North Carolina
Rip current risks higher at NC beaches as Tropical Storm Alex churns in Atlantic


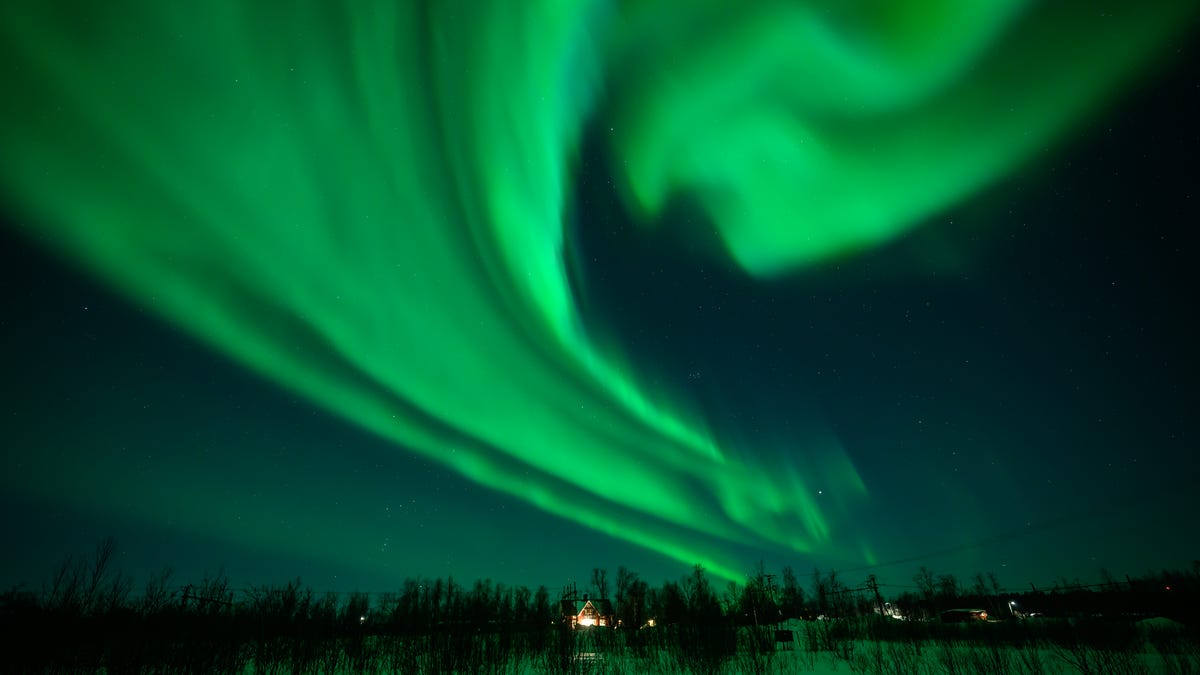
Tropical Storm Alex may convey harmful surf situations and better rip present dangers to North Carolina seashores, forecasters mentioned.
Nationwide Climate Service
Tropical Storm Alex may make swimming situations harmful at North Carolina’s seashores.
Alex is the primary named storm of Atlantic hurricane season, which started June 1. It strengthened right into a tropical storm early Sunday, June 5, after bringing heavy rain, flooding and robust winds to elements of Florida, The Related Press reported. Tropical storms have wind speeds between 39 and 73 mph.
As of 11 a.m. June 5, Alex was situated about 550 miles west of Bermuda with most sustained wind speeds of 60 mph, in line with the Nationwide Hurricane Middle. It’s transferring east-northeast at 23 mph and is anticipated to convey tropical storm situations to Bermuda late June 5 or early Monday, June 6.
Forecast for North Carolina seashores
Forecasters haven’t mentioned in the event that they count on any land impacts in North Carolina. However the storm is anticipated to convey harmful surf situations and elevated rip present dangers to the coast.
The Nationwide Climate Service’s Wilmington workplace, which covers southeastern North Carolina, tweeted June 5 that Alex “will churn up the Atlantic Ocean ensuing with rising surf the subsequent 2 days that can favor an elevated rip present risk throughout all seashores.”
