Science
An asteroid will just miss us in 2029. Scientists are making the most of a rare opportunity

To be clear: The asteroid will not be going to hit us.
There was some time there when it appeared prefer it may. Suffice to say these have been heady days within the asteroid-tracking group. However as of March 2021, NASA has confirmed that there’s completely zero probability the area rock often called 99942 Apophis will strike this planet for a minimum of 100 years. So, phew. Cross that specific doomsday state of affairs off the listing.
What stays true, nevertheless, is that on Friday, April 13, 2029, an asteroid wider than three soccer fields will move nearer to Earth than something its dimension has are available in recorded historical past.
An asteroid strike is a catastrophe; an asteroid flyby, a possibility. And Apophis presents among the best probabilities science has ever needed to learn the way the Earth got here to be — and the way we’d at some point forestall its destruction.
Within the motion pictures, incoming asteroids seem with out warning from the depths of area and velocity immediately towards us till missiles or Bruce Willis heroically destroy them.
In actual life, asteroids orbit the solar on elliptical paths. They’re usually noticed years, if not many years, earlier than a possible collision — which isn’t nice for dramatic rigidity however higher for planetary survival.
Apophis was found in 2004. After calculating its potential orbits, astronomers have been startled to comprehend it had a 3% probability of hitting Earth in 2029. In a nod to its horrifying potential, they named it Apophis, an Egyptian god of chaos.
“We have been shocked,” mentioned Paul Chodas, who manages NASA’s Close to-Earth Object Program Workplace on the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in La Cañada-Flintridge. “That may be very critical and, really, a really sudden and uncommon occasion.”
Astronomers use a color-coded warning system referred to as the Torino Scale to gauge the diploma of hazard an asteroid or comet presents to Earth within the subsequent 100 years. For the reason that scale’s creation in 1995, not one of the roughly 30,000 near-Earth objects recognized to exist within the photo voltaic system had ranked increased than 1 on the zero-to-10 scale.
Apophis was a 4.
The longer astronomers observe an asteroid, the extra clearly outlined its orbit turns into. Inside a couple of months, scientists have been in a position to rule out the potential for a 2029 strike. Inside a couple of years, they have been in a position to dismiss the even smaller probability of a success in 2036.
Pictures of the asteroid Apophis, captured in 2012, allowed scientists to find out that it’ll not strike Earth throughout an in depth flyby in 2036.
(NASA / JPL-Caltech)
And in 2021, radar observations confirmed that Apophis won’t strike when it passes us in 2068, leaving Earth within the clear for a minimum of a century.
With humanity’s security assured — from this risk, a minimum of — the coast was clear to geek out on some asteroid science.
“We’ve by no means seen one thing that enormous get that shut,” mentioned Lance Benner, a principal scientist at JPL.
“Shut,” within the area world, is a relative time period. At its nearest, Apophis will move roughly 19,000 miles (31,000 kilometers) above Earth’s floor. That’s about one-Tenth the space to the moon.
Nobody on the bottom shall be tempted to duck, and it’ll not seem as a fireball swooshing throughout the heavens.
On the large evening, Apophis shall be seen with the bare eye from components of Europe and Africa. (In Los Angeles, skilled stargazers would possibly be capable to spot it with binoculars round 3:30 a.m. on April 13.)
The asteroid shut encounter presents “an unprecedented alternative to check its bodily properties and to assist us study issues that we’ve by no means been in a position to study earlier than,” Benner mentioned.
An strategy this shut from an asteroid this huge happens at most each few thousand years, mentioned Davide Farnocchia, a navigation engineer at JPL.
“It’s one thing that just about by no means occurs, and but we get to witness it in our lifetime,” Farnocchia mentioned. “We normally ship spacecraft on the market to go to asteroids and discover out about them. On this case, it’s nature doing the flyby for us.”
From the bottom, Apophis will resemble a star traversing the evening sky, as shiny because the constellation Cassiopeia and slower than a satellite tv for pc. Although it could seem far-off for these of us down right here, it’ll in actual fact be close to sufficient for NASA to succeed in out and contact it.
OSIRIS-REx, a spacecraft at the moment ferrying house samples from the floor of an asteroid referred to as Bennu, will rendezvous with Apophis in 2029. Shortly after April 13, the craft — by then renamed OSIRIS-APophis EXplorer, or OSIRIS-APEX — will steer towards the asteroid till it’s drawn into its orbit, finally getting shut sufficient to gather a pattern from its floor.
Apophis is formed like a peanut shell, a type astronomers name a “contact binary.” The hunk of nickel, iron and silicate is a relic from the earliest days of the photo voltaic system, a byproduct of the large cloud of fuel and mud that fashioned 4.6 billion years in the past and finally led to us.
