Science
Desperate parents turn to magnetic therapy to help kids with autism. They have little evidence to go on
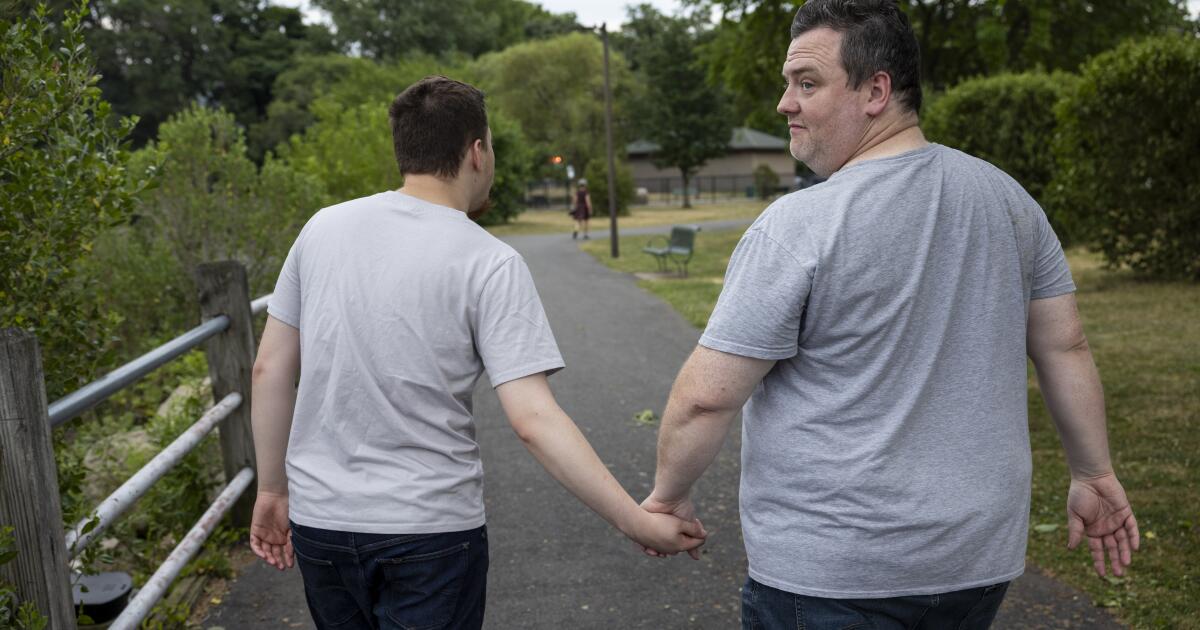

