Science
The desperate hours: a pro baseball pitcher's fentanyl overdose
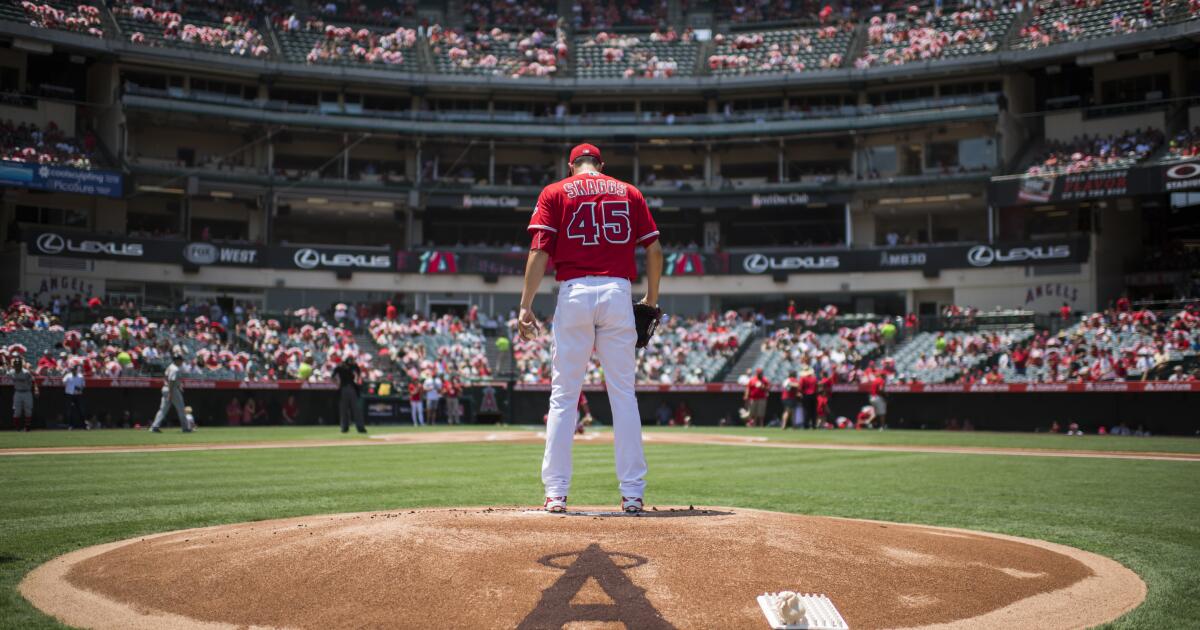

Not many victims of the opioid crisis in America make national headlines. Tyler Skaggs was different.
The 27-year-old was a professional athlete, a pitcher for the Angels, wealthy and famous. On a road trip with the team, he was found in his hotel room. He had choked on his own vomit after consuming a mix of alcohol, oxycodone and fentanyl.
His death on July 1, 2019, sent shock waves through the sports world. A highly publicized criminal investigation not only revealed that Skaggs had secretly used painkillers for years, but also led to the arrest of a team employee accused of providing him with tainted, black market pills.
Five years later, The Times has pored over hundreds of pages of court documents and cellphone records to reconstruct Skaggs’ final hours. Playing cards with teammates on a three-hour flight. Teasing rookies on the bus. Trading affectionate texts with his wife until late at night.
Even the most ordinary details tell an important story, offering an intimate look at an epidemic that has ravaged the country.
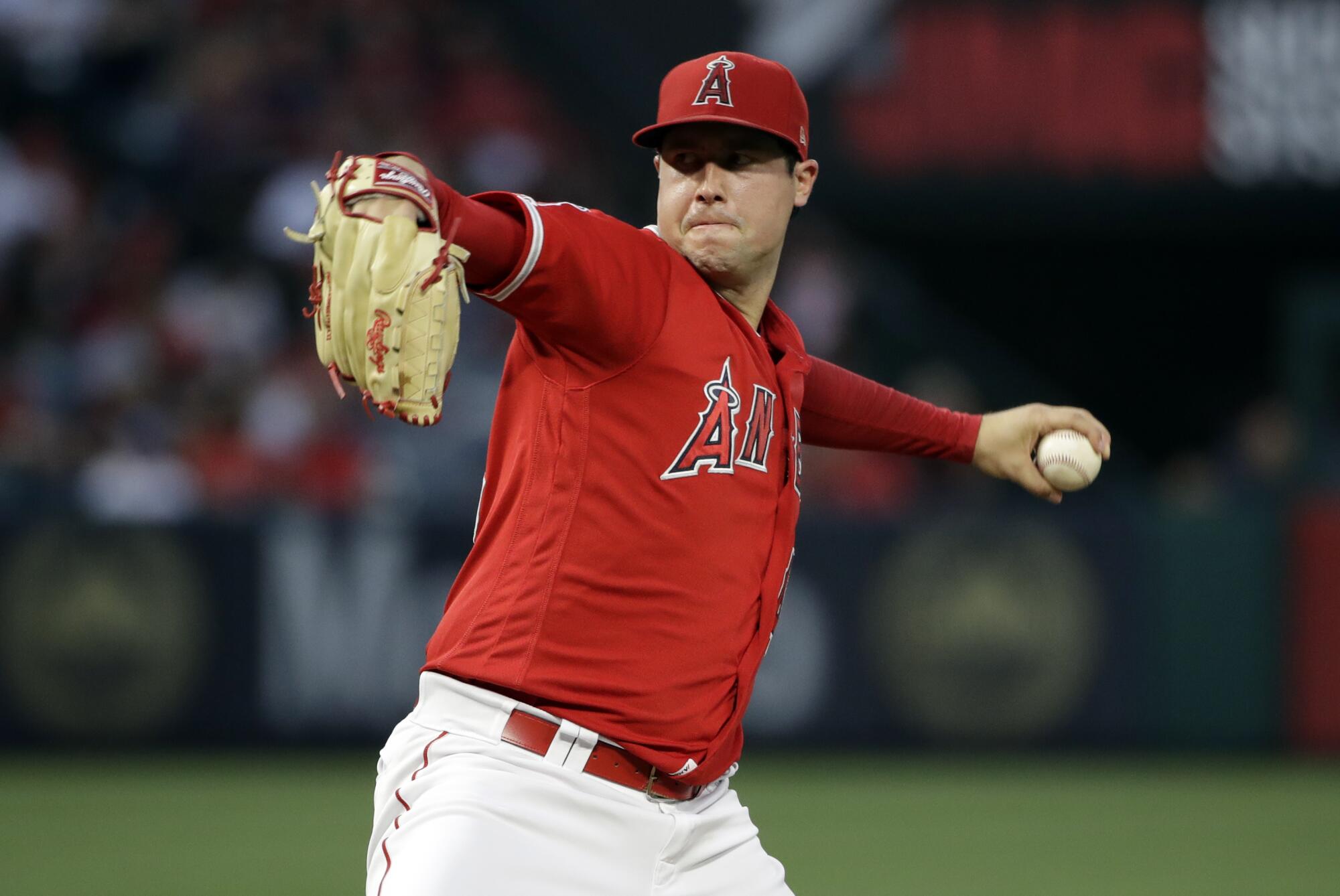