“These asteroids are primordial samples,” Chodas mentioned. “Studying in regards to the composition will assist us perceive the historical past of the photo voltaic system and the place this stuff got here from.”
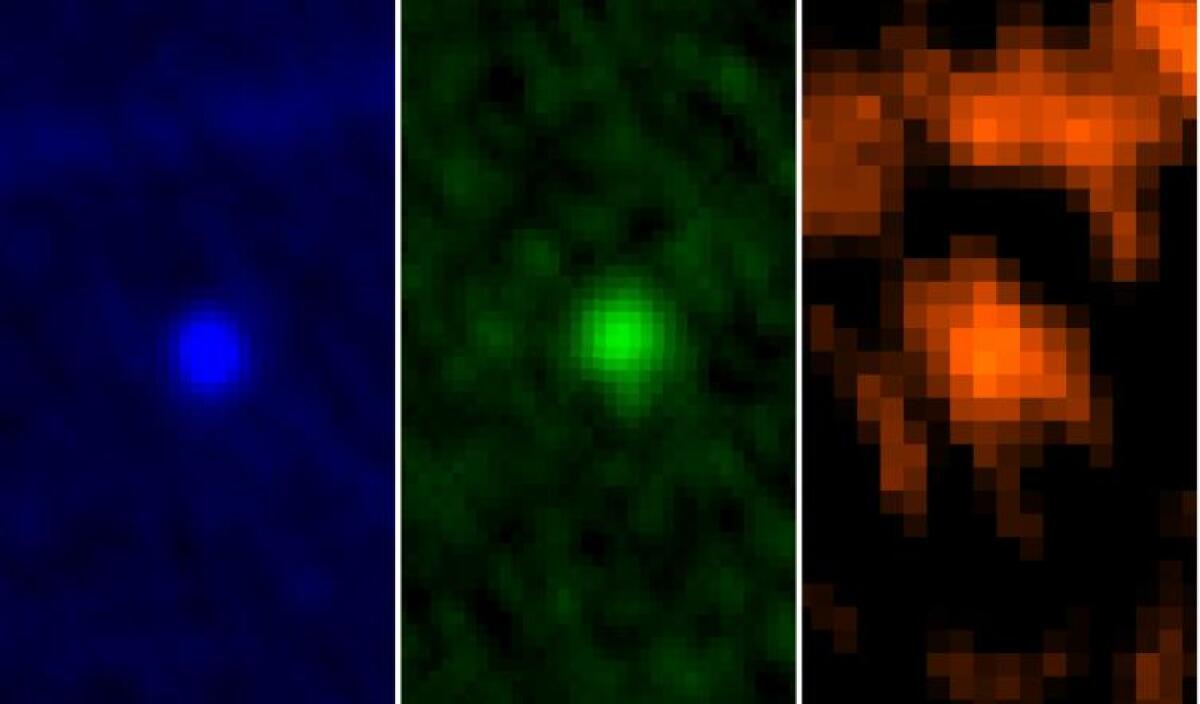
The European House Company’s Herschel House Observatory noticed Apophis throughout the strategy to Earth on Jan. 5 and 6, 2013. The picture reveals the asteroid in three wavelengths.
(European House Company )
Given the proximity, researchers will even be capable to research Apophis with ground-based instruments which have by no means been deployed for an object this dimension.
On Dec. 27, researchers on the Excessive-frequency Lively Auroral Analysis Program (HAARP) in Gakona, Alaska, despatched a low-frequency radio sign to an asteroid referred to as 2010 XC15. It was a part of a check to see if radio waves may penetrate an asteroid and ship again knowledge on its inside construction, mentioned Mark Haynes, the JPL radar methods engineer who led the venture.
Understanding an asteroid’s inner mass distribution can be extraordinarily useful if we wanted to knock it out of our method.
Column One
A showcase for compelling storytelling from the Los Angeles Occasions.
A whole bunch of area rocks hit Earth yearly, and most are innocent. An enormous one, although, can wreak havoc far past its preliminary affect web site.
The huge Chicxulub asteroid that 66 million years in the past slammed into what’s now the Yucatán peninsula in Mexico launched an estimated 420 zettajoules of vitality. (For context, the world’s collective electrical energy output in 2021 was about 0.5 zettajoules.)
The ensuing warmth pulse vaporized rock and sparked wildfires throughout a lot of the planet, adopted by a years-long affect winter as a choking cloud of particulate matter blocked out the solar. By the point it was over, 75% of species have been gone for good, together with all non-avian dinosaurs.