Elements of the coast are beneath a average rip present danger on June 5, and a few areas might be beneath a excessive danger on Monday, June 6, the NWS mentioned. The danger is anticipated to begin “slowly de-escalating by the mid to late week interval.”
A average danger means situations are “favorable for the event of life threatening rip currents” whereas a excessive danger means situations “will possible help the event of life threatening rip currents.”
The climate service’s Newport/Morehead workplace, which covers Japanese North Carolina, together with elements of the state’s Outer Banks, mentioned on Twitter that there’s an elevated danger of rip currents on June 5 “because of the mixture of robust winds and arriving swell from Tropical Storm Alex.”
A number of areas are beneath a excessive danger of rip currents, that means “everybody ought to keep out of the water.”
“Rip currents might be strongest late within the day. Please heed the warnings of lifeguards and seaside flags,” the workplace wrote on Twitter.
The elevated danger of rip currents is anticipated to proceed “for the subsequent few days” within the space, the NWS mentioned.
A lot of the North Carolina coast can also be beneath a small craft advisory. Forecasters say “inexperienced mariners, particularly these working smaller vessels, ought to keep away from navigating in hazardous situations.”
Rip present security
Rip currents are “channelized currents of water flowing away from shore,” in line with the NWS.
“Rip present speeds differ,” the NWS mentioned. “Common speeds are 1-2 toes per second, however they’ve been measured as quick as 8 toes per second — quicker than an Olympic swimmer!”
Whereas they’ll pull swimmers away from shore, they won’t pull them beneath the water.
If caught in a rip present, don’t attempt to swim in opposition to it, the NWS mentioned.
As an alternative, keep calm and attempt to swim parallel to the shore till you’re out of the rip present, then “observe breaking waves again to shore at an angle,” the Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration mentioned.
“You could possibly escape by floating or treading water if the present circulates again towards shore,” the climate service mentioned. “For those who really feel you may be unable to succeed in shore, draw consideration to your self. For those who need assistance, yell and wave for help.”
For those who see somebody caught in a rip present, get assist from a lifeguard or name 911, direct the swimmer to observe the shoreline to flee the present and throw them a flotation gadget if attainable, the NWS mentioned.
However don’t enter the water with out a flotation gadget, the NWS mentioned, as “many individuals have died making an attempt to rescue rip present victims.”
This story was initially printed June 5, 2022 11:33 AM.

North Carolina
North Carolina HBCUs cash in as gambling losses hit $100 million

The introduction of sports gambling in North Carolina has resulted in losses for millions, but it will be a windfall for athletics at several HBCUs as well as other schools within the state.
The state lottery commission reports that more than $105 million was lost in the state on sports betting in the first full month since it became legal. The number was $66 million for March, which only accounted for the final two-thirds of the month. Eighteen percent of that money goes back to the state, coming out to more than $30 million in tax revenue so far.

The five public HBCUs stand to benefit from the move. Those HBCUs are Elizabeth City State University, Fayetteville State University, N.C. Agricultural & Technical State University, N.C. Central University, and Winston-Salem State University. Up to $300,000 annually will go to these universities along with Appalachian State University, East Carolina University, University of North Carolina at Asheville, University of North Carolina at Charlotte, University of North Carolina at Greensboro, University of North Carolina at Pembroke and University of North Carolina at Wilmington.
Millions will also go to the Department of Health and Human Services for gambling addiction education and treatment programs and youth sports iniatives.
Once all the primary money has been distributed, twenty percent of what remains will be distributed evenly among the 13 state universities to support collegiate athletic departments.
Related

North Carolina
NC schools are struggling with segregation 70 years after Brown v. Board, new research shows
North Carolina schools — and schools across the nation — remain segregated and often are more segregated now than they were just a few decades ago, according to two new studies.
Friday marks the 70th anniversary of the U.S. Supreme Court ruling in Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, in which the court ruled that laws racially segregating schools were unconstitutional and that separate facilities were inherently unequal.
