “We need those kinds of people — we need Rick Caruso. That would be great,” Ross said. To sweeten the deal: “I’ll cook for him. I would make him all his favorite dishes.”
Science
A virus without a vaccine or treatment is hitting California. What you need to know

A respiratory virus that doesn’t have a vaccine or a specific treatment regimen is spreading in some parts of California — but there’s no need to sound the alarm just yet, public health officials say.
A majority of Northern California communities have seen high concentrations of human metapneumovirus, or HMPV, detected in their wastewater, according to data from the WastewaterScan Dashboard, a public database that monitors sewage to track the presence of infectious diseases.
A Los Angeles Times data analysis found the communities of Merced in the San Joaquin Valley, and Novato and Sunnyvale in the San Francisco Bay Area have seen increases in HMPV levels in their wastewater between mid-December and the end of February.
HMPV has also been detected in L.A. County, though at levels considered low to moderate at this point, data show.
While HMPV may not necessarily ring a bell, it isn’t a new virus. Its typical pattern of seasonal spread was upended by the COVID-19 pandemic, and its resurgence could signal a return to a more typical pre-coronavirus respiratory disease landscape.
Here’s what you need to know.
What is HMPV?
HMPV was first detected in 2001, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It’s transmitted by close contact with someone who is infected or by touching a contaminated surface, said Dr. Neha Nanda, chief of infectious diseases and hospital epidemiologist for Keck Medicine of USC.
Like other respiratory illnesses, such as influenza, HMPV spreads and is more durable in colder temperatures, infectious-disease experts say.
Human metapneumovirus cases commonly start showing up in January before peaking in March or April and then tailing off in June, said Dr. Jessica August, chief of infectious diseases at Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa.
However, as was the case with many respiratory viruses, COVID disrupted that seasonal trend.
Why are we talking about HMPV now?
Before the pandemic hit in 2020, Americans were regularly exposed to seasonal viruses like HMPV and developed a degree of natural immunity, August said.
That protection waned during the pandemic, as people stayed home or kept their distance from others. So when people resumed normal activities, they were more vulnerable to the virus. Unlike other viruses, there isn’t a vaccine for human metapneumovirus.
“That’s why after the pandemic we saw record-breaking childhood viral illnesses because we lacked the usual immunity that we had, just from lack of exposure,” August said. “All of that also led to longer viral seasons, more severe illness. But all of these things have settled down in many respects.”
In 2024, the national test positivity for HMPV peaked at 11.7% at the end of March, according to the National Respiratory and Enteric Virus Surveillance System. The following year’s peak was 7.15% in late April.
So far this year, the highest test positivity rate documented was 6.1%, reported on Feb. 21 — the most recent date for which complete data are available.
While the seasonal spread of viruses like HMPV is nothing new, people became more aware of infectious diseases and how to prevent them during the pandemic, and they’ve remained part of the public consciousness in the years since, August and Nanda said.
What are the symptoms of HMPV?
Most people won’t go to the doctor if they have HMPV because it typically causes mild, cold-like symptoms that include cough, fever, nasal congestion and sore throat.
HMPV infection can progress to:
- An asthma attack and reactive airway disease (wheezing and difficulty breathing)
- Middle ear infections behind the ear drum
- Croup, also known as “barking” cough — an infection of the vocal cords, windpipe and sometimes the larger airways in the lungs
- Bronchitis
- Fever
Anyone can contract human metapneumovirus, but those who are immunocompromised or have other underlying medical conditions are at particular risk of developing severe disease — including pneumonia. Young children and older adults are also considered higher-risk groups, Nanda said.
What is the treatment for HMPV?
There is no specified treatment protocol or antiviral medication for HMPV. However, it’s common for an infection to clear up on its own and treatment is mostly geared toward soothing symptoms, according to the American Lung Assn.
A doctor will likely send you home and tell you to rest and drink plenty of fluids, Nanda said.
If symptoms worsen, experts say you should contact your healthcare provider.
How to avoid contracting HMPV
Infectious-disease experts said the best way to avoid contracting HMPV is similar to preventing other respiratory illnesses.
The American Lung Assn.’s recommendations include:
- Wash your hands often with soap and water. If that’s not available, clean your hands with an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Clean frequently touched surfaces.
- Crack open a window to improve air flow in crowded spaces.
- Avoid being around sick people if you can.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose and mouth.
Assistant data and graphics editor Vanessa Martínez contributed to this report.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoExclusive: DeepSeek withholds latest AI model from US chipmakers including Nvidia, sources say
-

 Wisconsin6 days ago
Wisconsin6 days agoSetting sail on iceboats across a frozen lake in Wisconsin
-

 Massachusetts5 days ago
Massachusetts5 days agoMassachusetts man awaits word from family in Iran after attacks
-

 Maryland7 days ago
Maryland7 days agoAM showers Sunday in Maryland
-

 Florida6 days ago
Florida6 days agoFlorida man rescued after being stuck in shoulder-deep mud for days
-

 Denver, CO1 week ago
Denver, CO1 week ago10 acres charred, 5 injured in Thornton grass fire, evacuation orders lifted
-

 Oregon1 week ago
Oregon1 week ago2026 OSAA Oregon Wrestling State Championship Results And Brackets – FloWrestling
-

 Pennsylvania2 days ago
Pennsylvania2 days agoPa. man found guilty of raping teen girl who he took to Mexico





















