World
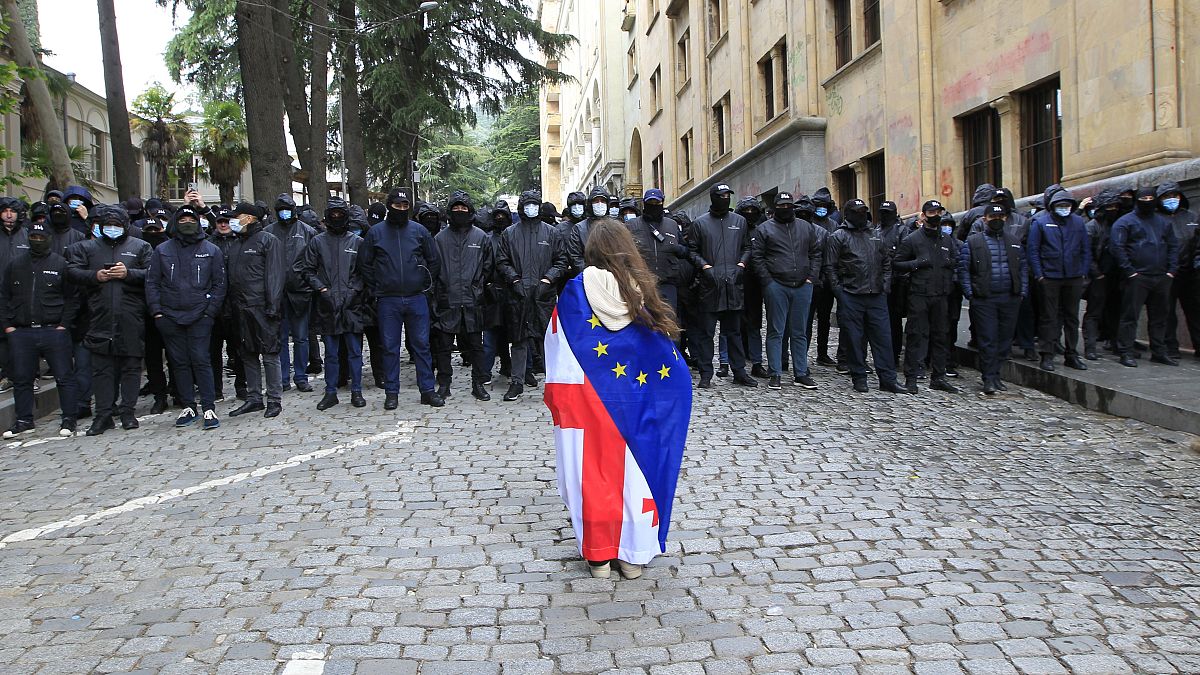
Nearly half of Europeans say their standards of living have declined

