Colorado
What does Colorado’s largest home manufacturing plant shutting down mean for industry?

Colorado is losing its top facility in the push to make home construction more efficient and, by extension, the costs of new homes more affordable.
Clayton Homes filed a notice with the Colorado Department of Labor on Tuesday that it will shut down its Heibar Installation manufacturing plant at 475 W. 53rd Place in unincorporated Adams County. By the end of January, 74 workers will lose their jobs at the 200,000-square-foot facility near the intersection of Interstates 70 and 25.
“The layoffs involving the manufacturing department at the Heibar Colorado location will be permanent, and there will be no ‘bumping’ or transfer rights. Affected employees will be able to apply for open positions at other company locations,” Mike Whitmore, the senior director of Human Resources at Clayton Homes, informed the state in a Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification Act letter.
The impact goes far beyond the 74 jobs being lost. The plant was a key supplier to Oakwood Homes, which is building some of the most affordable non-subsidized homes along the northern Front Range. It offered a model to emulate when Gov. Jared Polis made fostering innovation and introducing manufacturing efficiencies into the home construction process a top economic development priority.
Oakwood, the state’s largest privately-owned homebuilder, launched Precision Building Systems (PBS) in 2003. Clayton Properties Group, a subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway, acquired Oakwood in 2017, and placed PBS under its Heibar Installation subsidiary, which is based in Maryville, Tenn. The PBS plant kept its name until early 2024, when it was rebranded as Heibar Colorado.
Heibar declined to provide a reason for why it closed the Colorado plant. It also appears that shipping components from its remaining plants in Indiana, Utah and Tennessee long distances to Colorado won’t make economic sense.
Oakwood Homes, in a statement, emphasized that it remains committed to providing attainable homes and that its sales remain strong, rising more than 25% this year over last. While new home construction has slowed nationwide this year, low demand at Oakwood does not appear to be an issue.
“We remain focused on opening doors to home ownership for more families. Heibar’s decision to close its Denver facility will have no long-term impact on Oakwood Homes,” the company said in a statement.
Oakwood Homes did not provide details on how it would replace the components or which manufacturing plant would do so. Although the companies were once closely intertwined, Heibar may not be as essential to Oakwood’s plans as it once was.
Pat Hamill, Oakwood’s founder, focused on building homes affordable for first-time buyers and PBS was key to that strategy. Building more home components indoors, from trusses to floors to complete walls and eventually larger modules, helped lower costs. A wall, for example, would include the framing, insulation, drywall, and electrical wiring and connections.
Components were sent to a homesite, where they could be assembled much faster than with traditional stick build methods. Manufacturing could take place while the lot was being prepared and then the home assembled. That process could take a month or two versus nine months or more for a traditional approach.
Oakwood Homes used the PBS plant most heavily for its On2 Homes, which remain available in Reunion. That line, which is smaller in size and uses larger modules, starts in the mid-$300,000 range in a market where the median price of an existing single-family home sold last month was $640,000.
Building larger sections of homes in a more controlled environment indoors allows for higher precision, tighter quality control and less material waste. Workers could focus on specific tasks along an assembly line, and that line could run day and night, depending on demand.
The construction industry has long struggled with severe labor shortages, which are expected to only worsen as the workforce ages and immigration tightens. Attracting young adults to the field has been a challenge, and manufacturing is viewed as a more palatable option for them than working outdoors in bad weather and dealing with seasonal layoffs.
Manufacturing wages are below what a skilled tradesman could make, providing additional savings to builders. But for workers, manufacturing jobs can provide higher pay and more consistent schedules than many service jobs.
The closure comes despite the Polis administration’s push to make Colorado a national leader in integrating manufacturing into the construction process and fostering innovative technologies, something the state has spent $50 million to encourage via grants and loans.
Heibar Colorado received a $1 million grant under the state’s Innovative Housing Incentive Program in return for a pledge to build 285 homes in the state.
“To date, the company has been awarded $283,000 for 57 units that qualified for the IHIP incentive funding,” said Alissa Johnson, communications director of the Colorado Office of Economic Development and International Trade.
It is not clear if Heibar will fulfill the terms of its grant. But its departure will not deter the state in its efforts, Johnson said.
“The off-site construction industry is growing, advancing our commitment to build more housing now that Coloradans can afford. Some companies will succeed and some will fail and technologies will evolve, but the sector continues to grow,” she said. “We do not believe these layoffs are a reflection of Colorado’s off-site construction industry as a whole, and our state is advancing the development of this important industry across the state.”
Nearly two-thirds of the cost of a new home nationally is tied to construction, with 14% reflecting the cost of land and 22% coming from government-imposed costs, according to the Construction Cost Survey from the National Association of Homebuilders.
In Colorado, construction costs are roughly split between labor and materials. So roughly a third of the cost of a home is linked to how it is put together, and if that cost can be lowered in a meaningful way, so can the overall price tag.
Since the 1970s, the productivity in manufacturing has more than doubled in the U.S., meaning workers today produce twice as much output per hour of work. Construction workers, by contrast, are 30% less efficient today than they were in 1970, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
That runs counter to almost every other part of the U.S. economy, and that lack of efficiency helps explain, in part, why the industry can’t meet the demand for new homes and struggles to provide a product people can afford. The nation’s shortfall of 5 million homes, and Colorado’s shortfall of 106,000 homes, while improving, has contributed to a surge in home prices, both new and existing, and locked more people into renting.
The median age of a first-time homebuyer in the U.S. is now 40, up from 28 in 1991, according to the National Association of Realtors. And the lack of affordable entry-level homes is a big reason why.