The state and nation are more diverse now than in the 1990s. But while white students are now a minority of the state’s student traditional public school population, most white students still attend schools that are mostly white. At the same time, the average Black student attends schools that are disproportionately Black.
The changes are in part because of continued residential segregation, rising choices outside of the traditional school system and waning efforts to desegregate in the traditional public school system, researchers note. “Resegregation” of schools, then, is in part because of the loss of white students to other types of schools, like public charter schools.
“What we see in North Carolina is consistent with what’s happening in other parts of the nation,” said Jenn Ayscue, an assistant professor at North Carolina State University and co-author of one of the new studies that focused specifically on North Carolina. The study was done in partnership with the University of California-Los Angeles. “We did a similar report 10 years ago, and found that schools at that point were becoming more segregated. So in this last decade, it’s gotten even worse.”
The causes of the problem are often also out of the control of schools alone.
“Residential segregation has not gone anywhere in this country,” said Jerry Wilson, director of policy and advocacy at the Center for Racial Equity in Education, a Charlotte-based organization. “It remains and that’s the one that policymakers just seem unwilling to do much about. We’ve tinkered around with schools as a means of desegregating. But ultimately, our society and policymakers have proven unwilling to really address the heart of it, which is residential segregation.”
How segregated schools are can affect academic outcomes for the students who attend them, Ayscue said.
One of the reasons racial integration matters is that race often correlates with other meaningful demographic statistics, Ayscue said. In schools that were “intensely segregated” with students of color in 2021, 82.6% of the students were recipient of free or reduced-price lunch.
Intensely segregated refers to schools that enrolled 90% to 100% students of color. Students of color statewide comprise about 55% of the student population.
Ayscue said students tend to do better in schools where household incomes tend to be higher, although there are always outliers. More affluent schools tend to have fewer needs, more experienced teachers and less employee turnover.
During the 1989-90 school year, less than 10% of Black students attended a school that was intensely segregated with students of color. But during the 2021-22 school year, just under 30% of Black students did.
But white students are less likely now to attend schools that are intensely segregated with white students. During the 1989-90 school year, 21.6% of schools were intensely segregated with white students. But by 2021-22 school year, that was 1.9% of schools.
Integration is better in more rural school districts, where there aren’t as many schools. A single town might have only one school that all students attend, Ayscue said.
What can be done
Ayscue and her fellow researchers recommend expanding magnet school programs or other methods of offering a “controlled choice” for families. Magnet schools can take shape a few different ways but are essentially normal public schools with extra programming that outside families can apply to attend. They typically take neighborhood students and outside applicants. Because of that mix, they often are more diverse than other nearby schools.
Magnet schools are relatively rare, mostly concentrated in urban and suburban areas. North Carolina has 226 magnet schools this year, located in 17 school systems. Nearly all of the magnet schools are in Wake, Charlotte-Mecklenburg, Durham, Guilford, Winston-Salem/Forsyth and Cabarrus county school systems. The state has 115 school systems and more than 2,600 schools.
NC State’s researchers found some school systems are working to reduce segregation at their schools. Durham Public Schools next year will start is “Growing Together” student assignment plan, a heavily debated major overhaul that creates sub-districts in which students can attend a neighborhood or magnet school and limits choice options across the system. Winston-Salem/Forsyth County Schools is studying its enrollment and attendance trends before creating a student assignment policy that would attempt to increase socioeconomic diversity at the district’s schools.
A national study from Stanford University and the University of Southern California pointed to charter schools are a reason for the resegregation. Charters can often be heavily segregated — attracting mostly white families in suburban areas or attracting mostly families of color in urban areas. In North Carolina, charter schools tend to be whiter than the statewide average.
The demographics of charter schools have been shifting for several years to close to statewide averages. That’s in part because more of them are using weighted lotteries to admit students. Those lotteries give applicants more weight — and a greater likelihood fo getting into the school — if the applicant is “educationally disadvantaged.” Charter schools create their own rules for weighted lotteries but must include more weight for low-income students.