Tyler Skaggs pitches against the Oakland Athletics on June 29, 2019, two days before his death.
(Marcio Jose Sanchez / Associated Press)
Skaggs pitches at Angel Stadium against the Oakland A’s and is pulled after surrendering two runs in four-plus innings. CAA agent Nez Balelo texts to commiserate about “the quick hook … after cruising basically through 3 and 4.”
Skaggs is nothing if not dogged. At 6 feet 4 and 225 pounds, he has fought back from a string of serious injuries, refusing to quit, which might help explain his painkiller use. After the game, his mother, Debbie Hetman, a longtime softball coach at Santa Monica High, calls him and his wife.
“I didn’t FaceTime him because I was – we were super busy, so we just talked really quickly,” Hetman later testifies during the team employee’s trial. “I think he was in line at In-N-Out with Carli.”
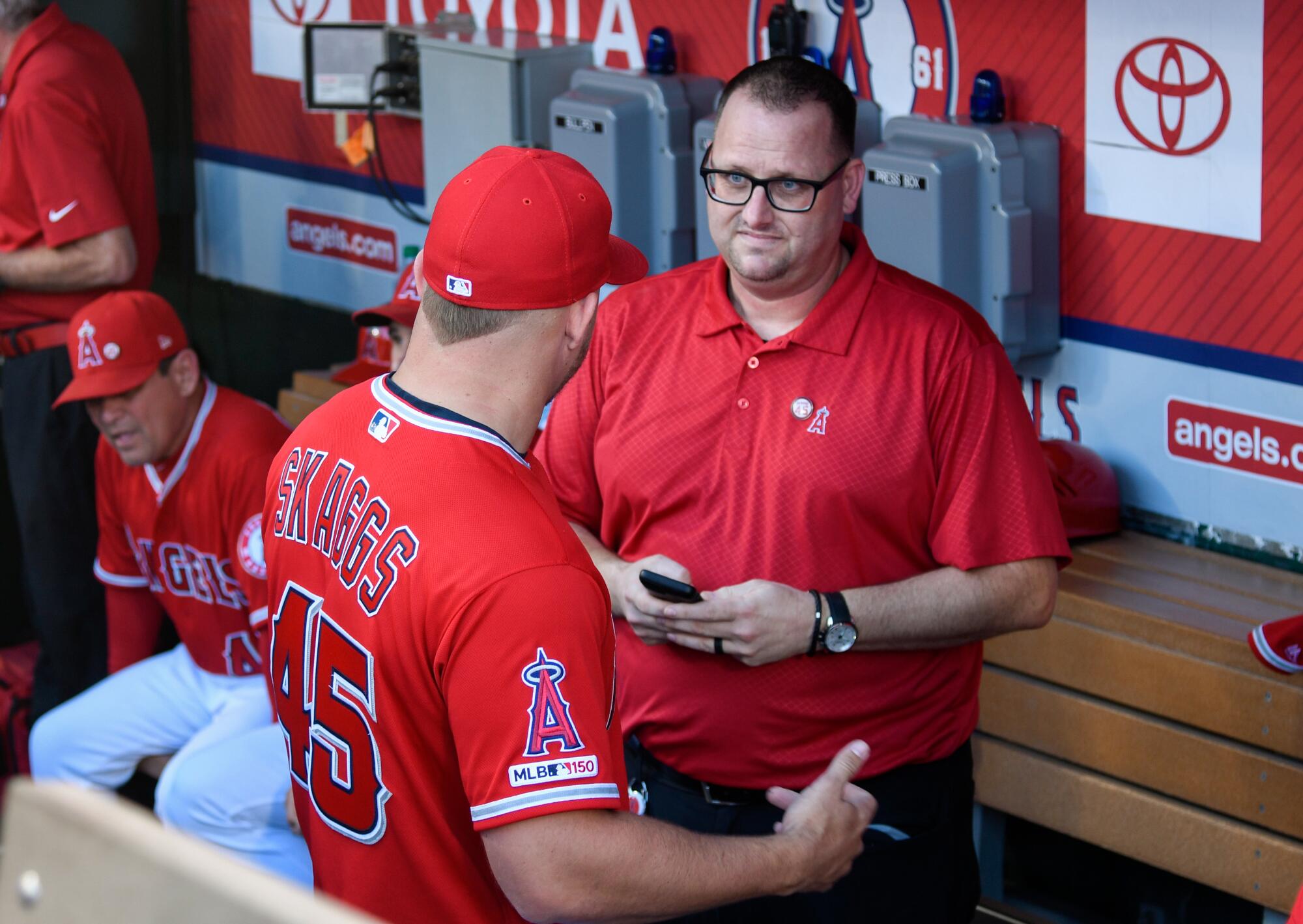

Mike Trout, wearing Tyler Skaggs’ number in his honor, speaks to Eric Kay in the dugout before a July, 12, 2019, home game against the Seattle Mariners.
( John McCoy / Getty Images)

(Animation by Kelvin Kuo/Los Angeles Times)
Shortly before a 1:07 p.m. game against the A’s, Skaggs receives a text from Eric Kay, the team communications director who for years has allegedly supplied him with “blue boys” — blue, 30-milligram oxycodone pills.
Kay: “Hoe [sic] many?”
Skaggs: “Just a few like 5”
Kay: “Word”
Skaggs: “Don’t need many”

4:25 p.m. Pacific Time
The Angels conclude their four-game home series with a 12-3 loss. It is a get-away day, meaning the team will head directly from the stadium to Long Beach Airport, where a charter plane waits for the start of the road trip.
Skaggs has previously asked his manager’s permission for the players to dress like cowboys for the flight to Texas. Before leaving the stadium, he meets his wife, Carli, so she can snap pictures of him in his black hat, bolo tie and boots.
“When did he buy that outfit?” a prosecutor later asks her during Kay’s trial.
“The day before.”
“Did you help him pick it out?”
“Yes.”
6:11 p.m. PT
Skaggs gathers with teammates on the tarmac beside a United Airlines charter plane for another photo to show off their Western wear. He hitches his thumbs in his belt like a cowboy. Seeing the picture on Instagram, Carli comments: “So cute”
8:07 p.m. PT
(Animation by Kelvin Kuo/Los Angeles Times)
With the Texas Rangers next on the schedule, the flight to Dallas Fort Worth International Airport lasts about three hours. Along the way, Carli texts to ask how things are going.
Skaggs: “Good gambling … losing”
Carli: “Damn babe … How much cool … Lol*”
Skaggs: “200 bucks … I’m winning now”
Carli: “Sweet”

11:06 p.m. Central Time
On the 15-minute ride from the airport to a Dallas-area hotel, Skaggs grabs a microphone at the front of the bus.
“So, he would have been kind of like emceeing, doing the music,” teammate Andrew Heaney later testifies. “You know, we would call younger guys up, ask them, you know, embarrassing questions or make them tell a funny story or whatever it may be, make them sing a song, something like that.”
Throughout the league, Skaggs is known as friendly, funny, eminently likable. Teammate Mike Trout later says: “The energy he brought to a clubhouse … every time you saw him, he’s just picking you up.”
11:25 p.m. CT
The Angels arrive at the Hilton Dallas/Southlake Town Square, where players receive key cards to their rooms and peruse a table of snacks, protein bars and Gatorade. A friend invites Skaggs to go out, but the pitcher remains in his room.
11:47 p.m. CT
(Animation by Kelvin Kuo/Los Angeles Times)
Skaggs texts his room number to Kay.
“469,” he writes, adding: “Come by”
“K,” the communications director responds.
Kay had used opioids enough to know black market oxycodone pills might be laced with dangerous drugs such as fentanyl, a synthetic opioid 50 to 100 times more powerful than morphine. In a jailhouse call recorded after his trial, he denies giving drugs to Skaggs that night, saying he visited the pitcher to talk about something else.
“I guess he hated the rookies or something — and he was one flight up so I flipped my door and went up,” he says.
The hotel does not have security cameras in the hallway, so it is unclear how long Kay spends in room 469.