The Chicxulub asteroid measured 7 miles throughout, the identical as town of Paris. Apophis is so long as the Eiffel Tower. A collision with an object that dimension can be much less catastrophic however may nonetheless trigger critical harm.
NASA is engaged on a plan to cope with that. Final yr, its Double Asteroid Redirection Check, or DART, spacecraft intentionally crashed right into a rock 7 million miles away to see whether or not people may change the trajectory of a celestial object. (Excellent news: We are able to.)
If we ever did need to deflect an incoming asteroid, that’s how we’d do it: not with a grand, Loss of life Star-style explosion however with a speedy projectile sturdy sufficient to knock it ever-so-slightly astray.
“That mission was spectacularly profitable and confirmed that that approach works,” Benner mentioned. “Don’t ship Bruce Willis and a bunch of oil drillers up there to blast it to smithereens.”

Science
L.A. County plans to put $5 million toward wiping out medical debt

Los Angeles County is moving forward with a pilot program to relieve medical debt for struggling residents, setting aside $5 million for a planned agreement with a national nonprofit that buys and erases such debts.
County supervisors voted Tuesday to allocate money for a county agreement with Undue Medical Debt to carry out the new program. The effort is expected to launch later this year, focusing on debt stemming from hospital care and targeting L.A. County’s “lowest income residents.”
“No one should be driven into poverty because they got sick,” Supervisor Janice Hahn, who put forward the proposal with Supervisor Holly Mitchell, said in a statement.
“But medical debt remains a huge problem in this country, and it can be devastating for families and their financial well-being. Luckily for us, we have an opportunity to make a difference.”
Hospitals stuck with unpaid bills can bundle and sell the debt at a discount to collection agencies that try to recoup the owed money for profit. Undue Medical Debt instead buys the discounted debt and forgives it. The nonprofit said it can erase an average of $100 in debt for every dollar that is donated.
“Five million dollars can really go a long way,” said its vice president of communications and marketing Daniel Lempert. County officials estimated that amount could eliminate $500 million of debt for 150,000 residents.
Across the country, Undue Medical Debt has partnered with local governments such as Cook County, Ill. and Toledo, Ohio. to fund such efforts. Lempert said that under such agreements, the nonprofit typically reaches out to local hospitals and other health care providers to identify and purchase medical debt affecting financially strapped patients, then gets reimbursed by the local government for the cost of debts affecting their residents.
Under its guidelines for financial hardship, Undue Medical Debt works to relieve debt for people from households making no more than four times the federal poverty level — a calculation equating to $124,800 this year for a family of four — or whose medical debt amounts to 5% or more of their income.
L.A. County is still working out who will be eligible under its pilot program, but its broad goal is to reach “our lowest-income residents and the working poor who have catastrophic amounts of medical debt,” said Dr. Naman Shah, director of the division of medical and dental affairs at L.A. County Public Health.
The L.A. County pilot program will focus specifically on medical debts for hospital care, Shah said. Local residents cannot apply directly for their medical debt to be wiped out, but will be informed if Undue Medical Debt has eliminated some or all of their unpaid debt.
“You’ll get a letter out of the blue saying, ‘X, Y or Z debts have been relieved. You no longer owe them. Keep this as a receipt,’” Lempert said.
In Los Angeles County, public health officials have estimated that medical debt totaled more than $2.9 billion in 2022, burdening 1 in 10 adults in the county — a higher percentage than suffered from asthma, according to the public health department. More than half of those who said they were burdened by medical debt had taken on credit card debt to pay medical bills, its analysis found.
The problem has persisted even as more L.A. County residents gained insurance coverage, underscoring the need for a targeted approach, the public health department said.
County officials estimated earlier this year that wiping out nearly $3 billion in medical debt for L.A. County residents through an intermediary would cost $24 million. Other municipalities have turned to funding from the American Rescue Plan Act for such debt relief, but L.A. County had “fully allocated” that money as of January, according to a staff report.
The public health department said it planned to instead use $5 million in one-time county funding for the pilot program, which it said would roll out in stages, starting with “the most vulnerable residents.” Shah said his hope was to raise enough additional money to not have to set priorities about which struggling residents to help.
A study released earlier this year raised questions about the effectiveness of buying up medical debt: A National Bureau of Economic Research working paper that examined medical debt relief for more than 83,000 people from 2018 to 2020 concluded it had no effect, on average, on financial distress or mental health. The research was done in partnership with Undue Medical Debt, then known as RIP Medical Debt.
Despite the “disappointing results,” the researchers wrote, “there is still potential that medical debt relief targeted further upstream or in different populations could yield meaningful benefits.” Stanford University professor of economics Neale Mahoney said the cheapest debts to buy often date back five years or more.