The price-of-living disaster triggered by the Ukraine conflict, the vitality crunch, surging inflation and the coronavirus pandemic has develop into the best fear for European Union residents, in keeping with a brand new Eurobarometer that reveals 45% of respondents are at the moment having “some” or “quite a bit” difficulties with their private revenue.
The ballot speaks of a “polycrisis temper” throughout the continent.
Moreover, 46% of Europeans admit their requirements of residing have already decreased on account of the mounting crises whereas 39% anticipate to see a decline someday this 12 months.
Simply 14% don’t anticipate any form of change or impression.
The international locations the place the perceived drop in residing requirements has been most pronounced are Cyprus (70% of respondents say requirements have “already been decreased”), Greece (66%), Malta (65%), France (62%) and Portugal (57%), the report reveals.
Folks in Nordic international locations are probably the most snug with their current revenue – 87% in Sweden, 86% in Denmark and 84% in Finland –, whereas solely 21% in Greece and Bulgaria are happy with their earnings.
Extra worryingly, 39% of respondents admit they wrestle to pay their month-to-month payments “once in a while” and 9% say that is the case “more often than not.” As soon as once more, Greece and Bulgaria report the best share of the inhabitants going by way of this type of hardship, with 86% and 64% respectively.
General, 56% of Europeans specific dissatisfaction with the measures taken on the EU stage to sort out the rising prices of residing, whereas 64% really feel the identical in regards to the actions of their nationwide governments.
In whole, 93% of ballot individuals say they’re frightened in regards to the cost-of-living disaster, together with surging meals and vitality costs. Poverty and social exclusion (82%), local weather change (81%) and the attainable unfold of the Ukraine conflict to neighbouring international locations (81%) additionally characterize sources of hysteria amongst EU residents.
Notably, almost three-quarters confess to being concerned in regards to the “threat of a nuclear incident,” a state of affairs fuelled by inflammatory rhetoric from the Kremlin.
Regardless of these widespread fears and struggles, European help for Ukraine stays steadfast: 74% of EU residents approve of the EU’s response to the conflict versus 23% who disapprove.
Approval of the EU’s help to Ukraine is overwhelming amongst respondents within the northern area: 97% in Sweden, 95% in Finland, 93% within the Netherlands and 92% in Denmark.
Solely in Slovakia (49%), Greece (48%) and Bulgaria (48%) this help falls beneath the 50% threshold.
When requested in regards to the conflict’s broader implications, 65% of all these surveyed say they’re “not very” or “by no means” assured that their private lives will proceed unchanged.
The Eurobarometer, launched by the European Parliament on Thursday morning, relies on greater than 26,000 face-to-face interviews carried out between October and November in all 27 member states.
In addition to cost-of-living and Ukraine, the outcomes additionally contact upon the EU as a complete, its establishments and the 2024 parliamentary elections.
The share of those that have a constructive picture of the EU has dropped from 52% in Might to 47% in November, with massive variations throughout international locations. On the identical time, 62% see their nation’s membership within the bloc as a “good factor” versus a small minority (10%) who name it a “unhealthy factor.”
Nonetheless, over half of respondents (51%) say issues within the EU are going within the “flawed path,” with slightly below a 3rd saying issues are going within the “proper path.”
Pessimism runs even deeper inside nationwide boundaries: 62% of EU residents say issues of their residence nation are going within the “flawed path.”
In an attention-grabbing twist, 63% of individuals declare issues of their private lives are going within the “proper path,” reflecting a stark dissonance between the house atmosphere and the political panorama.
These in Luxembourg (82%), Eire (80%) and Sweden (80%) are probably the most happy in regards to the present state of their private lives, whereas these in Romania (49%), Poland (47%) and Portugal (46%) are extra combined.
A majority of Europeans (57%) are optimistic in regards to the EU’s future, with 39% describing themselves as pretty or very pessimistic. France, Cyprus and Greece are the one thee member states the place a pessimistic outlook represents the bulk opinion.

World
Brussels, my love? Transparency over MEPs' side jobs

In this edition, we look at what lawmakers’ extracurricular activities mean for their core role.
This week, we are joined by Sophia Russack, senior researcher from the Centre for European Policy Studies, Petros Fassoulas, secretary general of European Movement International and Anna Nalyvayko, senior project officer from the Wilfried Martens Center.
Panelists debate the ethical questions raised by MEPs who have side jobs. Those extra roles are legal, but the political earthquake caused by the Qatarargate scandal led to tighter rules and more transparency.
Is this enough to bridge the gulf between citizens and politicians, in today’s fractured political landscape?
“We see that they have improved rules when it comes to reporting requirements, to laying open your financial situation before and after the offers, and so on. But to be honest, none of these things will prevent another Qatargate,” said Sophia Russack, a think tanker who is an expert in EU institutional architecture, decision-making processes and institutional reform.
Despite these concerns, Petros Fassoulas said MEPs shouldn’t abandon contact with the real world altogether.
“It’s important for them to have the opportunity to bring expertise from outside and engage also with the world outside of the chamber,” Fassoulas said. “An MEP or any parliamentarian should be in contact with the people that they regulate, the businesses that they have an impact on.”
Guests also discussed the reasons for the crisis of public confidence in politicians, and gave some ideas for solutions.
Watch “Brussels, my love?” in the player above.
World
Iraq's Kurdish Regional Security Council announces arrest of top aide of former Islamic State leader

The Kurdish Regional Security Council announced in a statement on Friday that it captured a senior Islamic State figure, Socrates Khalil.
Khalil was known to be a confidant of the late Islamic State leader, Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi.
“After spending five years in Turkey, Khalil returned to Kurdistan with a forged passport and was swiftly apprehended,” the statement said.
Khalil made bombs for the Islamic State and was entrusted by al-Baghdadi with various major operations, the statement added, saying that he was instrumental in the 2014 Islamic State takeover of Mosul, and participated in many battles against Iraqi forces and the Peshmerga forces.
World
UN experts say South Sudan is close to securing a $13 billion oil-backed loan from a UAE company