12:02 a.m. CT
(Animation by Kelvin Kuo/Los Angeles Times)
Skaggs texts with teammate Ty Buttrey. He then trades messages with his wife.
Skaggs: “Miss you babe”
Carli: “Miss u too”
When the two met in 2013, Skaggs reportedly fell hard. Now, they have a house and are thinking about kids. They text continually when the Angels are traveling.
12:42 a.m. CT
“What u Doin,” Carli asks.
No answer. She tries again: “Helllooooo.”
1:09 a.m. CT
It is late in Dallas — two hours later than Los Angeles — and Carli is still waiting for a “goodnight” from her husband. She writes: “U know better than to get drunk and fall asleep without texting me”
Approx. 12:53 p.m. CT
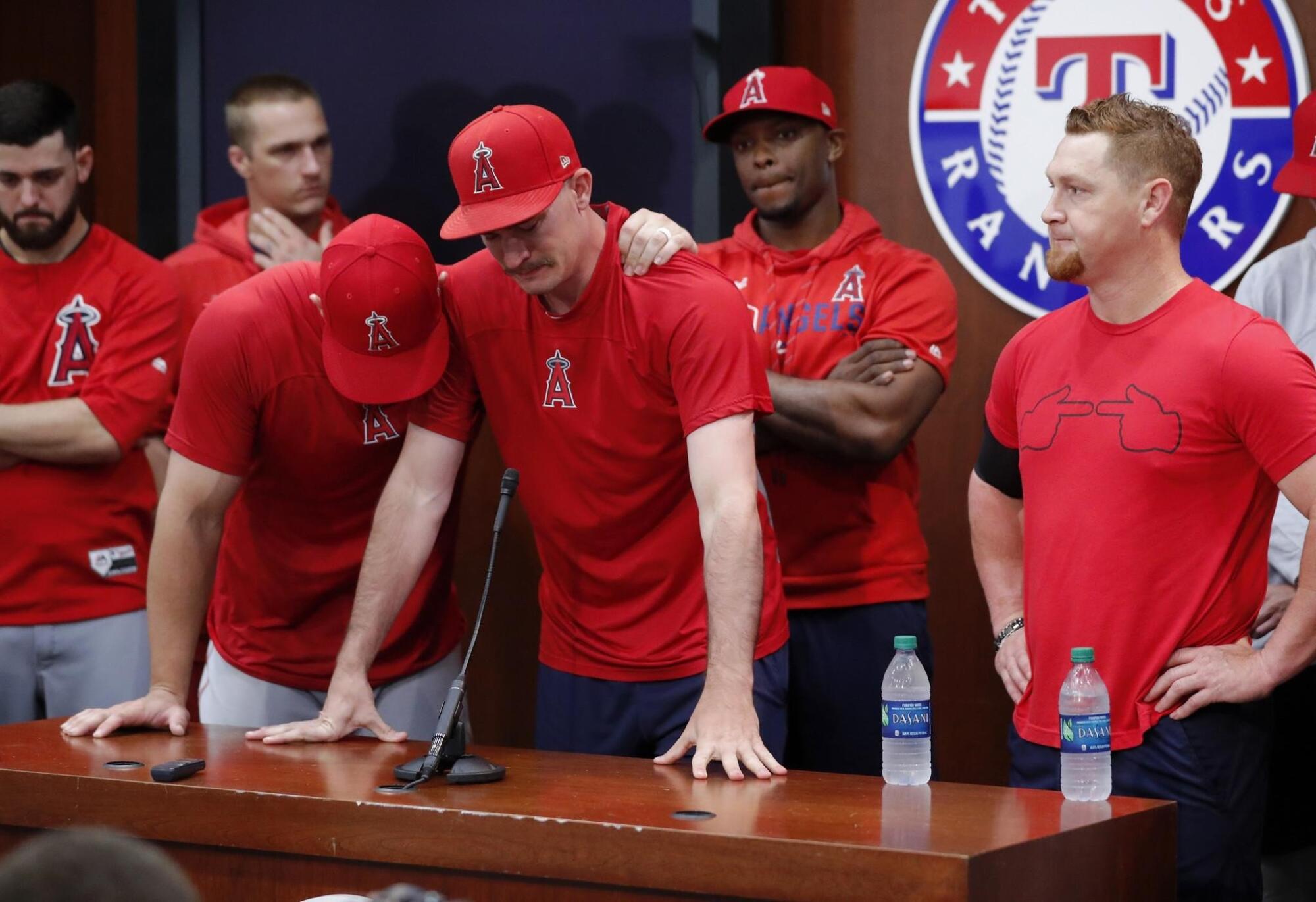