By that point, “a lot of these folks had a lot of other issues, and relieving one of their issues without helping … all of the other financial issues they had wasn’t enough to move the needle,” he said. One solution is to “move more upstream,” and provide debt relief earlier, “before people are too scarred by the debt collection process.”
Mahoney praised the response of the nonprofit, saying it was “taking the study to heart.” Undue Medical Debt president Allison Sesso said in April that it had already made changes since the period covered by the study, including buying medical debt directly from hospitals before it goes to debt buyers or collection agencies.
Sesso also said her group was “collaborating with local governments across the country to concentrate debt erasure to a specific locality to deepen our impact.”
Focusing such efforts in a targeted area ramps up the chances it may be able to wipe out multiple debts for an individual patient, Lempert said.
Shah added that the study did not show what would happen if debt relief happened alongside other prevention efforts. In L.A. County, “there is a larger agenda on medical debt — of which this is just one part.”
Under a broader plan to combat medical debt in L.A. County, the public health department also wants to gather data on how hospitals collect debt and assist strapped patients, create an online portal to apply for financial help, and expand legal aid services, among other proposed steps.
Public health department director Barbara Ferrer told county supervisors Tuesday that their goal is to stop medical debt “at the source,” before it starts piling up for L.A. County residents.
“We don’t want to be coming back to you in five years trying to pay off medical debt again,” Ferrer said.
Science
L.A.'s newest dinosaur has its forever name

The people have spoken, and L.A.’s newest Jurassic-era resident has its forever name.
Dinosaur fans who responded to the museum’s request for input overwhelmingly chose to call the Natural History Museum’s new 70-foot-long sauropod “Gnatalie.”
More than 36% of roughly 8,100 participants in a public poll chose that name, which is pronounced “Natalie,” from among five options offered by the museum.
A rendering of the new dinosaur display at the Natural History Museum. Dinosaur fans who responded to a museum poll have decided to call the 70-foot-long sauropod “Gnatalie.”
(Frederick Fisher and Partners, Studio MLA, and Studio Joseph / NHMLAC)
The punny moniker is a reference to the relentless swarm of gnats that plagued paleontologists, students, museum staff and volunteers during the 13-year effort to unearth the dinosaur’s remains from a quarry in southeast Utah. Museum staff nicknamed the dinosaur Gnatalie while they were still digging it up, a process that lasted from 2007 to 2019.
The long-necked, long-tailed skeleton will be the focal point of the NHM Commons, a $75 million welcome center currently under construction on the southwest end of the museum in Exposition Park. Slated to open this fall, the Commons will offer gardens, an outdoor plaza, a 400-seat theater and a glass-walled welcome center that can be toured without a ticket.
“The efforts of hundreds of people contributed to what you see here, ground to mount,” said paleontologist Luis Chiappe, director of the Dinosaur Institute at the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County.
The specimen appears to be part of a new species, similar to the Diplodocus, which will be scientifically named in the future. Thanks to celadonite minerals that replaced organic matter during the fossilization process, the mounted skeleton has a unique greenish-brown hue.
The skeleton is made up of about 350 fossils from six different animals whose bones washed into a river after death some 150 million years ago and commingled.
“We are delighted to see how many people voted and how much they loved our name for this unusual dinosaur,” said Lori Bettison-Varga, President and Director of the Natural History Museums of Los Angeles County.
Science
Mexico may legalize magic mushrooms. Will this traditional medicine lose its meaning?
