Health
One Step Closer to a Universal Flu Vaccine?

Think about a single dose of vaccine that prepares your physique to struggle each identified pressure of influenza — a so-called common flu vaccine that scientists have been attempting to create for many years.
A brand new examine describes profitable animal checks of simply such a vaccine, providing hope that the nation could be protected towards future flu pandemics. Just like the Covid vaccines made by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, the experimental flu vaccine depends on mRNA.
It’s in early phases — examined solely in mice and ferrets — however the vaccine gives essential proof {that a} single shot could possibly be used towards a whole household of viruses. If the vaccine succeeds in individuals, the method could possibly be used towards different virus households, maybe together with the coronavirus.
The vaccine wouldn’t exchange annual flu pictures however would offer a defend towards extreme illness and dying from potential pandemic threats.
“There’s an actual want for brand new influenza vaccines to supply safety towards pandemic threats which are on the market,” mentioned Scott Hensley, an immunologist on the College of Pennsylvania who led the work.
“If there’s a brand new influenza pandemic tomorrow, if we had a vaccine like this that was extensively employed earlier than that pandemic, we’d not should shut all the things down,” he mentioned. He and his colleagues described the vaccine final week within the journal Science.
By the age of 5, most kids have been contaminated with the flu a number of instances and have gained some immunity — however solely towards the strains they’ve encountered.
“Our childhood exposures to influenza lay down long-lived immune reminiscence that may be recalled later in life,” Dr. Hensley. However “we’re type of residing the remainder of our life depending on the random likelihood of no matter we bought contaminated with as a child.”
Present influenza vaccines defend towards seasonal flu however would offer little safety towards a brand new pressure which will emerge as a pandemic menace. Throughout the 2009 H1N1 swine flu pandemic, for instance, the traditional vaccine provided little protection towards the virus. However older adults who had been uncovered to H1N1 strains in childhood developed solely gentle signs.
Scientists have lengthy tried to create a vaccine that might introduce youngsters to each potential pressure of flu they might encounter later in life. However researchers have been constrained by technical hurdles and by the variety of the flu virus.
Broadly talking, there are 20 subgroups of influenza that every signify hundreds of viruses. Present vaccines can goal 4 subgroups at most. However the experimental vaccine comprises all 20, and it could be sooner to provide.
The vaccine elicited excessive ranges of antibodies to all 20 flu subtypes in ferrets and mice, the researchers discovered — a discovering that a number of specialists mentioned was surprising and promising.
If the vaccine behaves equally in individuals, “we’ll have a extra broad protection of influenza viruses — not solely these which are circulating, however people who would possibly spill over from the animal reservoir that may trigger the following pandemic,” Alyson Kelvin, a vaccinologist on the College of Saskatchewan in Canada, mentioned.
Packing 20 targets into one vaccine does have a draw back: Antibody ranges within the take a look at animals had been decrease than after they got vaccines aimed toward particular person strains. However the ranges had been nonetheless excessive sufficient to be efficient towards influenza.
As a result of a brand new pandemic pressure of influenza would possibly differ from the 20 targets included within the experimental vaccine, the researchers additionally examined it towards viruses that had been imperfectly matched. The vaccine nonetheless supplied sturdy safety, suggesting that it could stop no less than extreme sickness, if not an infection, from a novel pandemic flu virus.
This phenomenon is akin to that with the present Covid vaccines: Though the newest Omicron variants are so completely different from the ancestral virus that the unique vaccine doesn’t stop infections, it continues to assist safeguard most individuals towards extreme sickness.
This high quality could also be a specific benefit of mRNA vaccines, Dr. Kelvin mentioned. Typical flu vaccines goal solely the precise viruses they’re designed for. However mRNA vaccines appear to provide antibodies that defend the physique towards a broader vary of viruses than these included.
The specialists famous some essential caveats and questions that should be answered earlier than the vaccine turns into a viable candidate.
The animals within the examine constructed defenses towards all 20 flu strains equally. However “these animals haven’t seen flu earlier than,” mentioned Richard J. Webby, an professional in influenza viruses at St. Jude Youngsters’s Analysis Hospital in Memphis.
Such an entire lack of immunity towards flu is barely true of very younger youngsters, Dr. Webby famous. Older persons are uncovered to many various strains over their lifetimes, and it’s not clear whether or not their immune responses to a common vaccine could be fairly so uniform.
“The proof of the pudding can be what occurs when it goes into people and the way going right into a preimmune inhabitants skews the response to it,” Dr. Webby mentioned.
Designing common vaccines for various age teams, if needed, could be a problem. It might even be essential to see how lengthy safety from such a vaccine lasts, some specialists mentioned.
“The largest problem about common flu is what it is advisable goal and the way lengthy you possibly can proceed to make use of the identical vaccine,” Ted Ross, director of World Vaccine Growth on the Cleveland Clinic, mentioned. “If you need to hold updating it, it might not enhance the benefit of how we do vaccines right now.”
The following step for the vaccine could be to check it in monkeys and in individuals. However proving its effectiveness may be difficult. “How do you consider and regulate a vaccine the place their targets aren’t circulating, and so you possibly can’t actually present effectiveness?” Dr. Kelvin mentioned.
Maybe the vaccine could possibly be examined in small sporadic outbreaks, or in poultry employees who’re liable to turning into contaminated with an avian flu virus, she mentioned: “These are questions that I believe we have to reply earlier than now we have our subsequent pandemic.”