Angels’ Mike Trout, left, embraces Andrew Heaney, who fights back tears as he answers questions about their late friend and teammate Tyler Skaggs.
(Tony Gutierrez / Associated Press)
The night passes, followed by morning, and still no word from Skaggs. Heaney texts him: “Lunch?”
After a few minutes, Heaney stops by room 469. Light shines from under the door; the curtains must be open in there. Nearby, hotel workers are noisily cleaning a carpet. Heaney wonders how anyone could sleep through all this.
When his knock gets no response, he goes back to his room and tries calling Skaggs on the hotel phone.
1:49 p.m. CT
Tom Taylor, the Angels traveling secretary, is having lunch with Kay at a nearby barbecue joint and recalls Carli texting him. Heaney also reaches out to Taylor.
“He hadn’t heard from him either,” Taylor later testifies.
More than 12 hours after Carli’s last exchange with her husband, she messages again: “You have a drinking problem. I’m about to text tom Taylor.”
Carli later insists these words were sent “purely out of anger” with “no truth to it.”
Irritation gives way to another emotion. Carli contacts Skaggs’ mother, Hetman.
“She was really nervous,” Hetman later testifies. “I was really nervous because it was very unusual not to hear back from Tyler. Tyler was very good about returning text messages.” Hetman dials his number, and it sounds as if the call goes directly to voicemail. Her husband, Dan Ramos, sends a text:
“Hi kid. How r u doing. How is life treating u. How is your arm feeling”
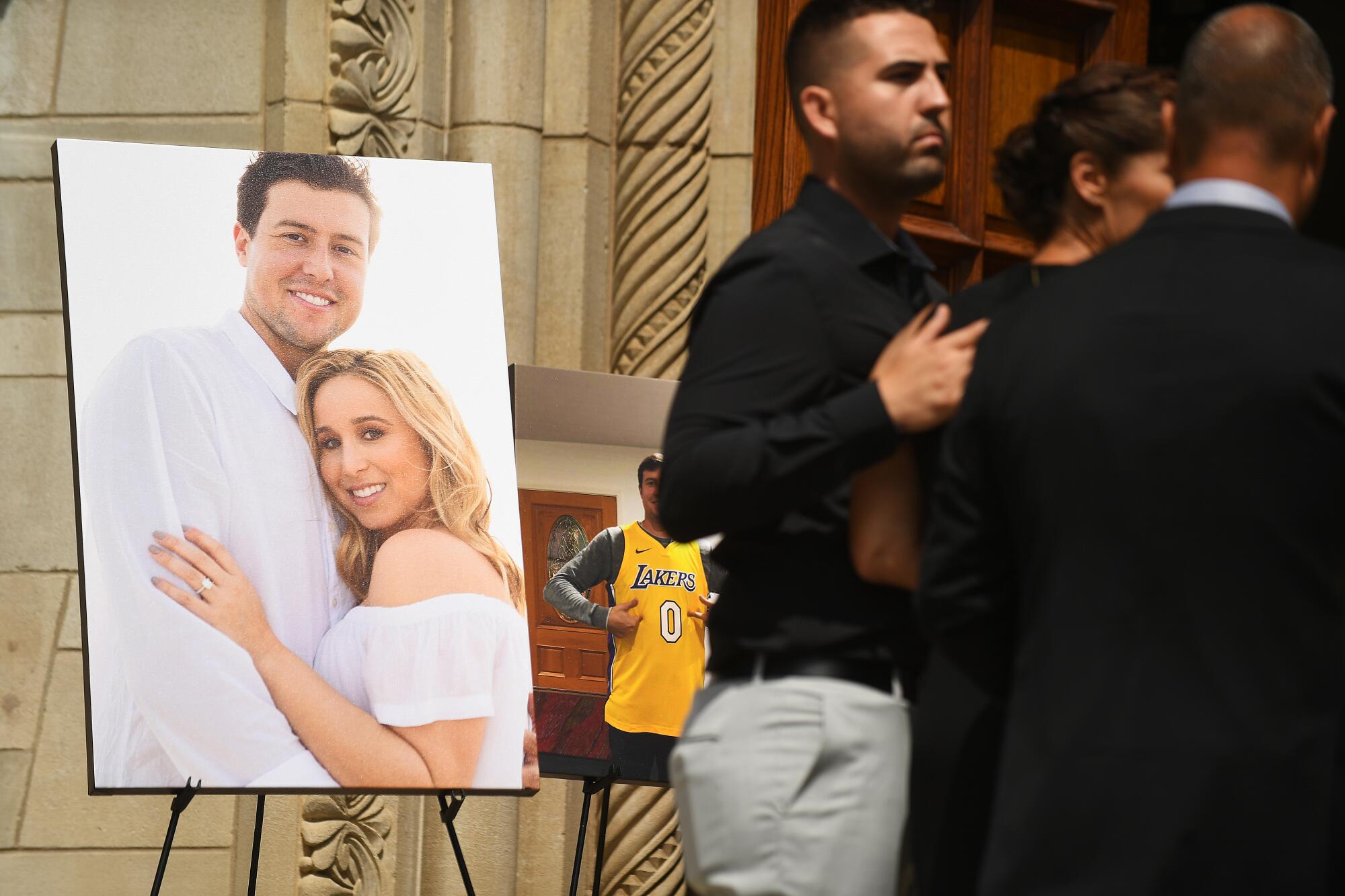

A photo of Tyler Skaggs and his wife, Carli, is displayed outside a memorial service for the Angels pitcher in 2019.
(Christina House / Los Angeles Times)
2:04 p.m. CT
Now Hetman tries texting: “Hey Ty Are you okay today?”
Around the same time, Taylor returns to the hotel and knocks on Skaggs’ door. He then summons Chuck Knight, one of the team’s security men, and they ask hotel management to let them into room 469.
A former Anaheim Police Department officer, Knight enters the room alone, staying less than a minute. Taylor later recalls him emerging with “a shocked-looking face, almost like, it’s not good, what he saw.”
2:16 p.m. CT
Knight calls 911. Asked later about what he encountered in the room, he testifies: “I saw two legs hanging off the end of the bed in a position that I thought was unusual for someone that might be sleeping … I walked closer in an attempt to obtain a pulse. I reached down to grab his wrist and noticed that his skin was very cool to the touch. I did not obtain a pulse.”
Heaney, who is getting messages from Carli, returns to the hallway outside room 469. Taylor tells him: “It’s not good.”
“I knew what was going on, but his wife didn’t,” Heaney later testifies. “And she was texting me, so it was — I just felt like I wanted her to know what was going on.”
He decides not to answer.
A call crackles over the scanner: “Medic 4-1, truck 4-1 respond. Medical emergency, Hilton Southlake Town Square.” The dispatcher adds: “It’s gonna be … a possible death investigation. PD is arriving on scene now.”
A Southlake police officer finds Skaggs’ room looking mostly undisturbed — the bed still made, a backpack and another bag on the couch, unopened beers on the coffee table. There is a white, “almost chalky” substance on the desk. Skaggs’ cellphone lies near his head.
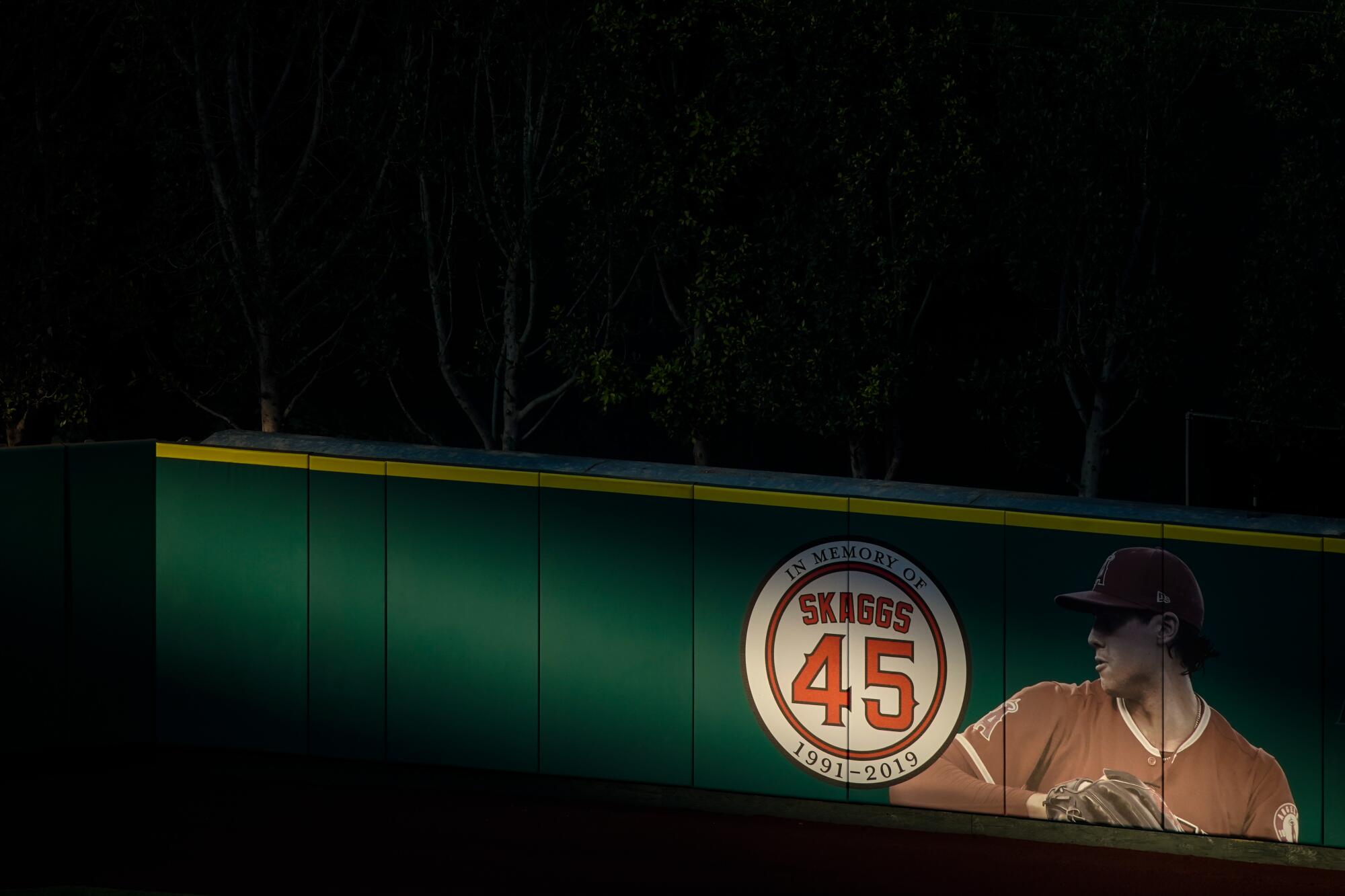