Thomas VanCott compares his son Jake’s experience with autism to life on a tightrope. Upset the delicate balance and Jake, 18, plunges into frustration, slapping himself and twisting his neck in seemingly painful ways.
Like many families with children on the autism spectrum, Jake’s parents sought treatments beyond traditional speech and behavioral therapies.
One that seemed promising was magnetic e-resonance therapy, or MERT, a magnetic brain stimulation therapy trademarked in 2016 by a Newport Beach-based company called Wave Neuroscience.
The company licensed MERT to private clinics across the country that offered it as a therapy for conditions including depression, PTSD and autism.
Those clinics described MERT as a noninvasive innovation that could improve an autistic child’s sleep, social skills and — most attractive to the VanCott family — speech. Jake is minimally verbal.
It was expensive — $9,000 — and not covered by insurance. “It’s too much for most things,” VanCott said, “but not for the potential of my child speaking.”
“It just did nothing,” Thomas VanCott says of the $9,000 MERT sessions his son received.
(Claudia Paul / For The Times)
After raising money through GoFundMe, VanCott met with a doctor at a New Jersey clinic who described how MERT would reorganize Jake’s brain waves. VanCott does not have a scientific background, and the technical details went over his head. What he had was a severely disabled son he was desperate to help.
The doctor “seemed pretty confident. And his confidence gave me confidence,” VanCott said. “It made me think, tomorrow Jake’s gonna wake up and say a sentence.”
Autism diagnoses in children have risen steadily since 2000, in part due to increased awareness and screening. As the number of people living with autism has grown, so have alternative therapies promising to alleviate or even reverse its associated behaviors.
“There’s also a lot of pressure put on parents,” said Zoe Gross, a director at the Autistic Self Advocacy Network, a nonprofit group run by and for autistic adults. “People will be saying things like, ‘Time’s ticking, your kid’s missing milestones … you have to fix it now.’”
One therapy that often surfaces in Google searches, social media groups and word-of-mouth discussions is MERT, which is based on a brain stimulation therapy approved by the Food and Drug Administration for depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Clinics offering MERT sell it as a “safe and effective treatment for autism” that yields “miraculous results” for kids on the spectrum.
Most compelling to many families is an oft-cited marketing claim that research has shown MERT to improve speech and eye contact in a majority of autistic patients, research that several clinics attributed to Wave.
The Times spoke to parents who said MERT caused positive, lasting changes in their autistic children’s sleep, communication and concentration.
Other parents told The Times they saw only minimal changes in their children’s behavior. Many, including Thomas VanCott, saw no changes at all. “It just did nothing,” VanCott said. And a few saw worrying behavioral regressions that persisted long after the therapy ended.
All remember being told by MERT providers that while results weren’t guaranteed, many patients saw positive results. When the dramatic changes they hoped for didn’t happen, these families left believing they were unlucky. Without quality data, it’s impossible to know if any of these outcomes are outliers or typical patient experiences.
Wave has not conducted any studies on whether its signature product works for autism. A Wave executive argued that the need for new autism therapies is strong enough to justify moving forward with commercial solutions before rock-solid evidence is available.
“Academics pointing towards insufficient evidence for clinical adoption may not represent a true reflection of clinical utility in a population where there are very few therapeutic options, great suffering, and a willingness of physicians and patients to seek innovative treatment choices with diligent clinical care and oversight,” said Dr. Erik Won, Wave’s chief medical officer.
For many parents, even a small possibility of a life-changing breakthrough is worth any price. Although some families have reported benefits from the treatment, no large scientific studies exist that show MERT is significantly better than a placebo, according to nine psychiatrists, psychologists and neuroscientists with expertise in brain stimulation and autism.
MERT is Wave’s trademarked version of a therapy called transcranial magnetic stimulation. The product of decades of research, TMS is approved by the FDA to treat major depression, OCD and cigarette addiction.
It is also used to treat conditions for which it is not FDA-approved, in what’s known as “off-label” prescribing. Off-label use of drugs and devices is a common practice in medicine.
Clinics offering cash-pay TMS for a variety of off-label conditions, including autism, have proliferated in recent years. MERT in particular has become especially popular among families with autistic children.
Autism spectrum disorder is a complex neurological and developmental condition that manifests differently in nearly every individual who has it. Symptoms cluster around difficulties in communication, social interaction and sensory processing.
Many autistic people need minimal support to live, work and thrive independently, while others require intense daily care and are unable to express themselves verbally. There are few evidence-based interventions to alleviate the disorder’s most profoundly disabling traits.
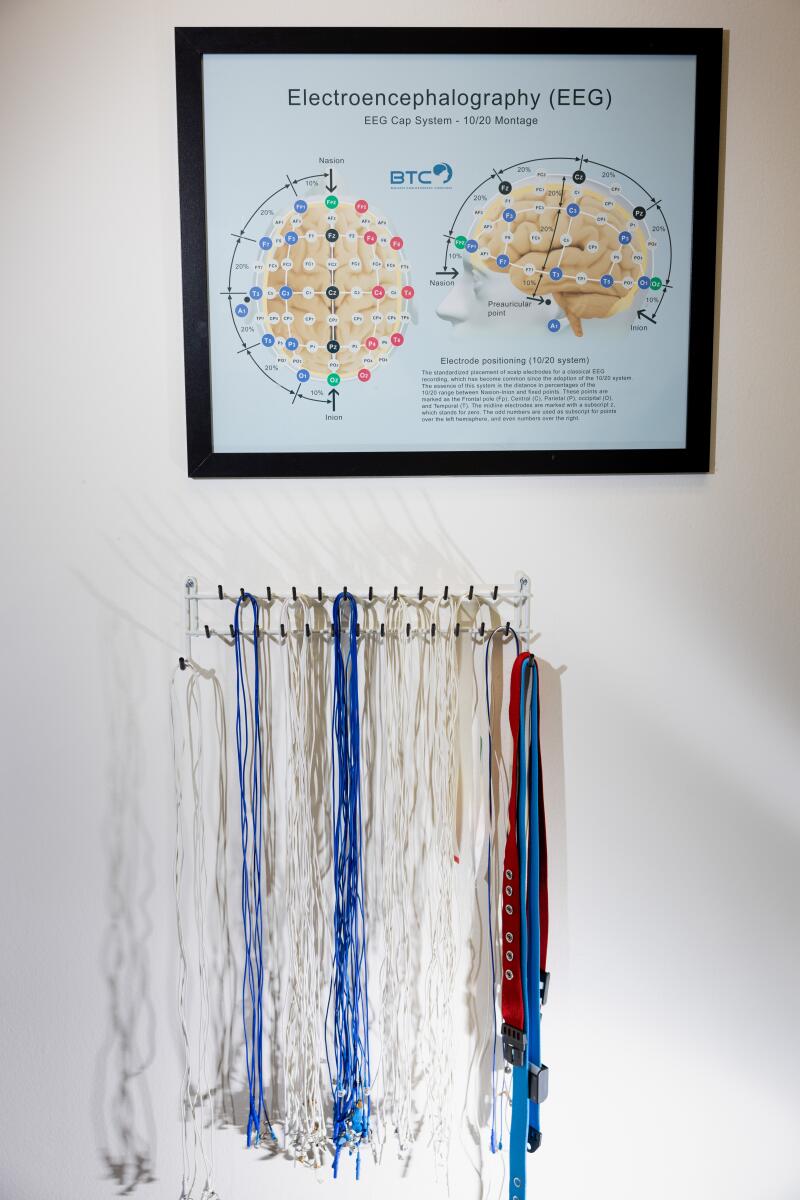