But most schools don’t have weighted lotteries and charter schools are still more concentrated in urban areas, said Kris Nordstrom, a senior policy analyst with the Education & Law Project at the left-learning North Carolina Justice Center, which has been critical of charter schools. From what Nordstrom has researched, the demographic disparities between urban charter schools and the counties they are located in are more stark than when simply comparing statewide averages.
The impact on segregation of the expansion of private school vouchers will be hard to measure, Ayscue said. Individual private schools don’t report their demographic data publicly. Demographic data are available on voucher recipients only on a statewide basis.
North Carolina
In a debut book, a love letter to eastern North Carolina — and an indictment of colonialism as a driver of climate change

This story was produced in partnership with Covering Climate Now.
As the planet grapples with the ever-starker consequences of climate change, a debut book by Lumbee citizen and Duke University scientist Ryan Emanuel makes a convincing argument that climate change isn’t the problem — it’s a symptom. The problem, Emanuel explains in On the Swamp: Fighting for Indigenous Environmental Justice, is settler colonialism and its extractive mindset, which for centuries have threatened and reshaped landscapes including Emanuel’s ancestral homeland in what today is eastern North Carolina. Real environmental solutions, Emanuel writes, require consulting with the Indigenous peoples who have both millennia of experience caring for specific places, and the foresight to avoid long-term disasters that can result from short-term material gain.
Born in Charlotte, North Carolina, in 1977, Emanuel was one of a handful of Native students at school. He spent summers visiting family in Robeson County, North Carolina, the cultural center of the Lumbee Tribe, or People of the Dark Water, where he played outside with other children, occasionally exploring a nearby swamp, one of the many lush waterways that slowly wind through the region, with a cousin. Today, Emanuel visits those swamps to conduct research. He describes them with an abiding, sometimes poetic affection, such as one spring day when he stands calf-deep in swamp water, admiring white dogwood flowers floating on the dark surface as tadpoles dart underneath.
But that affection lives with tension. Emanuel describes trying to collect “reeking” floodwater samples from a ditch after 2018’s Hurricane Florence. In Emanuel’s retelling, a nearby landowner — a white farmer who uses poultry waste as fertilizer — threatens to shoot Emanuel. The sampling, the man believes, would threaten his livelihood, which is wrapped up in North Carolina’s extractive animal farming industry — a system of giant, polluting “concentrated animal feed operations” overwhelmingly owned and operated by white people, and exposing mainly racial minorities to dirty air and water. They are a sharp contrast to the small backyard farms and truck crops grown by Emanuel’s aunties and uncles back in Robeson County a generation ago. As the man holds his gun and lectures about environmental monitoring, Emanuel reflects silently that they are standing on his ancestors’ land. Ever the researcher, he later finds deed books from around the Revolutionary War showing Emanuels once owned more than a hundred acres of land in the vicinity. Still, he holds a wry sympathy for the man, who, he notes, is worried that environmental data will jeopardize his way of life in a place his family has lived for generations.
Eastern North Carolina is a landscape of sandy fields interwoven with lush riverways and swamplands, shaded by knobby-kneed bald cypress trees and soaked with gently-moving waterways the deep brown of “richly steeped tea,” Emanuel writes. In addition to water, the region oozes history: It includes Warren County, known as the birthplace of the environmental justice movement, where local and national civil rights leaders, protesting North Carolina’s decision to dump toxic, PCB-laden soil in a new landfill in a predominantly-Black community, coined the term “environmental racism.” It’s also the mythological birthplace of English colonialism, Roanoke Island. On the Swamp draws a through line from early colonization of the continent to ongoing fights against environmental racism and for climate justice, with detailed stops along the way: Emanuel’s meticulous research illustrates how the white supremacism that settlers used to justify colonialism still harms marginalized communities — both directly, through polluting industries, and indirectly, through climate change — today.