A memorial for Tyler Skaggs on the outfield wall at Angel Stadium.
(Los Angeles Times)
2:23 p.m. CT
Cory Teague, a Southlake Fire Department paramedic, arrives at room 469. His medical supplies include Naloxone, which can be administered to reverse the effects of opioid overdose.
“Did you use it?” a prosecutor later asks at trial.
“No.”
“Why not?”
“The patient had signs incompatible with life, unable to be revived.”
3:05 p.m. CT
Carli’s phone rings as she pulls up to her parents’ house in Santa Monica. It’s Billy Eppler, the Angels’ general manager. “I’ll never, ever forget that call,” she later says. She dials Hetman, who is at her Los Angeles home, and breaks the news. Hetman later recalls “crying and yelling and screaming.”
Buses are scheduled to take the Angels to their evening game. Instead, players and staff are told of Skaggs’ death and shepherded into a hotel banquet room where police take statements.
“The questions that we asked were generic for each player and employee,” Cpl. Delaney Green of the Southlake Police Department later testifies. “And it was along the lines of: When was the last time that you had seen or spoken to Tyler Skaggs? Had you seen him consume any alcohol on the plane? And did you know of any drug use that you were aware of?”
Kay is among those interviewed. He tells police that Skaggs was drinking on the flight to Texas but adds, “I didn’t think he had a lot.” He says he last saw the pitcher when they collected their room keys in the lobby.
3:52 p.m. CT
The Times and other news agencies report Skaggs’ death on social media. Family members call his mother at home. She later testifies that “before I could even talk to anybody, that whole — everything was like blowing up and it was super-crazy.”
4:11 p.m. CT
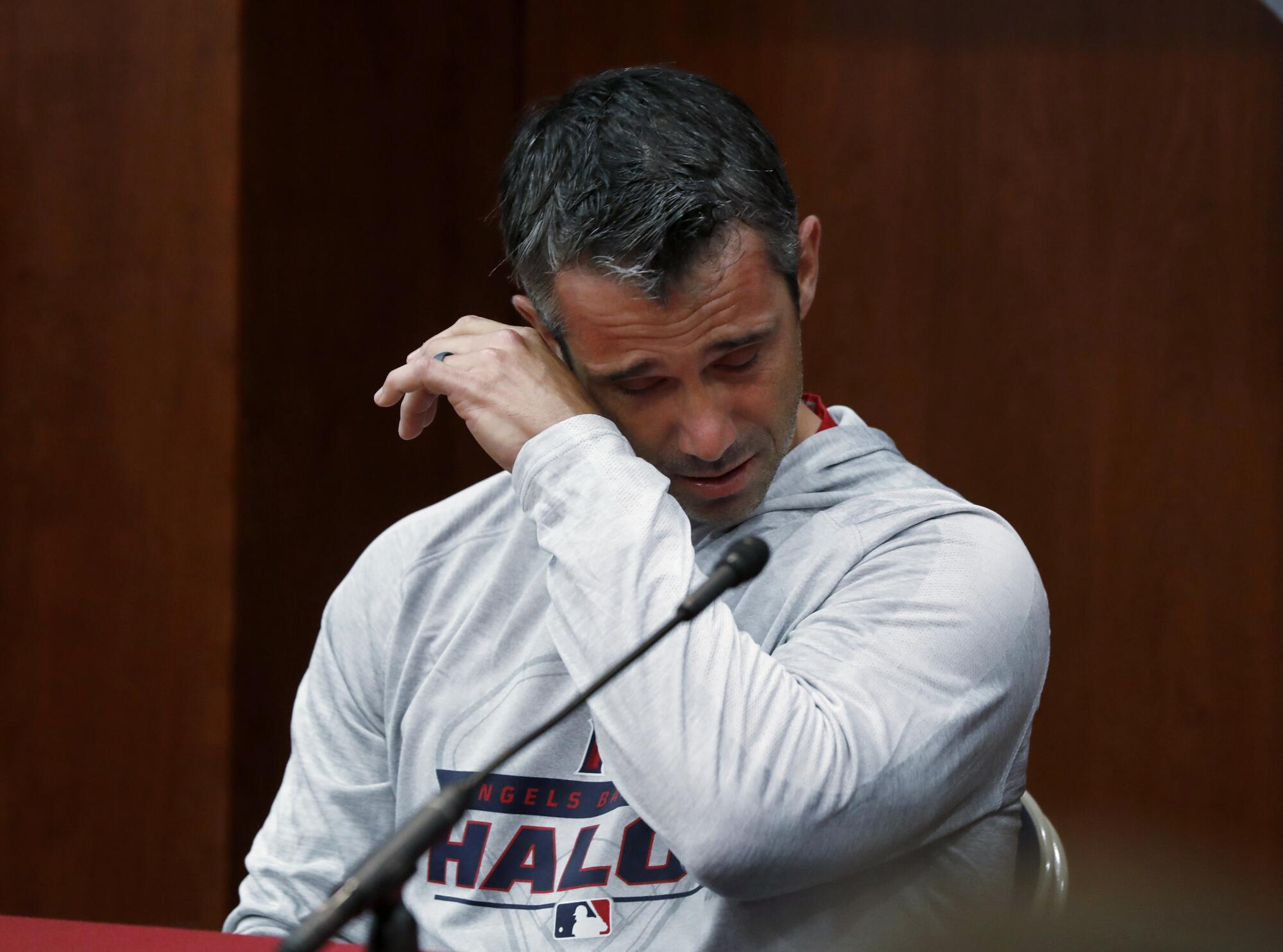