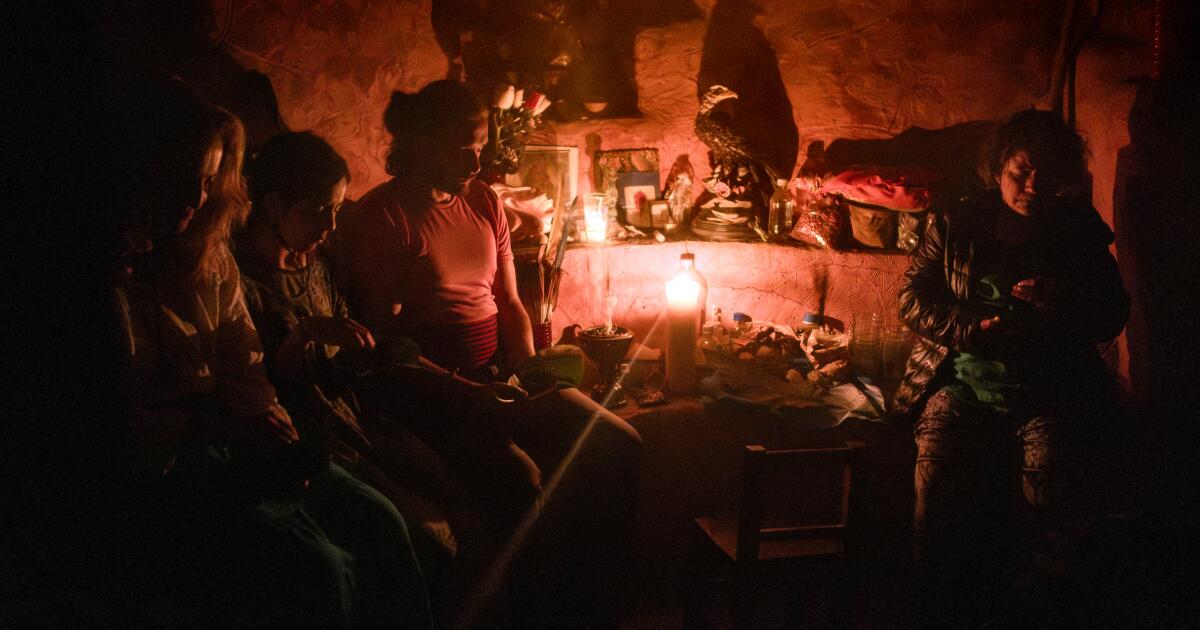
Alejandrina Pedro Castañeda opened a brown paper package and pulled out a handful of magic mushrooms, which many residents of this Indigenous Oaxacan town tenderly refer to as “child saints” or “the little ones that sprout.”
Then she handed each of her six visitors — who had driven seven hours from Mexico City and paid up to $350 apiece for a healing retreat — a generously sized portion, prompting a few dubious looks.
It was nighttime, and the guests were sitting in a hut that was barely illuminated by two candles, making it difficult for them to see what they were about to eat.
Pedro Castañeda has used mushrooms in her healing practice for years and was comfortable stepping outside as the group crunched slowly in silence.
One person said the fungi tasted like stale popcorn. Another tasted dirt.
The healer returned a few minutes later.
“Now we’re starting the trip,” she said. “Let’s go to work.”
Indigenous communities in Mexico have long considered psychedelic mushrooms to be intermediaries to the spiritual world. But their growing popularity outside of Mexico has spurred a debate over who should have access to them and whether science and Indigenous medicine can or should be reconciled.
Magic mushrooms have been used in Mesoamerican religious rituals since pre-Hispanic times. But it wasn’t until the 1950s that a New York banker and mushroom enthusiast named R. Gordon Wasson made them famous — perhaps too famous — in the Western world.
(Alejandra Rajal / For The Times)
Some Indigenous healers are courting tourists. Scientists interested in their chemical properties have been studying mushrooms in hopes of developing treatments for depression and other mental health problems. And growing demand from recreational users has fueled a thriving black market.
Currently, the fungi can only be used in Indigenous rituals or in government-approved research. But a senate bill proposes making psilocybin, a psychedelic compound in the mushrooms, more widely available.
In addition to making psilocybin available to anyone with a doctor’s prescription, the bill would permit therapy that uses the actual mushroom that a government office of traditional medicine would help regulate. It also calls for scientific research on Indigenous medicine and providing compensation to Indigenous people for “patents” involving their traditions.
The bill’s supporters say that they’re trying to protect Indigenous medicine by making sure the traditional use of magic mushrooms is enshrined into law.
But the prospect of expanding the availability of magic mushrooms has created friction within Indigenous communities that have used them for centuries. Will the spirituality associated with this traditional medicine be lost?
::
Magic mushrooms have been used in Mesoamerican religious rituals since pre-Hispanic times. A mural from the ancient city of Teotihuacán, just outside Mexico City, shows the Toltec rain god Tlaloc with two figures alongside him holding mushrooms that have risen from where his raindrops fell. A Franciscan missionary documenting 16th century life in New Spain referred to the mushrooms as the “flesh of the gods.”
But it wasn’t until the 1950s that a New York banker and mushroom enthusiast named R. Gordon Wasson made Mexico’s magic mushrooms famous — perhaps too famous — in the Western world.
On a trip to Huautla, in southern Mexico, he ate mushrooms with Indigenous Mazatec healer María Sabina and wrote about the experience in a 1957 article for Life magazine titled “ Seeking the Magic Mushroom.” The story inspired thousands to travel to Huautla — some seeking out Sabina. The Mexican press described the foreigners as addicts, and the military ultimately set up a checkpoint on the road to Huautla to try to block the outsiders.