U.N. experts say South Sudan is close to securing a $13 billion loan from a company in the United Arab Emirates, despite the oil-rich country’s difficulties in managing debts backed by its oil reserves.
The panel of experts said in a report to the U.N. Security Council that loan documents it has seen indicate the deal with the company, Hamad Bin Khalifa Department of Projects, would be South Sudan’s largest-ever oil-backed loan.
SOUTH SUDAN MEDIATION TALKS LAUNCHED IN KENYA WITH A HOPE OF ENDING CONFLICT
The experts, who monitor an arms embargo against South Sudan, said in the oil section of the report obtained by The Associated Press this week that “servicing this loan would likely tie up most of South Sudan’s revenue (for) many years, depending on oil prices.”
U.N. experts say South Sudan is close to securing a $13 billion loan from a company in the United Arab Emirates, despite the oil-rich country’s difficulties in managing debts backed by its oil reserves. (Photo by TIZIANA FABI/AFP via Getty Images)
Hamad Bin Khalifa Department of Projects, registered in Dubai, has no listed phone number and its website isn’t working. An email address associated with the company bounced back. The UAE Mission to the United Nations declined to comment, saying Hamad is a private company.
South Sudan gained independence from Sudan in 2011 following decades of civil war that cost million of lives, and oil is the backbone of the young nation’s economy.
Soon after independence, South Sudan fought its own civil war from 2013 to 2018, when rivals President Salva Kiir and Vice President Riek Machar signed a power-sharing agreement and formed a coalition government. South Sudan is under pressure from the United States and other nations to more quickly implement the 2018 peace deal that ended the civil war and prepare for elections.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s latest update, South Sudan produced an average of about 149,000 barrels of liquid fuels per day in 2023. The landlocked country uses Sudan’s pipelines to transfer its oil to Port Sudan for shipment to global markets in an agreement with the Sudanese government, which pockets $23 per barrel as transit fees for the oil exports.
South Sudanese Information Minister Michael Makuei Lueth told reporters in February that outside factors, including the civil war still raging in Sudan, have hurt South Sudan’s oil exports. He also said oil wells, which were water-logged by heavy floods during the past rainy season, weren’t yet fully operational.
The section on oil in the experts report said documents for the loan from the UAE company, signed between December and February by South Sudan’s minister of finance, indicate the loan is split into tranches.
According to the documents, around 70% of the loan is to be allocated to infrastructure projects, with the first payment in excess of $5 billion, the panel said. Following a three-year grace period, “the loan will be secured against the delivery of crude oil for a period of up to 17 years.”
The panel of experts raised serious questions about South Sudan’s oil-based debts.
South Sudan lost a case in the International Center for Settlement of Investment Disputes stemming from a $700 million loan it received from Qatar National Bank in 2012.
When the panel wrote its report, the tribunal had not reached a decision on how much the government would have to pay, but The Sudan Tribune reported Sunday that South Sudan has been ordered to pay more than $1 billion.
The panel of experts said it has also confirmed that the government owes $151.97 million to the Eastern and Southern African Trade and Development Bank stemming from a previous oil-related deal.
South Sudan was supposed to hold elections before February 2023, but that timetable was pushed back last August to December 2024.
In early April, South Sudan’s president warned lawmakers “not to cling to power just weeks after his former rival turned deputy proposed a further postponement of elections.
The panel of experts said would be “a significant milestone” and warned that the country’s leaders are running short of time “to ensure divergent expectations do not fuel further tensions and strife.”
The experts also noted South Sudan’s humanitarian crisis. in which an estimated 9 million of the country’s 12.5 million people need protection and humanitarian assistance, according to the U.N. The country has also seen an increase in the number of refugees fleeing the war in neighboring Sudan, further complicating humanitarian assistance to those affected by South Sudan’s internal conflict.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPentagon chief confirms US pause on weapons shipment to Israel
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoRFK Jr said a worm ate part of his brain and died in his head
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoOhio AG defends letter warning 'woke' masked anti-Israel protesters they face prison time: 'We have a society'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoNine Things We Learned From TikTok’s Lawsuit Against The US Government
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoBiden’s decision to pull Israel weapons shipment kept quiet until after Holocaust remembrance address: report
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: Police Use Pepper Spray on Protesters on G.W.U.’s Campus
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoA look at Chinese investment within Hungary
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoThe Major Supreme Court Cases of 2024