Angels manager Brad Ausmus speaks at a 2019 news conference about Tyler Skaggs’ death.
(Tony Gutierrez / Associated Press)
The Rangers announce the postponement of that night’s game as the Angels switch to another hotel. The team gathers for an emotional meeting. “We were able to talk about Tyler and laugh at some of the stories and some of the goofy things he did, listen to some of his music,” manager Brad Ausmus later says before breaking down.
On social media, players from around the league post messages.
“RIP to my longtime friend and Little League teammate,” then-St. Louis Cardinals pitcher Ryan Sherriff writes. “i love you brotha.”
About 8 p.m. CT
Carli and the Skaggs family board a flight to Texas.
About 10 a.m. CT
Carli and the Skaggs family visit the medical examiner’s office in Fort Worth. She later recalls kissing her husband’s cold lips as he lay on a gurney.
11:10 a.m. CT
The medical examiner begins an autopsy. He will eventually determine that “alcohol, fentanyl and oxycodone intoxication” caused Skaggs to choke on his own vomit.
Later that morning, Carli and the Skaggs family arrive at the Southlake police station to retrieve his luggage, iPad and other belongings.
In words that underscore the anguish of losing a loved one to opioids, Hetman later testifies: “I was angry because I knew that my son loved life and he did not want to die. He did not know that there was poison in that pill that cost him his life.”
About 5:30 p.m. CT
Team officials hold a news conference with Kay standing quietly to the side, hands clasped at his waist. At one point, he appears to take a deep breath, look toward the ceiling and exhale.
7:05 p.m. CT
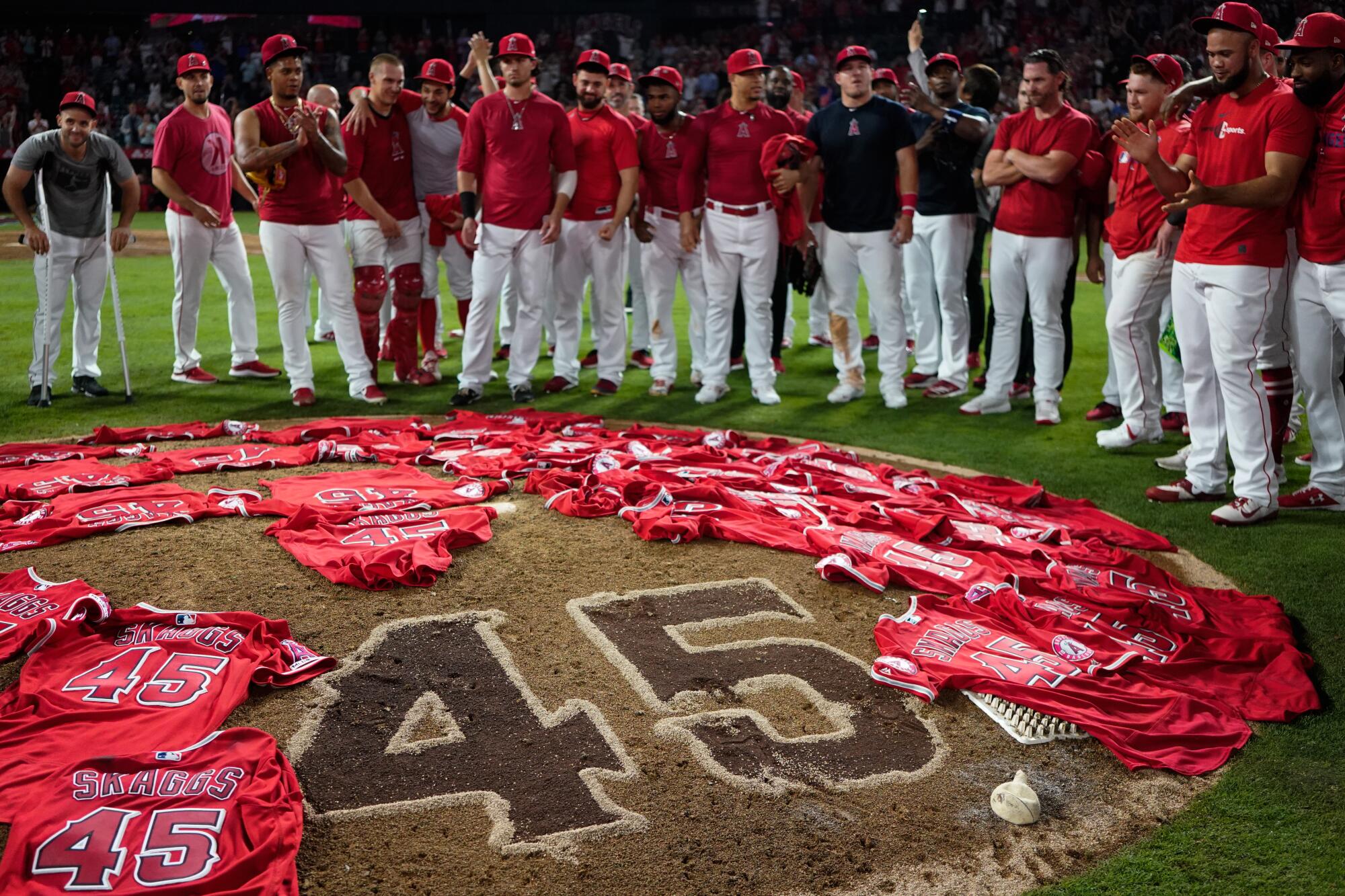

Teammates place jerseys with Tyler Skaggs’ number 45 on the mound at Angel Stadium at their first home game after his death.
(Kent Nishimura / Los Angeles Times)
The game against the Rangers proceeds as scheduled. The ballpark is eerily quiet, with the home team forgoing the usual walk-up music.
The Angels, wearing black No. 45 patches on their jerseys, score early and cruise to a surprising 9-4 victory, but Trout says: “All I was thinking about was Tyler. It was just a different feeling, you know. Just shock.”
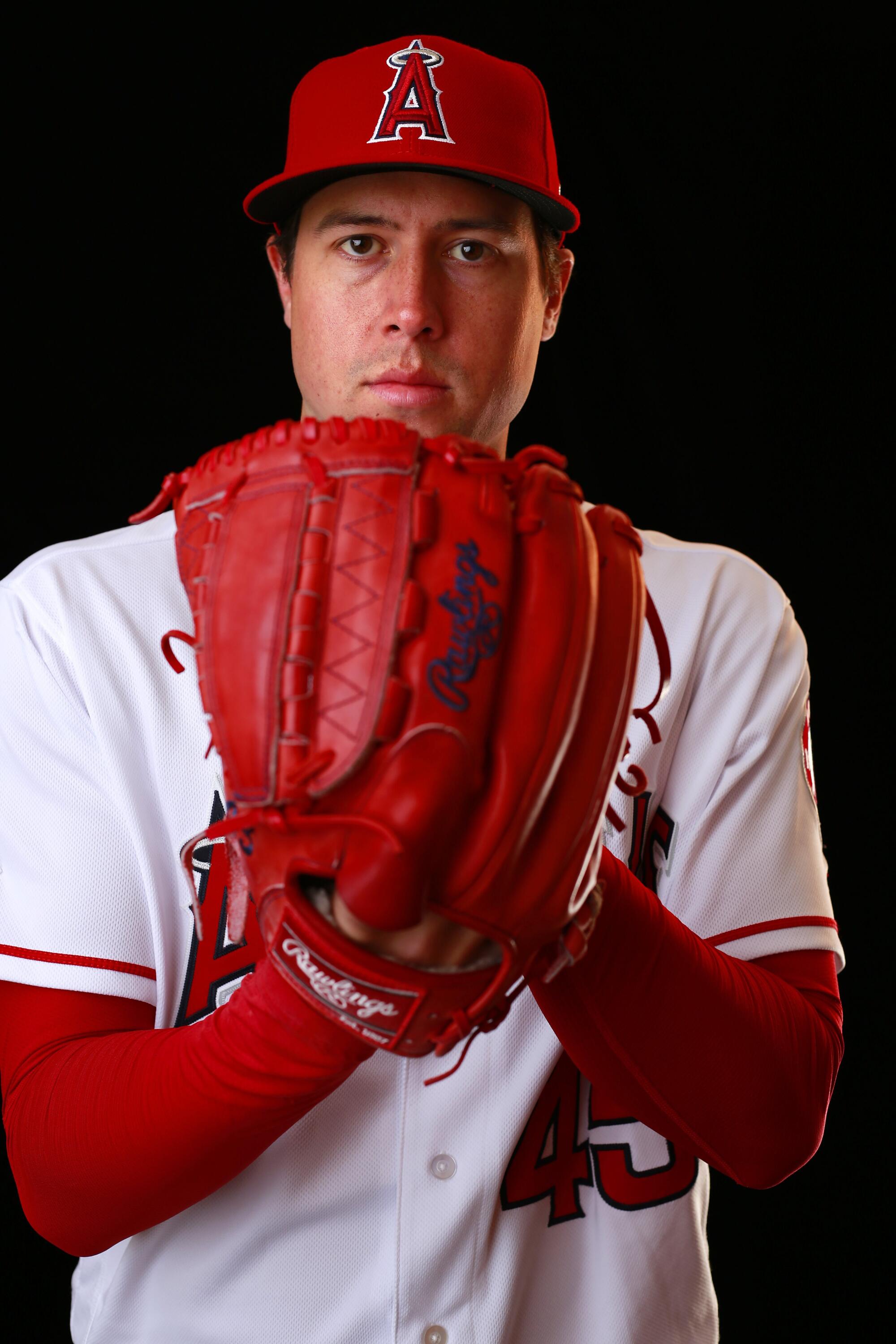