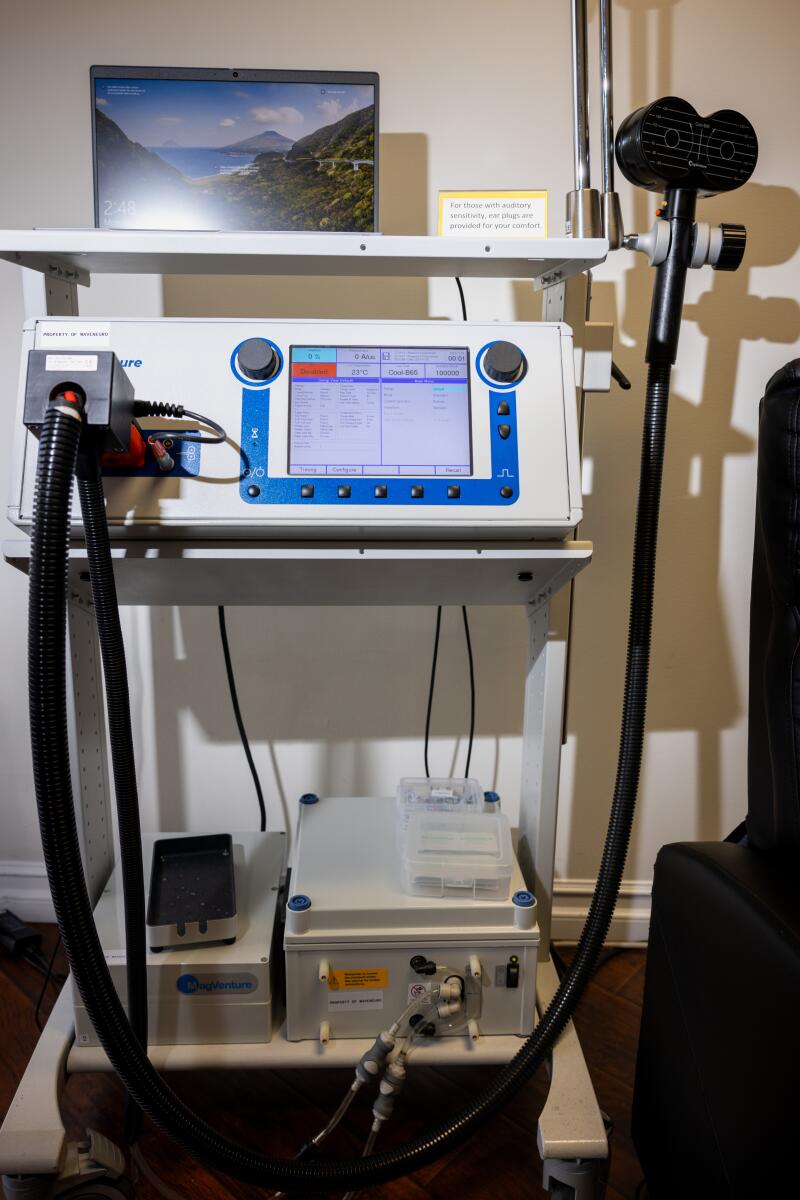
MERT providers first use EEG, a common brain scan, to assess patients. Wave’s proprietary technology, photographed at a Newport Beach clinic, then determines which areas of the brain to target for treatment. (Jay L. Clendenin / Los Angeles Times)
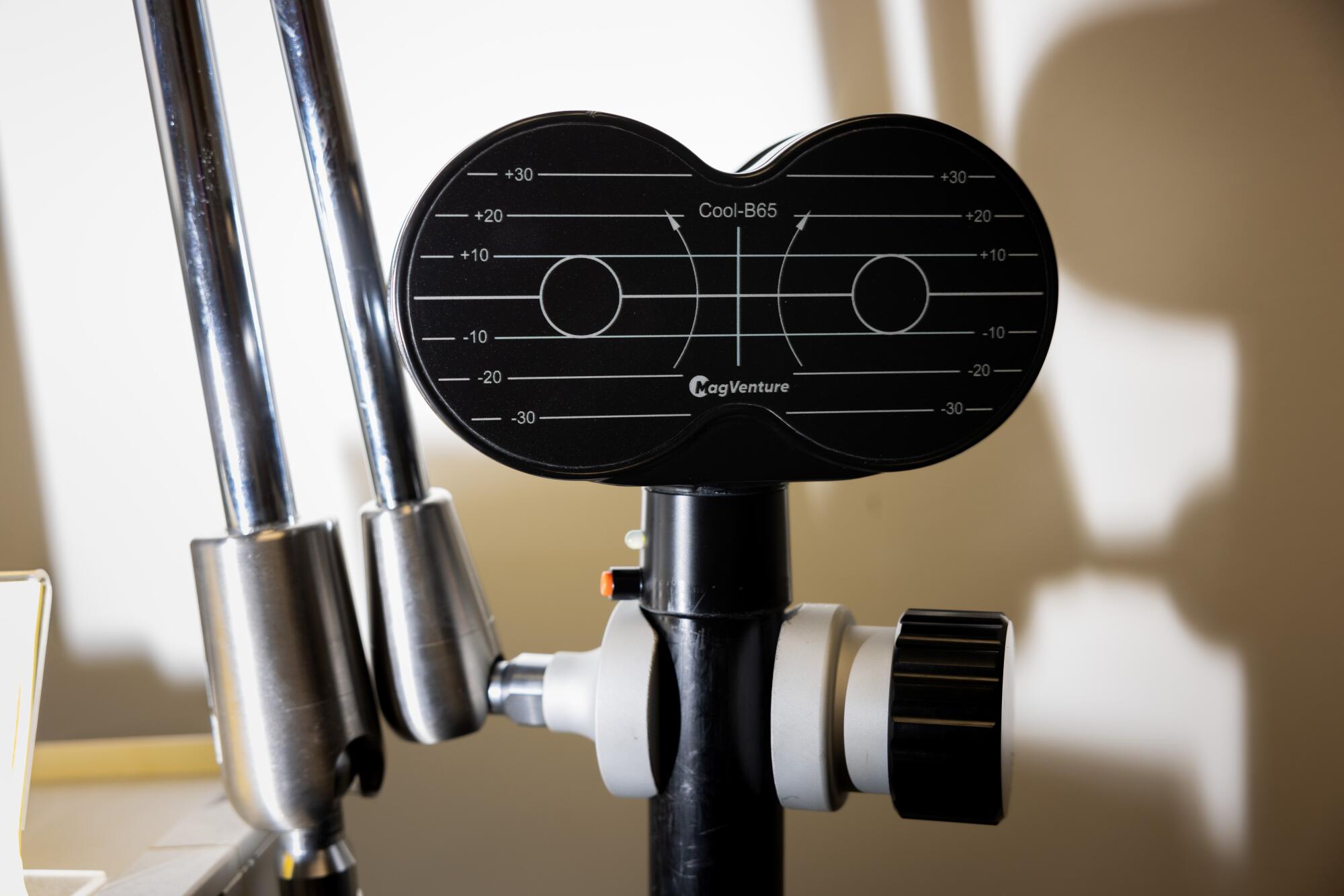