In July 1970, Reuters reported: “Hundreds of hippies are braving imprisonment and fines to penetrate this mushroom paradise in the State of Oaxaca, where the authorities are conducting a drive against mushroom eaters.”
Wasson said he felt guilty about the crowds in a New York Times op-ed published later that year. A “humble out-of-the-way” town had been overrun by “a torrent of commercial exploitation of the vilest kind.”
“The old ways are dead,” he wrote, “and I fear that my responsibility is heavy, mine and María Sabina’s.”
In an interview toward the end of her life, Sabina described how some outsiders would take the mushrooms “at whatever time and whatever place” and “don’t use them to cure themselves of a sickness.”
“From the moment the foreigners arrived to search for God,” she said, “the saint children lost their purity.”
In the mid-20th century, psilocybin was classified as a Schedule I substance in the U.S. — which put the kibosh on research. But interest in scientific research on mental health and psilocybin was rekindled in the 1990s.
::
Psilocybin is thought to boost neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to form new neural connections, and research indicates that it may be successful in treating depression, anxiety and substance abuse. Parts of the United States have legalized or decriminalized the substance. (Oakland decriminalized magic mushrooms in 2019.)
“That plasticity enhancement may allow people to shift how their brain is functioning into a mode that’s more helpful, more adaptive, that’s going to promote mental health,” said Greg Fonzo, who co-directs the Center for Psychedelic Research & Therapy at the Dell Medical School at the University of Texas at Austin.
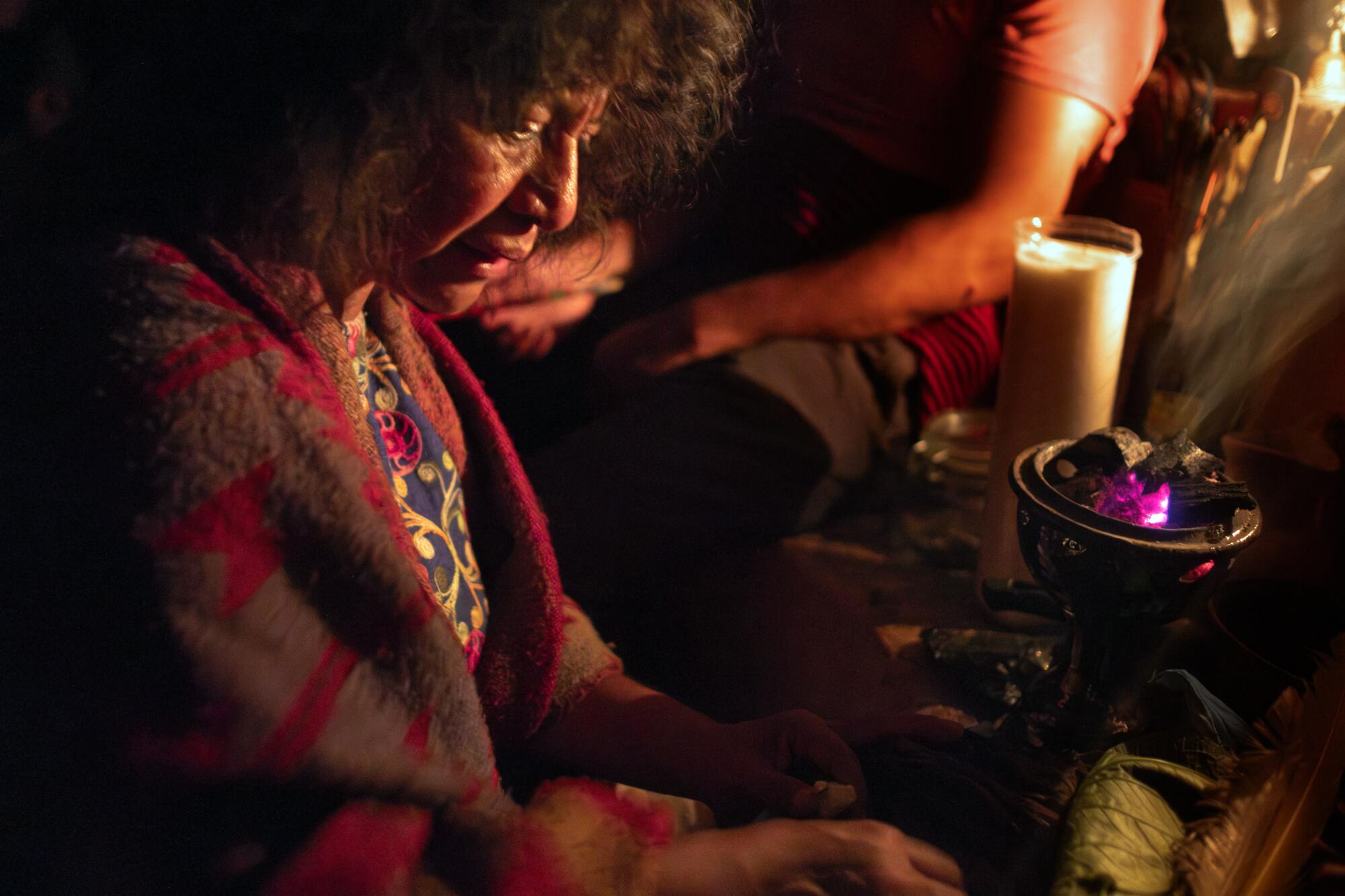

Alejandrina Pedro Castaneda, who has used mushrooms in her healing practice for years, hosts a mushroom ceremony once or twice a week.