Colorado
Colorado lawmakers duel over data centers: Grant millions in tax breaks or regulate them without incentives?

Colorado lawmakers are deciding this year between two disparate approaches on data centers — one that aims to lure them to the Centennial State with millions of dollars in tax incentives and another that would implement some of the strictest statewide regulations in the country on the booming tech industry.
Either of the two competing bills would create the state’s first regulations specific to data centers. Sponsors of both bills say they hope to minimize environmental impacts from the power and water demands of the centers, while also ensuring that the cost of new infrastructure they need doesn’t wind up on residents’ electric bills.
Both bills are sponsored by Democrats but differ widely in what they’d do.
The bill supported by the data center industry — House Bill 1030 — would incentivize companies to comply with regulations in exchange for large tax breaks. The legislation would not regulate data centers whose owners forgo a tax break.
The other bill — Senate Bill 102 — would offer no incentives, instead imposing regulations on all large data center development across the state. It is supported by environmental and community groups.
“We want to make sure that as data centers come here, they come on our terms,” said Megan Kemp, the Colorado policy representative for Earthjustice’s Rocky Mountain office.
The bills have landed as debate over the future of data center regulation intensifies across the state. Data centers house the computer servers that function as the main infrastructure for the digital world. They crunch financial data, store patients’ health information, process online shopping, register sports betting and — increasingly — make possible the heavy data demands of artificial intelligence.
Several companies have begun construction on large data centers across the Front Range in recent years. A 160-megawatt hyperscale facility is under development in Aurora and could consume as much power as 176,000 homes once completed.
The construction of a 60-megawatt data center campus in north Denver has angered those who live by the site and prompted Denver city leaders last week to call for a moratorium on new data center development while they craft regulations for the industry. Larimer County and Logan County have enacted similar moratoriums.
Hundreds gathered Tuesday night at a community meeting about the northern Denver campus owned by CoreSite. Frustration in the crowd — which filled overflow rooms and the front lawn of the building that hosted the meeting — erupted as residents of the neighborhoods surrounding the center expressed concerns about how it would impact their air quality, power and water supplies.
Attendees said they did not know the data center was being built until they saw construction underway.
CoreSite leaders had planned to attend the meeting. But they pulled out of participating the day before because of safety concerns, company spokeswoman Megan Ruszkowski wrote in an email. She did not elaborate on the concerns. A Denver police spokesman said the department did not have any record of a police report filed by CoreSite in the days prior to the meeting.
CoreSite’s absence left officials from the city and utilities to answer the crowd’s questions and field their frustrations. City leaders told attendees that they had no say in whether the data center could be built because there are no city regulations specific to the industry.
“Data centers are proliferating quickly and we don’t know all the impacts,” said Danica Lee, the city’s director of public health investigations. “That’s why we need this moratorium.”
Promises of future regulation meant little to the residents of Elyria-Swansea, where the data center is scheduled to go online this summer. More than an hour into the meeting, a man took the microphone. He noted that so much of the conversation had focused on technicalities — but the information provided had not answered a question on many residents’ minds.
“How do we stop it now?” he asked, to a loud round of applause from the room.
Transformative opportunity?
Some in the state Capitol think more data centers would be beneficial for Colorado.
Supporters of the tax incentive bill in the legislature said luring the industry to Colorado would create high-paying jobs, help pay for electrical grid modernizations and strengthen local tax bases.
“This could be transformative for the state,” said Rep. Alex Valdez, a Denver Democrat who is one of HB-1030’s sponsors.
In exchange for complying with rules, data center companies would be exempted from sales and use taxes for 20 years for purchases related to the data center, like the expensive servers they must replace every few years. After two decades, the companies could apply for an extension to the exemption.
To earn the tax break, data center companies would have to meet requirements that include:
- Breaking ground on the data center within two years.
- Investing at least $250 million into the data center within five years.
- Creating full-time jobs with above-average wages, though the legislation doesn’t specify how many jobs would be required.
- Using a closed-loop water cooling system that minimizes water loss, or a cooling system that does not use water.
- Working to make sure the data center “will not cause unreasonable cost impacts to other utility ratepayers.”
- Consulting with the Colorado Department of Natural Resources about wildlife and water impacts.
While the bill would exempt data centers from sales tax on some purchases, they would still be on the hook for all other taxes, Valdez said, and would bring both temporary and permanent jobs. The bill does not specify how many permanent jobs must be created to qualify for the tax break.
Dozens of other states have enacted tax incentive programs for data centers. Such incentives are a key factor that companies weigh when deciding where to build, said Dan Diorio, the vice president of state policy for the Data Center Coalition, an industry group.
“Colorado is not competitive right now,” he said.
Figuring out the projected impact of the bill on the state’s finances gets complicated.
The legislature’s nonpartisan analysts estimated that the state would miss out on $92.5 million in sales tax revenue in the first three years, assuming a total of 17 data centers would qualify for the tax breaks in that time period.
But Valdez said that is revenue that the state otherwise wouldn’t see if the data centers weren’t built here. And the companies would still pay all other state and local taxes, he said.
“We see it as unrealized revenue, rather than a tax cut,” he said.
Some of that lost tax revenue would be offset by an increase in income taxes paid by low-income families, according to the bill’s fiscal note.
That’s because the projected decrease in sales tax revenue in the first year of the program would decrease the amount of money available for the state to provide its recently enacted Family Affordability Tax Credit. State law ties the amount available for the family tax credit to state revenue growth and whether the state collects money above a revenue cap set by the Taxpayer’s Bill of Rights. TABOR requires money above that level to be returned to taxpayers.
If the state doesn’t have excess revenue, it can’t fund that tax credit.
In the next fiscal year, which begins in July, data center companies would avoid paying $29 million in sales taxes, which would trigger a change in the family tax credit. Low-income families would be made to pay a total of $106 million more, the fiscal note estimates.
Bill sponsors are planning to address the fallout for the tax credit in forthcoming amendments, Valdez said.
“We’re not out to trigger any negative impacts to low-income families,” he said.