During treatment, a magnetic coil is placed against the patient’s scalp. Each session of gentle electromagnetic pulses lasts about 30 minutes.
(Jay L. Clendenin / Los Angeles Times)
A MERT patient first sits for a 10-minute quantitative electroencephalogram, a noninvasive test that measures the brain’s electrical activity, and an electrocardiogram, which gauges electrical activity in the heart.
Results are then analyzed by Wave’s proprietary software. If its algorithm identifies “areas of the brain that are not functioning properly,” clinic providers will recommend a protocol of TMS-style treatments. In these sessions, the provider places a magnetic coil against the patient’s scalp that emits a gentle electromagnetic pulse. Sessions typically last about 30 minutes and are administered five days a week, for two to six weeks.
Won, Wave’s president and chief medical officer, said the goal is “to help the brain function most efficiently as an organ. And the hypothesis was, if we improve the metabolic efficiency of the brain, would we see some changes in a variety of different medical conditions?
“As we sort of tested this, there was a realization: Wow, we can do something pretty special for autism,” he said.
A six-week course of MERT — the standard protocol Wave recommends for autistic patients — typically costs $9,000 to $12,000, families and clinic owners said, and is not covered by insurance.
MERT was originally developed as a therapy for post-traumatic stress disorder and traumatic brain injury. Since Wave’s inception in 2019, it has described military veterans as its primary patient demographic.
Wave is in Phase II of a clinical trial to test MERT for PTSD, Won said. The company has not conducted any clinical trials on autism.
“The strategic decision to focus on PTSD was largely dictated by market factors,” Won said. He added that his company is dedicated to helping those with autism and is working to obtain funding “for further studies and ultimately an FDA indication.”
Dr. Andrew Leuchter is the director of UCLA’s TMS Clinical and Research Service, which has provided FDA-approved and off-label treatments to more than 1,000 patients.
Given its solid safety profile and effectiveness at treating other complex brain-based disorders, Leuchter said that he and many other TMS clinicians believe the therapy could have benefits for conditions other than the few for which it is FDA-approved.
When a patient approaches the clinic seeking treatment for an off-label condition Leuchter believes could be helped by TMS, the psychiatrist reviews the case with his colleagues. If they decide to proceed, he explains to the patient that the efficacy of TMS for their condition isn’t proven, though there is reason to believe it is safe and effective.
But when parents call asking whether he can treat autistic characteristics such as sensory challenges, minimal speech or lack of eye contact, Leuchter says no.
“Off-label treatment can be just fine so long as there’s data to support this and the risks are low,” he said. For autism, he said, “the evidence base is not very strong. … And I don’t think that there is sufficient evidence to recommend the use of TMS for the treatment specifically of autism.”
Multiple researchers are currently examining whether TMS could improve certain symptoms of autism. But eight researchers interviewed for this article said there isn’t yet enough evidence to recommend TMS as an autism therapy, or to say with confidence that it works for that condition.
Lindsay Oberman, director of the Neurostimulation Research Program at the National Institute of Mental Health, published a paper last year summarizing the current state of research on TMS and autistic children. Nearly all published studies on the treatment to date have been very small, open-label (meaning both patients and providers knew which treatment they were receiving) or focused on a very specific subgroup, she and her co-authors wrote.
Without large, randomized controlled trials — the gold standard in medicine — “broad off-label use of these techniques in this population is not supported by currently available evidence,” the paper concluded.
Won acknowledged that the company has so far not pursued such research on MERT and autism.
“We owe the community some academically rigorous science,” he said. “This is not going to be a panacea. I don’t want to misrepresent anything to the parents who are making these difficult decisions. But for a subgroup, this is clearly something that’s leading to a response.”
Medical research moves far more slowly than most patients and their families would like, and many are willing to try experimental therapies long before researchers and regulators are ready to sign off on them.
“When you’re a parent of a child and you think that this can help, it’s like, FDA be damned, right?” VanCott said. “If I think it’s gonna help my kid, I want to do it.”
Wave’s provider directory now lists more than 60 U.S. licensees and an additional 18 internationally. More than 400,000 MERT sessions have been administered to more than 20,000 people, according to the company.
Won said Wave does not maintain comprehensive data on patients treated at licensee clinics. In an interview, he estimated that about half of these patients were seeking treatment for autism. He later said that 20% to 30% was a better estimate.
Although some clinic owners said they treat few autistic children, staffers at multiple facilities told The Times that most or all of their patients were autistic.
To pay for the procedure, families have used savings or turned to crowdfunding. Others placed the treatment on credit cards. Their experiences vary widely.
Though initially skeptical, Joo Flood booked a six-week course of treatment at a Dallas clinic in 2022 for her minimally verbal son Max, then almost 5. They returned for another round in May 2023.
Max now responds far more often to his name, makes regular eye contact and has an easier time following directions, his mother said.
“If I didn’t do the MERT, I’m not sure Max can be at this level,” she said.
Yestel Concepcion and her husband sought MERT for her stepson after hearing about it on a talk show.
The New Jersey couple scraped together savings and gratefully accepted donations from friends and family for the $10,000 cost. They spent nearly $5,000 more relocating the family to Maryland during the monthlong treatment.
Apart from an increase in the boy’s hyperactivity, the couple saw “no result whatsoever,” Concepcion said. The clinic suggested more sessions, at an additional cost. But their money and trust had run out.
Most parents who spoke to The Times about their children’s MERT treatments said the possibility of speech for their nonverbal or minimally verbal children was the primary reason they pursued it, even if it meant taking on debt.