Angels pitcher Tyler Skaggs died of an overdose in a hotel room on July 1, 2019.
(K.C. Alfred/San Diego Union-Tribune)
Federal prosecutors charged Kay with distribution of a controlled substance resulting in death and conspiracy to possess with intent to distribute controlled substances. A trial began in February 2022.
“This was a case of one, one person who went up to that room on June 30,” a prosecutor said in court. “One person who went into that room and gave Tyler Skaggs fentanyl.”
The jury deliberated less than 90 minutes before returning a guilty verdict on both counts.
At a hearing where the judge sentenced him to 22 years in federal prison, Kay — who didn’t testify during trial — apologized to his family for the “disgrace and embarrassment” he had caused them.
Privately, however, he continued to profess innocence. In a recorded jailhouse call, he told a friend: “The worst thing, though, is that text that he sent me … because I didn’t know what he wanted. I had no idea. In my head, I think he thought I already got more [pills] for him but I told him they were going to be s—.”
By then, the Skaggs family had filed a wrongful-death suit against the Angels. The team has denied wrongdoing, and the case continues.
In the five years since Skaggs died, opioid overdoses — fueled by illicitly manufactured pills — have claimed hundreds of thousands of American lives.
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has a 24-hour helpline for individuals and families facing mental and substance abuse disorders. The number is (800) 662-HELP (4357).

Science
Video: Why Mountain Lions in California Are Threatened

new video loaded: Why Mountain Lions in California Are Threatened
By Loren Elliott, Gabriel Blanco and Rebecca Suner
February 9, 2026
Science
Torrance residents call for the ban of ‘flesh-eating’ chemical used at refinery

Residents and advocates gathered Saturday to demand the ban of a chemical that’s used at a Torrance oil refinery and that they say has the potential to cause a mass casualty disaster.
Hydrofluoric acid is used in about 40 gasoline refineries across the United States, according to the National Resources Defense Council. The defense council states that “exposing as little as 1% of a person’s skin to HF (about the size of one’s hand) can lead to death. When inhaled, HF can fatally damage lungs, disrupt heart rhythms, and cause other serious health effects.”
The Torrance Refinery uses modified hydrofluoric acid, or MHF, which the refinery considers to be a safer alternative to HF, though the claim is disputed by advocates. Steve Goldsmith, president of the Torrance Refinery Action Alliance, which hosted the Saturday event, said that if MHF were to be been released into the air, it would create irreversible health effects within 6.2 miles of the refinery, trickling into other parts of Los Angeles County.
And in 2015, he said, this almost happened.
On Feb. 18, 2015, there was an explosion at the refinery, then operated by ExxonMobil, caused by the rupture of an eroded valve. The incident, which released flammable hydrocarbons, injured four workers and forced 14 schools into lockdown.
The Saturday event, held at North High School’s Performing Arts Center in Torrance, marked the 11th anniversary of the explosion.
Goldsmith described the chemical as “murderous.”
Audience members participate in a “peace clap” at North Torrance High as they listen to speakers against the use of hydrofluoric acid in the Los Angeles region and across the country.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
“Torrance Refinery had an enormous explosion, and a piece of equipment the size of a bus came within five feet of the hydrofluoric acid, causing a near miss,” Goldsmith said. “We’ve been working to get rid of it.”
Residents like Christopher Truman say replacing MHF with an alternative option is the least that can be done. His parents live near the refinery.
“I’m born and raised in the South Bay, and my family lives in, effectively, what would be the blast radius if another accident happened,” Truman said. “So just in that aspect, I’m very worried about it.”
MHF is also used to clean semiconductor surfaces and produce pesticides and herbicides in the agricultural and pharmaceutical industries, according to the Torrance Refinery.
County Supervisor Janice Hahn said residents should not assume “they will be lucky” if another refinery accident were to occur.
“Only two refineries in California use MHF, Torrance Refinery and the Valero Refinery in Wilmington,” Hahn said. “MHF is simply too dangerous to use. It is a flesh-eating, low-crawling, toxic vapor cloud. Our communities will not be safe until this chemical is gone.”
Goldsmith said a Chevron refinery in Salt Lake City found an ionic-liquid alkylation process as an alternative to MHF. He added that the 2025 Chevron refinery explosion in El Segundo “would have been different if they had been using MHF.”
“They used another chemical that did not endanger the community,” Goldsmith said. “And that’s the thing about refineries, they have explosions. But that’s why you can’t have [MHF] around things that can blow up.”
U.S. Representative

U.S. Rep. Maxine Waters (D-Los Angeles) appears on a video message explaining her legislation, which she says will have a positive impact for communities in the Los Angeles region.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
U.S. Rep. Maxine Waters, (D-Los Angeles), who represents the city of Torrance, greeted attendees in a prerecorded message, in which she reintroduced her bill, the “Preventing Mass Casualties from Release of Hydrofluoric Acid at Refineries Act,” which targets plants using MHF.
“I originally introduced this bill in December of 2024,” Waters said in the video. “I faced considerable opposition, especially from the United Steel Workers Union, [who were] concerned that if refineries converted to safer technologies, some of the refineries might close, leaving workers without jobs. They agreed with me that hydrofluoric acid is dangerous. But they still would not support my bill. So I decided to go ahead and reintroduce this bill, [without] union support.”
The bill would give refineries five years to find an alternative to the dangerous chemical. Violators may be subject to fines up to $37,000 per infraction.