Baseline guardrails
Forgoing tax dollars during a state budget crisis is a hard sell to Rep. Kyle Brown, a Louisville Democrat sponsoring the regulatory bill. He and other supporters of SB-102 aren’t convinced tax incentives are necessary to bring data centers to the state.
Major construction projects are already underway, he said. In Denver, CoreSite chose not to pursue $9 million in tax breaks from the city but continued construction on its facility regardless.
“The point of our policy is (putting) reasonable, baseline guardrails on this development so it can be smart,” Brown said.
Brown last session co-sponsored a failed bill with Valdez that offered tax incentives to data centers. Since then, however, he’s seen other states that offer tax incentives express buyers’ remorse, he said.
Brown pointed to concerns in Virginia about rising electricity costs due to data center demand and a proposal by the governor of Illinois to suspend the state’s tax credit so that the impacts of the data center boom it sparked could be studied.
His bill this session — co-sponsored by Sen. Cathy Kipp, a Fort Collins Democrat — requires that data centers over 30 megawatts:
- Draw as much power as possible from newly sourced renewable energy by 2031.
- Pay for any additions or changes to the grid needed to serve the data center.
- Adhere to local rules about water efficiency.
- Limit the use of backup generators that consume fossil fuels; if such generators are necessary, they must be a certain type that limits emissions.
- Conduct an analysis of the data center’s impacts on local neighborhoods, engage in community outreach and sign a legally binding good-neighbor agreement if the community is disproportionately affected by pollution.
Owners of data centers would also need to report metrics annually to the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment. They would cover the center’s annual electricity consumption, how much of that power came from renewable sources, the total number of hours backup generators were used and annual water use.
Utilities, too, would face additional requirements.
The legislation would ban utilities from offering discounted rates to large data centers. It also would prohibit them from supplying electricity to a data center if doing so would affect the utility’s ability to provide power to its other customers — or its ability to meet state emissions reduction goals.
Environmental groups supporting the bill say the state needs regulations to make sure the increased electrical demand generated by data centers doesn’t expand the state’s use of fossil fuels or slow the retirement of fossil fuel-powered plants.
If not done thoughtfully, the groups said, the increased electrical load could imperil the state’s climate goals.
“What we need to avoid is a race to attract data centers that turns into a race to the bottom,” said Alana Miller, the Colorado policy director for the Natural Resources Defense Council’s climate and energy program.
If the legislature enacts SB-102, it would implement the strictest data center regulations in the country and would ward off future data center development, Diorio said. He sees many of the rules as unattainable.
“It would make it nearly impossible to develop a data center in the state of Colorado,” he said.
Conversations between the sponsors of the two bills are underway, Valdez and Brown said. Both expressed hope that a consensus could be found between the two pieces of legislation.
Neither bill had been scheduled for a committee hearing.
Stay up-to-date with Colorado Politics by signing up for our weekly newsletter, The Spot.
Colorado
Colorado family pushes for change after rare disease clinical trial abruptly ends
Colorado
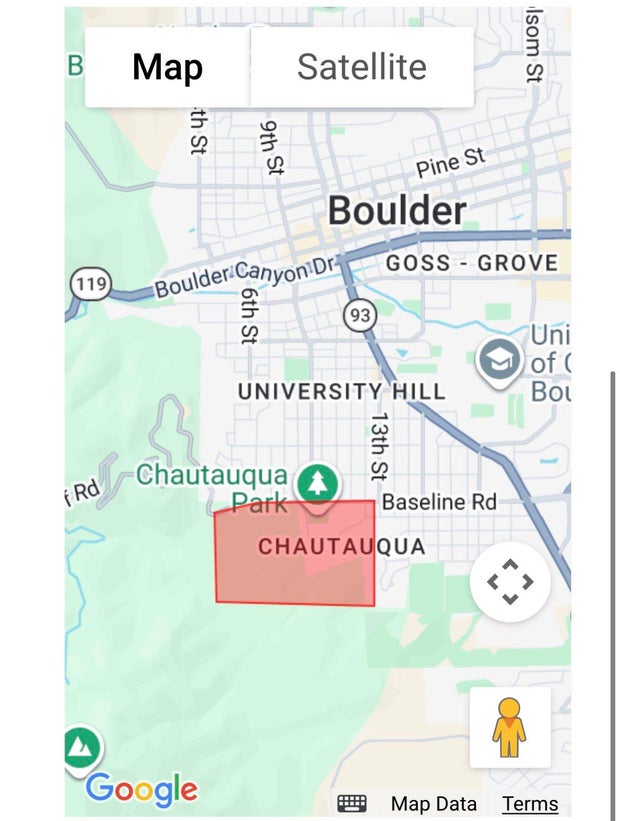
Evacuation warning issued for area near wildfire in southwest Boulder