Until recently, more than a dozen MERT clinics around the country, under the headline “Results that ‘Speak,’” cited an “internal double-blind randomized control trial” that had produced striking results: Two out of three patients who had difficulties with verbal and nonverbal communications “experienced improvement” after MERT. In the same trial, the ad copy read, 70% of patients who had trouble maintaining eye contact saw “improved eye contact behavior.”
Four clinics attributed those statistics to Wave.
According to Wave, the source of that claim is a small study of 28 patients that was conducted around 2017 by the Newport Brain Research Laboratory. It has not been published nor vetted by independent scientists. The study was among assets of the now-defunct laboratory that Wave purchased in 2019.
The only part of this work available to the public is an undated poster presentation that roughly outlines the study.
Wave declined to release details of the study or name its authors, but Won described the results. He said 71% of subjects in the group of 14 patients that received MERT instead of a placebo had positive changes in their visual response afterward, and 67% of subjects had positive changes in their verbal communication, according to their parents’ responses on the Childhood Autism Rating Scale, known as CARS.
“I never put much weight into the findings I see in a poster or talk, especially if it isn’t followed by a later peer-reviewed publication,” said Christine Conelea, an associate professor at the University of Minnesota Medical School who runs the university’s Non-Invasive Neuromodulation Laboratories.
“Small samples like this aren’t good for establishing the benefits of a treatment, conclusively showing safety or demonstrating that an investigational treatment is better than placebo,” Conelea said.
Statistics taken from the unpublished study have featured prominently on the websites of at least 17 MERT clinics, as well as the primary website for the Brain Treatment Center, a trademark owned by Wave under which many MERT clinics do business.
Won said he was not aware that so many clinics were using the study’s conclusions as a marketing tool. Shortly after The Times asked Wave about the statistics, almost all of those clinics took them down.
“I don’t feel good about it,” he said. “A lot of families benefited from it [MERT], and their children are doing better, and that’s wonderful. But I don’t want to misrepresent or overrepresent things. … I would always want there to be published, peer-reviewed, academically rigorous science to back up a claim.”
Following The Times’ questions, Won said that Wave contacted the study authors and requested that they expedite the preparation and submission of a research paper containing the study results to a peer-reviewed journal. The company has also asked the authors to release the manuscript on a preprint server, a website where scientists can post preliminary findings.
“We need to get that publication out so that people can make informed decisions,” he said. “It would be easier if it’s in the public domain, and other people can critique it and break it down and take it for what it’s worth.”
Manuel Casanova, a retired University of South Carolina professor who spent years studying TMS as a potential autism therapy, questioned why MERT providers had so little empirical data to share after administering the treatment to thousands of autistic patients — a gap, he said, that “raises a red flag as to the therapeutic benefits of the technique.”
MERT providers operate in an “ethical gray area,” said Anna Wexler, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania who studies the ethics of emerging technologies.
Doctors can use approved therapies to treat any condition they deem appropriate, Wexler said. But if the condition being treated isn’t the same one for which the therapy has been cleared, providers must be “as transparent as possible” about the evidence they’re relying on, she said. If there is little or no evidence to support MERT’s efficacy for a given condition, she said, “it is unethical for providers to advertise that it is effective.”
“If someone opts for an experimental therapy, that in itself is not problematic,” Wexler said. “What is problematic is if they are making that decision based on erroneous or incorrect beliefs about efficacy.”
Won did not respond to a question about Wexler’s critique.
Nine psychiatrists, psychologists and neurologists with expertise in transcranial magnetic stimulation say there is to date no evidence to suggest this kind of therapy can reliably prompt a nonverbal autistic child to develop speech, or to significantly alter an autistic child’s sensory and communication abilities.
“The plain English is that it’s not there yet, and I have not seen it working convincingly outside of a strong placebo effect,” said Dr. Alexander Rotenberg, a professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School and director of Boston Children’s Hospital’s Neuromodulation Program.
Peter Enticott, a psychologist at Australia’s Deakin University, is leading a multisite trial of TMS for autism funded by the Australian government. Enticott has spoken with families whose children received MERT from Wave licensees in Australia and were thrilled with the outcomes. But for a scientist, uplifting anecdotes are not a substitute for data.
“It’s too early,” he said. “And I think it’s particularly problematic given that they are charging large amounts of money for an unverified therapy.”
Criticisms of the treatment’s pricing were “not a reflection of Wave Neuroscience,” Won said. “The comments seem to be objecting to the realities of the healthcare market.”
Scientists consulted by The Times said they would encourage families interested in TMS and autism to look for a clinical trial that would provide the treatment free of charge in exchange for using the patient’s data in a study.
“I would consider this something that should be researched, but nobody should be paying $5,000 to $10,000 out of pocket for this,” said Alycia Halladay, chief science officer at the Autism Science Foundation, one of five autism advocacy groups The Times consulted that said there is not enough evidence for them to recommend MERT.
Despite his disappointment, VanCott does not regret his decision. Had he not pursued the treatment, he would always have wondered whether he had turned down something that could have helped his son — no matter how high the cost, no matter how slim the chance.
“I mean, being able to sleep at night?” he said. “What’s that worth?”
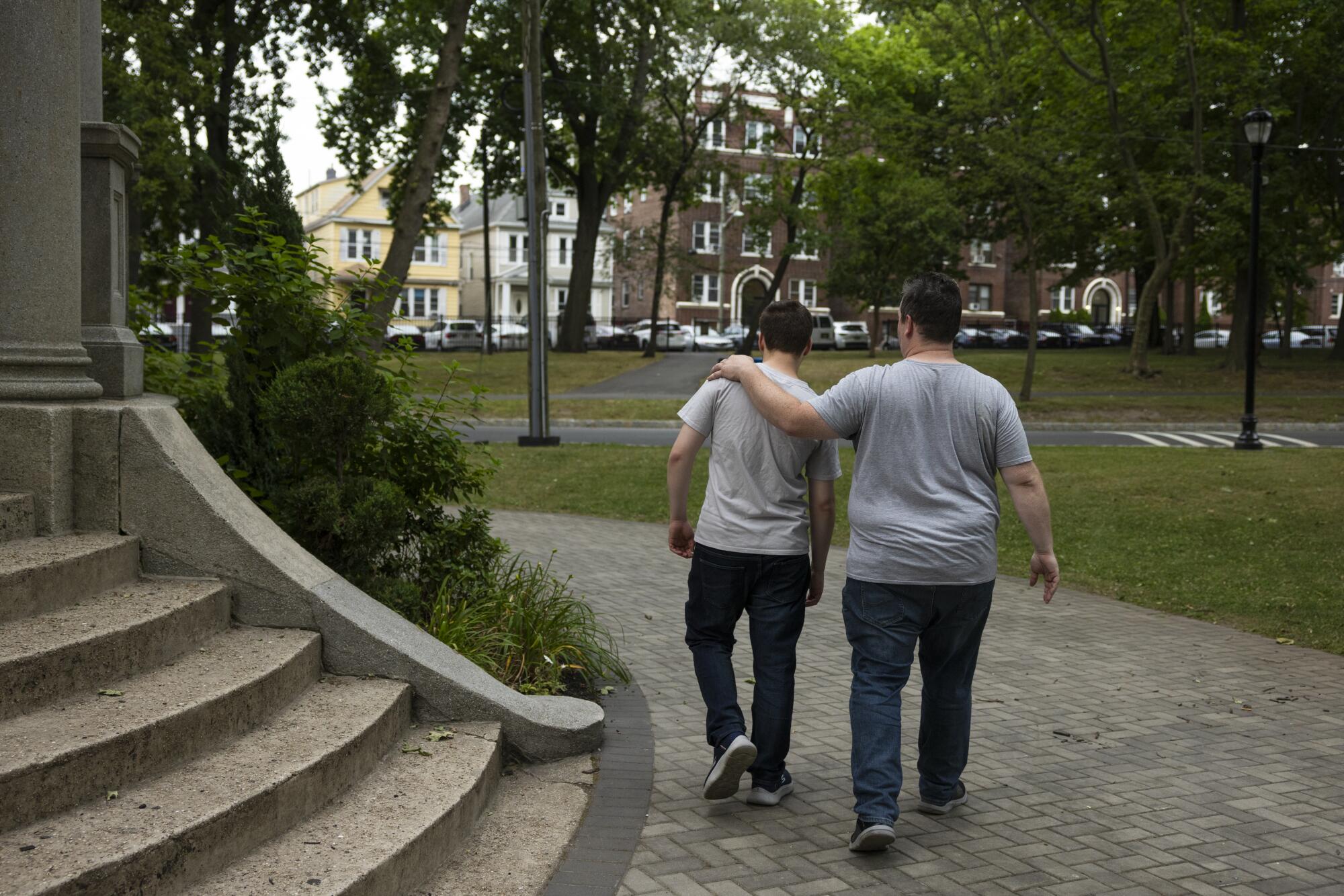
Thomas VanCott said he signed up son Jake for MERT sessions because he did not want to be wondering whether he turned down something that could have helped his child.
(Claudia Paul / For The Times)