(Alejandra Rajal / For The Times)
Some people who ingest magic mushrooms report overwhelming feelings of joy or the presence of family. Others have said they feel deeply sad or that they are having an out-of-body experience.
The risk of a lethal overdose is considered very low, Fonzo said. What’s more common is having a difficult experience or a “bad trip” due to anxiety.
Pedro Castañeda, who compares the bill with a birth certificate, supports the legislation, insisting the world must not forget that the Mazatecs, as well as other Indigenous communities, have preserved rituals with magic mushrooms for centuries.
“The medicine is not protected now. It’s out of control,” she said. “Everyone has it in their home, like cannabis,” she said, referring to black market purchases. “What we need is a record that says the Mazatecs are the custodians, the Mazatecs are the ones that for millennia have defended the medicine.”
But other Mazatecs in Huautla are worried about appropriation and misuse, that traditions associated with Indigenous culture will be disrespected as increasing numbers of people rush to pick up their prescriptions.
In an Indigenous mushroom ceremony, the healer will use mushrooms to communicate with their spiritual world to inquire about a patient’s illness. A patient may also experience revelations.
If the bill passes, “It’ll be taken like an aspirin,” said Isaias Escudero Rodriguez, a local doctor. It will no longer have the “spirituality that it carries for us.”
::
The push to legalize magic mushrooms in Mexico dates back to the early days of the pandemic. Alejandra Lagunes, 52, a senator in Mexico’s national congress, started to experience anxiety attacks that were reminiscent of the severe depression she suffered in her 20s. The depression from decades ago, she said, was resolved after she took ayahuasca — a psychoactive brew made from the Amazonian Banisteriopsis caapi vine — with an Indigenous healer.
Lagunes researched psychedelics and introduced legislation in November to increase access to magic mushrooms while recognizing the long tradition of Indigenous medicine. She hopes it opens the door for non-Indigenous Mexicans to learn from Indigenous practices.
The initiative has supporters at Mexico’s National Institute of Psychiatry, where scientists have government permission to investigate the potential therapeutic effects of magic mushrooms.
Jesús María González Mariscal, a clinical psychologist in Mexico City who has advised the senator, said much can be learned from traditional medicine, including the importance of companionship in Mazatec mushroom ceremonies. These ceremonies occur at night under the guidance of a healer with candles, flowers, incense and an altar with Catholic images. A patient’s family members may accompany them.
The result, Mariscal said, “is a space of care and protection so a person can explore their inner world in a context that’s safe, trustworthy and ethical” — and that’s what Mexico City psychotherapist Oscar O’Farrill is trying to teach his students.
O’Farrill runs a master’s and doctoral degree program affiliated with the National School of Psychologists and Experts of Mexico where his approximately dozen students listen to Indigenous guest speakers talk about traditional medicine. He schedules group therapies in his home, a two-story house where a large container on his kitchen counter has powder from lion’s mane, a non-psychedelic mushroom, that he takes with his morning coffee. Indigenous healers have led his students through ceremonies with mushrooms, peyote and bufo, the smoked secretions of a Sonoran desert toad.
“Psychiatry in this moment can’t understand what psilocybin is if it doesn’t understand all the aspects of the customs of Indigenous people,” he said. “Like it or not, the mushrooms have a spirit.”
But Eros Quintero, a biologist who co-founded the Mexican Society of Psilocybin in 2019, said he would have preferred that Indigenous communities were not singled out in the bill, that psilocybin simply be reclassified.
Indigenous people, he said, may not view illness through the prism of Western science. In Mazatec culture, for example, people may believe that a person fell ill because they walked through a cave where spirits are thought to reside or broke a communal rule.
“They have their own traditions and their own way of seeing things, and what we see is that there are few who are interested in what we’re interested in with psilocybin,” he said.