With convoluted waterways accessible only by small boats, and hidden hillocks of high ground where people could camp and grow crops, the swamplands of eastern North Carolina protected Emanuel’s ancestors, along with many other Indigenous peoples, from genocide and enslavement by settlers. Today, with climate change alternately drying out swamplands or flooding them with polluted water from swine and poultry operations, it’s the swamps that need protection, both as a geographic place, and an idea of home. The Lumbee nation is the largest Indigenous nation in the eastern United States, but because the Lumbee Tribe gained only limited federal recognition during the 1950s Termination Era, its sovereignty is still challenged by the federal government and other Indigenous nations. Today, federal and state governments have no legal obligation to consult with the Lumbee Tribe when permitting industry or development, although the federal government does with Indigenous nations that have full federal recognition, and many industrial projects get built in Robeson County.
In writing that’s both affectionate and candid, On the Swamp is a warning about, and a celebration of, eastern North Carolina. Though the region seems besieged by environmental threats, Indigenous nations including the Lumbee are fighting for anticolonial climate justice.
Grist recently spoke with Emanuel about On the Swamp.
This interview has been edited for clarity and length.
Q. What motivated you to write this book?
A. Many years ago, I thought that I wanted to write a feel-good book about celebrating the Lumbee River and the Lumbee Tribe’s connection with it, and talking about all the reasons why it’s beautiful, and amazing, and important to us. So I thought that I would write this essentially nature story, right? But as my work evolved, and as I started thinking more critically about what I actually should be writing, I realized that I couldn’t tell that love story about the river without talking about difficult issues around pollution, climate change, and sustainability, and broader themes of environmental justice and Indigenous rights.
Q. Could you tell me about your connection to place?
A. I have a relationship to Robeson County that’s complicated by the fact that my family lived in Charlotte, and I went to school in Charlotte, and we went to church in Charlotte. But two weekends every month, and every major holiday, we were in Robeson County. And so I’m an insider, but I’m also not an insider. I’ve got a different lens through which I look at Robeson County because of my urban upbringing, but it doesn’t diminish the love that I have for that place, and it doesn’t keep me from calling it my home. I’ve always called it home. Charlotte was the place where we stayed. And Robeson County was home.
I can’t see the Lumbee River without thinking about the fact that it is physically integrating all of these different landscapes that I care about, [and] a truly beautiful place.
Q. In 2020, after years of protests and legal battles, Dominion Energy and Duke Energy canceled the Atlantic Coast pipeline, which would have carried natural gas 600 miles from West Virginia to Robeson County. In On the Swamp, you note that a quarter of Native Americans in North Carolina lived along the proposed route of the Atlantic Coast Pipeline. What was the meaning of the Atlantic Coast pipeline project for Lumbee people?
A. That was an issue very few Lumbee people paid attention to, until they saw the broader context to the project and realized that such an outsized portion of the people who would be affected by the construction and operation of that pipeline were not only Native American, but were specifically Lumbee. I think that’s what generated a lot of outrage, because for better or for worse, we’re used to being treated like a sacrifice zone.
The Atlantic Coast pipeline gave us an easy way to zoom out and ask questions like, “OK, who is going to be affected by this project? Who’s making money off of this project?”
It was also a way to engage with larger questions about things like energy policy in the face of climate change and greenhouse gas emissions. [It] brought up philosophical questions of how we feel about the continued use of fossil fuels and the investment in brand new fossil fuel infrastructure that’s going to last 30, 40, or 50 years, at a time when everybody knows we shouldn’t be doing that.
Q. At the end of the day, the Atlantic Coast pipeline didn’t happen. What do you think is the main reason?
A. The collective resistance of all of these organizations — tribal nations, committed individuals, grassroots organizations — was enough to stall this project, until the developers realized that they had fallen into the Concorde fallacy. Basically, they got to the point where they realized that spending more money was not going to get them out of the hole they had dug in terms of opposition to this project.
But as long as [developers] hold on to those [property] easements, there’s certainly a threat of future development.
Q. You write that people can physically stay on their ancestral land and still have the place taken away by climate change, or by development projects. Can you talk a little bit about still having the land but somehow losing the place?