Authorities have issued an evacuation warning for homes near a wildfire that broke out in southwest Boulder on Saturday afternoon.
Just before 1 p.m., Boulder Fire Rescue said a wildfire sparked in the southwest part of Boulder’s Chautauqua neighborhood. The Bluebell Fire is currently estimated to be approximately five acres in size, and more than 50 firefighters are working to bring it under control. Mountain View Fire Rescue is assisting Boulder firefighters with the operation.
Around 1:30, emergency officials issued an evacuation warning to the residents in the area of Chatauqua Cottages. Residents in the area should be prepared in case they need to evacuate suddenly.
Officials have ordered the DFPC Multi-Mission Aircraft (MMA) and Type 1 helicopter to assist in firefighting efforts. Boulder Fire Rescue said the fire has a moderate rate of spread and no containment update is available at this time.
Red Flag warnings remain in place for much of the Front Range as windy and dry conditions persist.
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoExclusive: DeepSeek withholds latest AI model from US chipmakers including Nvidia, sources say
-

 Massachusetts4 days ago
Massachusetts4 days agoMother and daughter injured in Taunton house explosion
-

 Denver, CO4 days ago
Denver, CO4 days ago10 acres charred, 5 injured in Thornton grass fire, evacuation orders lifted
-

 Louisiana7 days ago
Louisiana7 days agoWildfire near Gum Swamp Road in Livingston Parish now under control; more than 200 acres burned
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoYouTube TV billing scam emails are hitting inboxes
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoOpenAI didn’t contact police despite employees flagging mass shooter’s concerning chatbot interactions: REPORT
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoStellantis is in a crisis of its own making
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoWorld reacts as US top court limits Trump’s tariff powers