Science
There were 13 full-service public health clinics in L.A. County. Now there are 6

Because of budget cuts, the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health has ended clinical services at seven of its public health clinic sites.
As of Feb. 27, the county is no longer providing services such as vaccinations, sexually transmitted infection testing and treatment, or tuberculosis diagnosis and specialty TB care at the affected locations, according to county officials and a department fact sheet.
The sites losing clinical services are Antelope Valley in Lancaster; the Center for Community Health (Leavy) in San Pedro, Curtis R. Tucker in Inglewood, Hollywood-Wilshire, Pomona, Dr. Ruth Temple in South Los Angeles, and Torrance. Services will continue to be provided by the six remaining public health clinics, and through nearby community clinics.
The changes are the result of about $50 million in funding losses, according to official county statements.
“That pushed us to make the very difficult decision to end clinical services at seven of our sites,” said Dr. Anish Mahajan, chief deputy director of the L.A. County Department of Public Health.
Mahajan said the department selected clinics with relatively lower patient volumes. Over the last month, he said, the department has sent letters to patients about the changes, and referred them to unaffected county clinics, nearby federally qualified health centers or other community providers. According to Mahajan, for tuberculosis patients, particularly those requiring directly observed therapy, public health nurses will continue visiting patients.
Public health clinics form part of the county’s healthcare safety net, serving low-income residents and those with limited access to care. Officials said that about half of the patients the county currently sees across its clinics are uninsured.
Mahajan noted that the clinics were established decades ago, before the Affordable Care Act expanded Medi-Cal coverage and increased the number of federally qualified health centers. He said that as more residents gained access to primary care, utilization at some county-run clinics declined.
“Now that we have a more sophisticated safety net, people often have another place to go for their full range of care,” he said.
Still, the closures have unsettled providers who work closely with local vulnerable populations.
“I hate to see any services that serve our at-risk and homeless community shut down,” said Mark Hood, chief executive of Union Rescue Mission in downtown Los Angeles. “There’s so much need out there, so it always is going to create hardship for the people that actually need the help the most.”
Union Rescue Mission does not receive government funding for its healthcare services, Hood said. The mission’s clinics are open not only to shelter guests, up to 1,000 people nightly, but also to people living on the streets who walk in seeking care.
Its dental clinic alone sees nearly 9,000 patients a year, Hood said.
“We haven’t seen it yet, but I expect in the coming days and weeks we’ll see more people coming through our doors looking for help,” he said. “They’re going to have to find help somewhere.” Hood said women experiencing homelessness are especially vulnerable when preventive care, including sexual and reproductive health services, becomes harder to access.
County officials said staffing impacts so far have been managed through reassignment rather than layoffs. Roughly 200 to 300 positions across the department have been eliminated amid funding cuts, officials said, though many were vacant. About 120 employees whose positions were affected have been reassigned; according to Mahajan, no one has been laid off.
The clinic closures come amid broader fiscal uncertainty. Mahajan said that due to the Trump administration’s “Big Beautiful Bill,” Los Angeles County could lose $2.4 billion over the next several years. That funding, he said, supports clinics, hospitals and community clinic partners now absorbing patients who previously went to the clinics that closed on Feb. 27.
In response, the L.A. County Board of Supervisors has backed a proposed half-cent sales tax measure that would generate hundreds of millions of dollars annually for healthcare and public health services. Voters are expected to consider the measure in June.
Science
Mobile clinic brings mammograms to women on Skid Row