A. The place is not a set of geographic coordinates. It’s an integration of all the natural and built aspects of the environment. And so climate change, deforestation, these other types of industrialized activities, they have the potential to sweep that place out from under you, like having the rug pulled out. All of the things that make a set of geographic coordinates a beloved place can become unraveled, by these unsustainable processes of climate change and unsustainable development. I think that the case studies in [On the Swamp] show some of the specific ways that that can happen.
Q. Could you talk about your experiences as a researcher going out in the field, navigating modern land ownership systems, and how that connects to climate change?
A. I don’t know if it’s fair to say that I have to bite my tongue a lot, but I kind of feel that way. When I hear people talk about their ownership of our ancestral lands — I’m a mix of an optimist and a realist, and I understand that we’re not going to turn back the clock. And frankly, I’m not sure I want to, because Lumbee people are ourselves a product of colonial conflict, and we wouldn’t exist as the distinct nation that we are today, if it were not for the colonial violence that we survived. We might exist as our ancestral nations and communities, but we definitely wouldn’t be Lumbee people. So this is a complicated issue for me.
When we think about the front lines of climate change, we don’t often think about Robeson County, North Carolina. But because our community is so attuned to that specific place, we’re not going to pick up and move if the summers get too hot, or if the droughts are too severe. That’s not an option for us. So I think that some of the urgency that I feel is not too different from the urgency that you hear from other [Indigenous] people who are similarly situated on the front lines of climate change.
Q. Something else that you make a really strong point about in this book is that something can be a “solution” to climate change, but not sustainable, such as energy companies trying to capture methane at giant hog farms in Robeson County. How should people think about climate solutions, in order to also take into account their negatives?
A. The reason why people latch onto this swine biogas capture scheme is if you simply run the numbers, based on the methane and the carbon dioxide budgets, it looks pretty good.
But a swine facility is a lot more than just a source of methane to the atmosphere, right? It’s all these other things in terms of water pollution, and aerosols, and even things like labor issues and animal rights. There are all these other things that are attached to that kind of facility. If you make a decision that means that facility will persist for decades into the future operating basically as-is, that has serious implications for specific people who live nearby, and for society more broadly. We don’t tend to think through all those contingencies when we make decisions about greenhouse gas budgets.
Q. What are some ways that the Lumbee tribe is proactively trying to adapt to climate change?
A. Climate change is not an explicit motivation [for the Lumbee Tribe]. If you go and read on the Lumbee Tribe’s housing programs website, I don’t think you’re going to find any rationale that says, “We’re [building housing] to address climate change.” But they are.
Getting people into higher-quality, well-insulated and energy-efficient houses is a big deal when it comes to addressing climate change, because we have a lot of people who live in mobile homes, and those are some of the most poorly insulated and least efficient places that you could be. And maybe 40 years ago, when our extreme summer heat wasn’t so bad, that wasn’t such a huge deal. But it’s a huge deal now.
Q. What is the connection between colonialism and climate change for eastern North Carolina, and why is drawing that line necessary?
A. The one sentence answer is, “You reap what you sow.”
The longer answer is, the beginning of making things right is telling the truth about how things became wrong in the first place. And so I really want this book to start conversations on solving these issues. We really can’t solve them in meaningful ways unless we not only acknowledge, but also fully understand, how we got to this point.
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoRFK Jr said a worm ate part of his brain and died in his head
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPentagon chief confirms US pause on weapons shipment to Israel
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoConvicted MEP's expense claims must be published: EU court
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoStudents and civil rights groups blast police response to campus protests
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCalifornia Gov Gavin Newsom roasted over video promoting state's ‘record’ tourism: ‘Smoke and mirrors’
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoOhio AG defends letter warning 'woke' masked anti-Israel protesters they face prison time: 'We have a society'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoNine Things We Learned From TikTok’s Lawsuit Against The US Government
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoBiden’s decision to pull Israel weapons shipment kept quiet until after Holocaust remembrance address: report



