::
Huautla presents itself as a place for the mushroom-seeker.
Taxis decorated with images of small mushrooms speed up and down narrow mountain roads that are lined with tin-roofed houses. In the summer, when mushrooms are in season, locals wait by a bus terminal to offer the fungi to tourists. Prices vary, but a dozen pairs of mushrooms (they’re sold by the pair) may cost $25 and a ceremony can cost $90 or more. After mushroom season, the fungi are often preserved in jars with honey.
Several signs announce the home of the family of María Sabina — who died in poverty in 1985 but whose life has since been celebrated in Mexican culture. Her descendants, who live on the property where Sabina once resided, maintain a small museum filled with portraits of the healer and sell mushroom-themed crafts.
Anselmo García Martínez, a farmer and a great-grandson of Sabina, says he was about 6 when he tried mushrooms for the first time during a ceremony with relatives who were accompanying a sick family member. (Many other locals say they first consumed mushrooms as children.)
Like some other residents, he said he didn’t mind if mushrooms are allowed outside Indigenous rituals because the general public already has access to them through the black market.
But he issued a reminder: “For us, for the Mazatecs, it’s something sacred.”
Lagunes said she’s invited Indigenous people to the forums she has sponsored, and last year she posted a video on the social media platform X that showed her with several healers and indigenous people in Huautla. They presented her with a baton that she said she’d carry to “bring the voice and knowledge of ancestral medicine to the place that it deserves.”
But some opponents have said that the Mazatec people haven’t been properly consulted on whether the bill should move forward, reminding supporters that, for the moment, there is no infrastructure to make it happen. Santos Martínez, one of the founders of Caracol Mazateco, a civil society group focused on preserving Mazatec culture, agrees there hasn’t been enough outreach to the Mazatecs.
Martinez said his experiences with magic mushrooms transformed his life. As a medical student working at a clinic in the state of Puebla, he fell into a depression after seeing patients suffer from inadequate care. He returned to his community in Huautla, where he participated in mushroom ceremonies, hoping they would help him find direction in his life.
During the ceremonies he felt happy and had visions of family members, including his grandfather. “It was as if he was saying, ‘adelante, hijo,’” he said, or, “go forward, son.”
Francisco Javier Hernandez García, a Huautla healer who leads mushroom ceremonies for tourists almost daily at some points of the summer, fears that mushrooms will “lose respect” if they are legalized for therapy outside of the Indigenous context.
Like others, he spoke about mushrooms as carrying wisdom.
“They sprout because they are waiting for that person,” he said, referring to the one who will eat them. “They already know who carries problems.”
::
In mid-April, O’Farrill organized a trip for six people — including himself — to visit Pedro Castañeda for the healing retreat. Two people, a man who works for a Wall Street asset management firm and a woman training to guide people during mushroom trips, had flown in from the U.S. A mother and daughter, both psychologists, and a literary editor were from Mexico.
They spent three days at the home of Pedro Castañeda, who lives with eight dogs in a house that has several floors under construction. She hosts a mushroom ceremony for locals or tourists once or twice a week and said that the “great spirit” tells her how many mushrooms to give each person.
The members of O’Farrill’s group had individual therapy sessions with Pedro Castañeda in which she asked them about their insecurities. After her guests ate mushrooms, Pedro Castañeda asked several of them to sing. At one point, the editor began to suddenly cry, and the younger psychologist said she felt pain, prompting the healer to rigorously brush her with a feather in a cleansing ritual. A few minutes later, the psychologist said she was having visions of “injustice in jail.”
The next morning, the group hiked — mostly barefoot — the Mountain of Adoration, which the Mazatecs consider sacred.
At the top of the mountain, which overlooked Huautla, the healer gave each person cacao beans to leave as an offering, giving thanks for the previous night. They placed them on a tower of rocks jutting out from the mountain, next to many little mounds of cacao left earlier by other visitors.
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoJoe Biden, Barack Obama And Jimmy Kimmel Warn Of Another Donald Trump Term; Star-Filled L.A. Fundraiser Expected To Raise At Least $30 Million — Update
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoRussia-Ukraine war: List of key events, day 842
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIt's easy to believe young voters could back Trump at young conservative conference
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoSwiss summit demands 'territorial integrity' of Ukraine
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoProtesters in Brussels march against right-wing ideology
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoA fast-moving wildfire spreads north of Los Angeles, forcing evacuations
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoAl-Qaeda affiliate claims responsibility for June attack in Burkina Faso
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoJudge rules Missouri abortion ban did not aim to impose lawmakers' religious views on others