Sharon Horton stepped through the door of a sky-blue mobile clinic and onto a Skid Row sidewalk. She wore a yellow knit beanie, gold hoop earrings and the relieved grin of a woman who has finally checked a mammogram off her to-do list.
It had been years since her last breast cancer screening procedure. This one, which took place in City of Hope’s Cancer Prevention and Screening mobile clinic, was faster and easier. The staff was kind. The machine that X-rayed her breast was more comfortable than the cold hard contraption she remembered.
Relatively speaking, of course — it was still a mammogram.
“It’s like, OK, let me go already!” Horton, 68, said with a laugh.
The clinic was parked on South San Pedro Street in front of Union Rescue Mission, the nonprofit shelter where Horton resides. Within a week, City of Hope, a cancer research hospital, would share the results with Horton and Dr. Mary Marfisee, the mission’s family medical services director. If the mammogram detected anything of concern, they’d map out a treatment plan from there.
Naureen Sayani, 47, a resident of Union Rescue Mission, left, discusses her medical history with Adriana Galindo, a medical assistant, before getting a mammogram on last week.
(Kayla Bartkowski / Los Angeles Times)
“It’s very important to take care of your health, and you need to get involved in everything that you can to make your life a better life,” said Horton, who is looking forward to a forthcoming move into Section 8 housing.
Horton was one of the first patients of a new women’s health initiative from UCLA’s Homeless Healthcare Collaborative at Union Rescue Mission. Staffed by third-year UCLA Medical School students and led by Marfisee, a UCLA assistant clinical professor of family medicine, the clinic treats mission residents as well as unhoused people living in the surrounding neighborhood.
The new cancer screening project arrives at a time of dire financial pressures on county public health services.
Citing rising costs and a $50-million reduction in federal, state and local grant and contract income, the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health on Feb. 27 ended services at seven of 13 public clinics that provide vaccines, tests and treatment for sexually transmitted diseases and other services to housed and unhoused county residents.
Although Union Rescue Mission’s own funding comes mainly from private sources and is less imperiled by public cuts, the 135-year-old shelter expects the need for its services to rise, Chief Executive Mark Hood said.
Even as unsheltered homelessness declined for the last two years across Los Angeles County, the unsheltered population on Skid Row — long seen as the epicenter of the region’s homelessness crisis — grew 9% in 2024, the most recent year for which census data are available.
For many local women navigating daily concerns over housing, food and personal safety, “their own health is not a priority,” Marfisee said.
Those whose problems have become too serious to ignore face daunting obstacles to care. Marfisee recalled one patient who came to her with a lump in her breast and no identification.
In order to get a mammogram, Marfisee explained, the woman first needed to obtain a birth certificate, and then a state-issued identification card. Then she needed to enroll in Medi-Cal. After that, clinic staff helped her find a primary care physician who could order the imaging test.
Given the barriers to preventative care, homeless women die from breast cancer at nearly twice the rate of securely housed women, a 2019 study found. Marfisee’s own survey of the mission’s female residents found that nearly 90% were not up to date on recommended cancer screenings like mammograms and pap smears, which detect early cervical cancer.
To address this gap, Marfisee — a dogged patient advocate — reached out to City of Hope. The Duarte-based research and treatment center unveiled in March 2024 its first mobile cancer screening clinic, a moving van-sized clinic on wheels that it deploys to food banks and health centers, as well as to companies offering free mammograms as an employee benefit.
“In true Dr. Mary fashion, she saw the vision,” said Jessica Thies, the mobile screening program’s regional nursing director. After working through some logistical hurdles, the mission and City of Hope secured a date for the van’s first visit.
The next challenge was getting the word out to patients. Marfisee and her students walked through the surrounding neighborhood, went cot to cot in the women’s dorm and held two informational sessions in December and January to answer patients’ questions.
At the sessions, the team walked through the basics of who should get a mammogram (women age 40 or older, those with a family history of breast cancer) and the procedure itself. (“Like a tortilla maker?” one woman asked skeptically after hearing a description of the mammography unit.)
The medical students were able to dispel rumors some women had heard: The test doesn’t damage breast tissue, nor do the X-rays increase cancer risk. Others questioned a mammogram’s value: What good was it knowing they had cancer if they couldn’t get follow-up care?
On this latter point, Marfisee is determined not to let patients fall through the cracks.
Thirteen patients received mammograms at the van’s first visit on Wednesday. Within a week, City of Hope will contact patients with their results and send them to Marfisee and her team. She is already mentally mapping the next steps should any patient have a situation that requires a biopsy or further imaging: working with their case manager at the mission, calling in favors, wrangling with any insurance the patient might have.
“It’ll be a good fight,” Marfisee said, as residents in the adjacent cafeteria carried trays of sloppy joes and burgers to their lunch tables. “But we’ll just keep asking for help and get it done.”
Science
Can fire-resistant homes be sexy? ‘You be the judge,’ says this Palisades architect
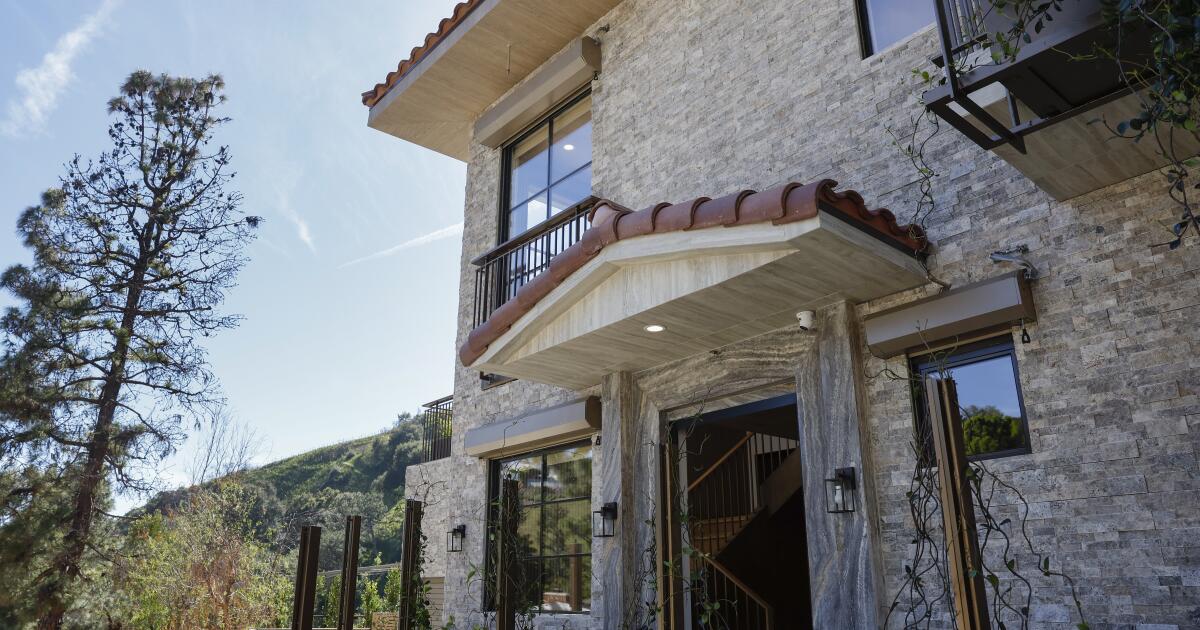