Los Angeles County Supervisor Janice Hahn speaks out against the use of hydrofluoric acid.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
Some residents stressed the need for transparency from local officials.
Ian Patton, a Long Beach resident, said most parts of the investigation into the 2015 explosion were withheld.
“Why can’t they not make this report public? The [Torrance Refinery Action Alliance] has been asking for it for years,” Patton said. “The next step was to look at litigation under the California Public Records Act. It’s not something that we want to do, but the public deserves to know whether these plants are safe.”
Science
TrumpRx is launched: How it works and what Democrats say about it

WASHINGTON — The White House’s TrumpRx website went live Thursday with a promise to instantly deliver prescription drugs at “the lowest price anywhere in the world.”
“This launch represents the largest reduction in prescription drug prices in history by many, many times, and it’s not even close,” President Trump said at a news conference announcing the launch of the platform.
Drug policy experts say the jury is still out on whether the platform will provide the significant savings Trump promises, though it will probably help people who need drugs not commonly covered by insurance.
Senate Democrats, meanwhile, called the site a “vanity project” and questioned whether the program presents a possible conflict of interest involving the pharmaceutical industry and the Trump family.
What is TrumpRx, really?
The new platform, trumprx.gov, is designed to help uninsured Americans find discounted prices for high-cost, brand-name prescriptions, including fertility, obesity and diabetes treatments.
The site does not directly sell drugs. Instead, consumers browse a list of discounted medicines, and select one for purchase. From there, they either receive a coupon accepted at certain pharmacies or are routed directly to a drug manufacturer’s website to purchase the prescription.
The White House said the reduced prices are possible after the administration negotiated voluntary “most favored nation” agreements with 16 major drugmakers including Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk.
Under these deals, manufacturers have agreed to set certain U.S. drug prices no higher than those paid in other wealthy nations in exchange for three-year tariff exemptions. However, the full legal and financial details of the deals have not been made public, leaving lawmakers to speculate how TrumpRx’s pricing model works.
What does it accomplish?
Though the White House has framed TrumpRx as a historic reset for prescription drug costs, economists said the platform offers limited new savings.
But it does move the needle on the issue of drug pricing transparency, away from the hidden mechanisms behind how prescription drugs are priced, rebated and distributed, according to Geoffrey Joyce, director of health policy at the USC Schaeffer Center for Health Policy and Economics.
“This has been a murky world, a terrible, obscure, opaque marketplace where drug prices have been inconsistently priced to different consumers,” Joyce said, “So this is a little step in the right direction, but it’s mostly performative from my perspective, which is kind of Trump in a nutshell.”
Still, for the uninsured or people seeking “lifestyle drugs” — like those for fertility or weight loss that insurers have historically declined to cover — TrumpRx could become a useful option, Joyce said.
“It’s kind of a win for Trump and a win for Pfizer,” Joyce said. “They get to say, ‘Look what we’re doing. We’re lowering prices. We’re keeping Trump happy, but it’s on our low-volume drugs, and drugs that we were discounting big time anyway.’”
Where does it fall short?
Early analyses by drug policy experts suggest many of the discounted medications listed on the TrumpRx site were already on offer through other drug databases before the platform launched.
For example, Pfizer’s Duavee menopause treatment is listed at $30.30 on TrumpRx, but it is also available for the same price at some pharmacies via GoodRx.
Weight management drug Wegovy starts at $199 on TrumpRx. Manufacturers were already selling the same discounted rates through its NovoCare Pharmacy program before the portal’s launch.
“[TrumpRx] uses data from GoodRx, an existing price-search database for prescription drugs,” said Darius N. Lakdawalla, a senior health policy researcher at USC. “It seems to provide prices that are essentially the same as the lowest price GoodRx reports on its website.”
Compared to GoodRx, TrumpRx covers a modest subset of drugs: 43 in all.
“Uninsured consumers, who do not use or know about GoodRx and need one of the specific drugs covered by the site, might benefit from TrumpRx. That seems like a very specific set of people,” Lakdawalla said.
Where do Democrats stand?
Democrats slammed the program this week, saying it would not provide substantial discounts for patients, and called for greater transparency around the administration’s dealings with drugmakers. To date, the administration has not disclosed the terms of the pricing agreements with manufacturers such as Pfizer and AstraZeneca.
In the lead-up to the TrumpRx launch, Democratic members of Congress questioned its usefulness and urged federal health regulators to delay its debut.
“This is just another Donald Trump pet project to rebrand something that already exists, take credit for it, and do nothing to actually lower healthcare prices,” Sen. Alex Padilla (D-Calif.) said Friday. “Democrats will continue fighting to lower healthcare costs and push Republicans to stop giving handouts to billionaires at the expense of working-class Americans.”
Three other Democratic senators — Dick Durbin, Elizabeth Warren and Peter Welch — raised another concern in a Jan. 29 letter to Thomas March Bell, inspector general for the Department of Health and Human Services.
The three senators pointed to potential conflicts of interest between TrumpRx and an online dispensing company, BlinkRx.
One of Trump’s sons, Donald Trump Jr., joined the BlinkRx Board of Directors in February 2025.
Months before, he became a partner at 1789 Capital, a venture capital firm that holds a significant stake in BlinkRx and led the startup’s $140-million funding round in 2024. After his appointment, BlinkRx launched a service to help pharmaceutical companies build direct-to-patient sales platforms quickly.
“The timing of the BlinkRx announcement so closely following the administration’s outreach to the largest drug companies, and the involvement of President Trump’s immediate family, raises questions about potential coordination, influence and self-dealing,” according to an October 2025 statement by Democrats on the House Energy and Commerce Committee.
Both BlinkRx and Donald Trump Jr. have denied any coordination.
What’s next?
The rollout of TrumpRx fits into a suite of White House programs designed to address rising costs, an area of vulnerability for Republicans ahead of the November midterms.
The White House issued a statement Friday urging support for the president’s healthcare initiative, dubbed “the great healthcare plan,” which it said will further reduce drug prices and lower insurance premiums.
For the roughly 8% of Americans without health insurance, TrumpRx’s website promises that more high-cost, brand-name drugs will be discounted on the platform in the future.
“It’s possible the benefits will become broader in the future,” Lakdawalla said. “I would say that the jury remains out on its long-run structure and its long-run pricing effects.”
-

 Indiana1 week ago
Indiana1 week ago13-year-old rider dies following incident at northwest Indiana BMX park
-

 Massachusetts1 week ago
Massachusetts1 week agoTV star fisherman, crew all presumed dead after boat sinks off Massachusetts coast
-

 Tennessee1 week ago
Tennessee1 week agoUPDATE: Ohio woman charged in shooting death of West TN deputy
-

 Indiana7 days ago
Indiana7 days ago13-year-old boy dies in BMX accident, officials, Steel Wheels BMX says
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoTrump unveils new rendering of sprawling White House ballroom project
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoDon Lemon could face up to a year in prison if convicted on criminal charges
-

 San Francisco, CA5 days ago
San Francisco, CA5 days agoExclusive | Super Bowl 2026: Guide to the hottest events, concerts and parties happening in San Francisco
-
Austin, TX1 week ago
TEA is on board with almost all of Austin ISD’s turnaround plans






















