News
Study links even mild Covid-19 to changes in the brain
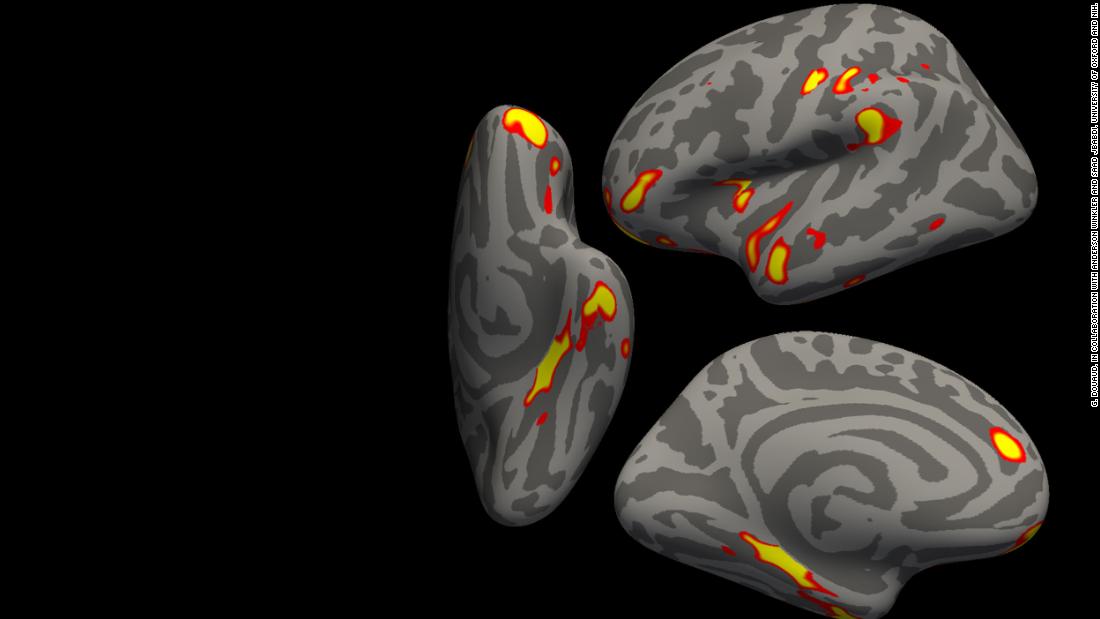
“We have been fairly shocked to see clear variations within the mind even with delicate an infection,” lead creator Gwenaëlle Douaud, an affiliate professor of neurosciences on the College of Oxford, informed CNN in an e-mail.
Douaud and her colleagues evaluated mind imaging from 401 individuals who had Covid-19 between March 2020 and April 2021, each earlier than an infection and a mean of 4½ months after an infection. They in contrast the outcomes with mind imaging of 384 uninfected folks related in age, socioeconomics and threat components equivalent to blood strain and weight problems. Of the 401 contaminated folks, 15 had been hospitalized.
The 785 individuals have been between the ages of 51 and 81 and have been all a part of the UK Biobank, an ongoing authorities well being database of 500,000 folks begun in 2012.
Douaud defined that it’s regular for folks to lose 0.2% to 0.3% of grey matter yearly within the memory-related areas of the mind as they age, however within the research analysis, individuals who had been contaminated with the coronavirus misplaced a further 0.2% to 2% of tissue in contrast with those that hadn’t been contaminated.
Along with imaging, the individuals have been examined for his or her government and cognitive perform utilizing the Path Making Take a look at, a instrument used to assist detect cognitive impairments related to dementia and take a look at an individual’s mind processing pace and performance. The researchers discovered that those that had the best mind tissue loss additionally carried out the worst on this examination.
Though the areas of the mind most affected look like associated to the olfactory system, Douaud stated it wasn’t clear why that was the case.
“For the reason that irregular modifications we see within the contaminated individuals’ brains is likely to be partly associated to their lack of scent, it’s potential that recovering it’d result in these mind abnormalities changing into much less marked over time. Equally, it’s possible that the dangerous results of the virus (whether or not direct, or oblique through inflammatory or immune reactions) lower over time after an infection. One of the best ways to seek out out can be to scan these individuals once more in a single or two years’ time,” she stated.
Douaud added that the researchers anticipate reimaging and testing the individuals in a single or two years.
And whereas the research finds some affiliation between an infection and mind perform, it is nonetheless not clear why. Earlier research have proven folks with vital and repeated lack of scent even have an related lack of grey matter. Nevertheless, this research didn’t consider whether or not folks truly had a lack of scent.
The authors cautioned that the findings have been solely of a second in time however famous that they “elevate the likelihood that longer-term penalties of SARS-CoV-2 an infection may in time contribute to Alzheimer’s illness or different types of dementia.”
The findings have been noticeable, however they weren’t sufficient to trigger alarm, stated Dr. Richard Isaacson, a neurologist and director of the Florida Atlantic College Heart for Mind Well being. Isaacson was not concerned within the research.
Isaacson stated the findings have been noticeable for clinicians, however he added that the general impression on people was troublesome to find out and might be small. “It is actually exhausting to know the long-term medical impression and high quality of life impression in a state of affairs like this,” he stated.
“The mind could also be affected by different mechanisms equivalent to immune, inflammatory, vascular or psychological/behavioral change however not direct an infection,” stated Dr. Alan Carson, a professor of neuropsychiatry on the Heart for Medical Mind Sciences on the College of Edinburgh, who was not concerned within the research.
“What this research virtually definitely exhibits is the impression, when it comes to neural modifications,” he stated. “However I do not assume it helps us perceive the mechanisms underpinning cognitive change after Covid an infection.”