At first glance, it looks like nothing more than a charming Spanish-revival, quintessentially Californian home — but this Pacific Palisades rebuild is constructed like a tank.
Every exterior wall of the steel-framed home is a foot-thick, fire-resistant barricade. The home is connected to a satellite fire monitoring service. Should a fire start in town, sturdy metal shutters descend to cover every window. An exterior sprinkler system can pump 40,000 gallons of water from giant tanks hidden behind the shrubs in the property’s yard. If the cameras and heat sensors around the house detect danger, the system can envelop the home in over 1,000 gallons of fire retardant and hundreds of gallons of fire-suppressing foam.
Palisades resident and architect Ardie Tavangarian is so confident in his design that he even asked the fire department if they could start a controlled fire on the property to test it all out. (They said no.)
Tavangarian built a career designing multimillion-dollar luxury homes in Los Angeles, but after the Palisades fire destroyed 13 of his works — including his family’s home — he found another calling: how to design a house that can handle what the Santa Monica Mountains throw at it. And how to do it quickly and affordably.
Water tanks form part of a backup water supply in a newly built fire-resistant home in Pacific Palisades.
“Nature is so powerful,” he said, sitting on a couch in the new house, which he built for his adult twin daughters. “We are guests living in that environment and expecting, ‘Oh, nature is going to be really kind to me.’ No, it’s not. It does what it’s supposed to do.”
Tavangarian watched the Jan. 1 Lachman fire from his property not far from here; a week later that fire rekindled, grew into the Palisades fire, and burned through his house. But the painful details of the fire — the missteps of the fire department, the empty reservoir — didn’t matter when it came to deciding how to rebuild, he said. The reality is, many fires have burned in these mountains. Many more will.

A sprinkler on the roof is part of a house-wide sprinkler system.
For the architect, who has spent much of his 45-year career designing for luxury, hardening a home against wildfire has brought a new kind of luxury to his homes: peace of mind.
It’s a sentiment that resonates with fire survivors: Tavangarian says he’s received considerable interest from other property owners in the Palisades looking to rebuild their houses.
The metal shutters and advanced outdoor sprinkler system are the flashiest parts of Tavangarian’s home hardening project, and the efficacy of these adaptations is still up for debate. Because the measures have not yet been widely adopted, there are few studies exploring how much or little they protect homes in real-world fires.

Architect Ardie Tavangarian inside the house he designed.
Anecdotal evidence has indicated the effectiveness of sprinklers can vary significantly based on the setup and the conditions during the fire. Extreme wind, for example, can make them less effective. Lab studies have generally found shutters can reduce the risk of windows shattering.
These measures aren’t cheap, either. Sprinkler systems can cost north of $100,000, for example. However, Tavangarian said when all was said and done, the home he built for his daughters cost around $700 per square foot — less than what Palisades residents said they expected to pay, but more than what Altadena residents expected for their rebuilds.
Tavangarian also hopes to see insurers increasingly consider the home-hardening measures property owners take when writing policies, which he said could potentially offset the extra cost in a decade or less. As he explored getting insurance for the new home, one insurer quoted him $80,000 a year. After he convinced the company to visit the property, it lowered the quote to just $13,000, he said.

The house includes metal heat shields that can drop down if a fire approaches.
The home also has essentially all of the other less flashy — but much cheaper and well-proven — home hardening measures recommended by fire professionals: The underside of the roof’s overhang is closed off — a common place embers enter a home. The roof, where burning embers can accumulate, is made of fire-resistant material. The windows, vulnerable to shattering in extreme heat, are made of a toughened glass. There is virtually no vegetation within the first five feet of the home.
When asked if he felt he had compromised on design, comfort or aesthetics for the extra protection — one of the many concerns Californians have with the state’s draft “Zone Zero” requirements that may significantly limit vegetation within five feet of a home — Tavangarian simply said, “You be the judge.”
-

 World6 days ago
World6 days agoExclusive: DeepSeek withholds latest AI model from US chipmakers including Nvidia, sources say
-

 Massachusetts7 days ago
Massachusetts7 days agoMother and daughter injured in Taunton house explosion
-

 Denver, CO7 days ago
Denver, CO7 days ago10 acres charred, 5 injured in Thornton grass fire, evacuation orders lifted
-

 Louisiana1 week ago
Louisiana1 week agoWildfire near Gum Swamp Road in Livingston Parish now under control; more than 200 acres burned
-

 Oregon5 days ago
Oregon5 days ago2026 OSAA Oregon Wrestling State Championship Results And Brackets – FloWrestling
-

 Florida3 days ago
Florida3 days agoFlorida man rescued after being stuck in shoulder-deep mud for days
-

 Maryland3 days ago
Maryland3 days agoAM showers Sunday in Maryland
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoTry This Quiz on Thrilling Books That Became Popular Movies




