Health
fatty15 has the essential nutrient to ease stress and well-being

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
Summer is tick season, but these tips can help you avoid the bloodsucking bugs
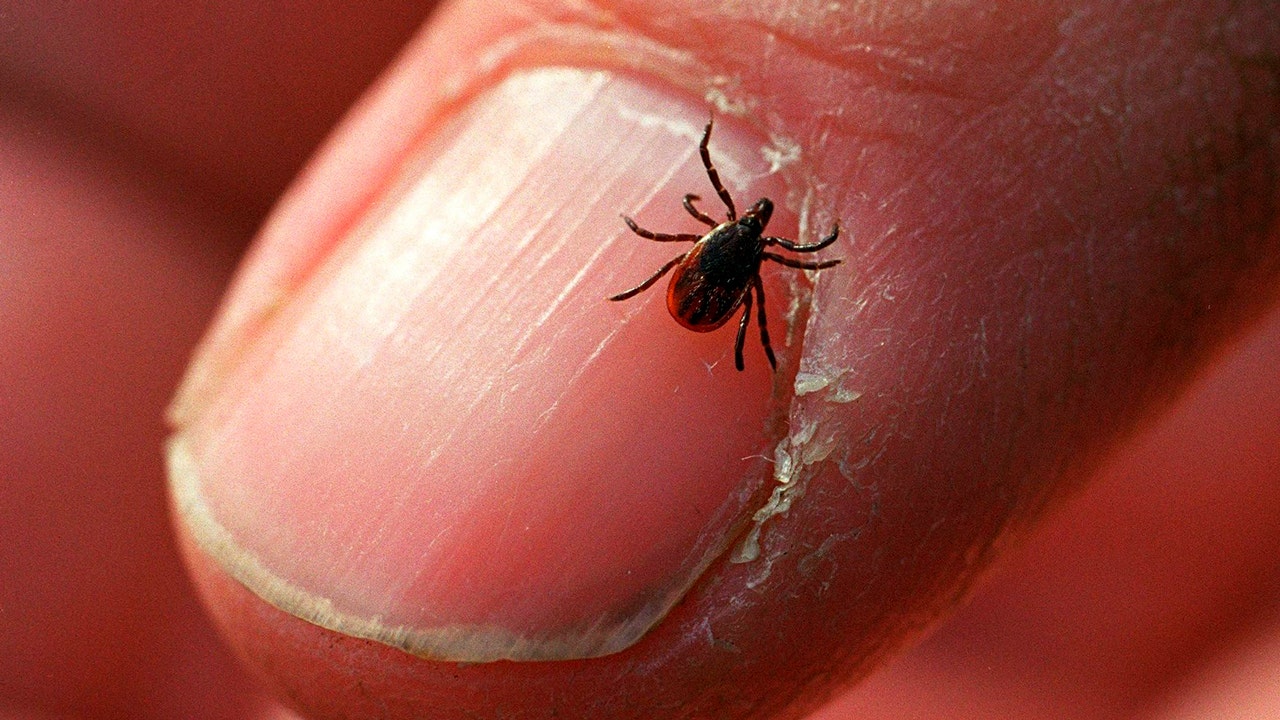
Tick season is starting across the U.S., and experts are warning the bloodsuckers may be as plentiful as ever.
Another mild winter and other favorable factors likely means the 2024 tick population will be equal to last year or larger, some researchers say.
“It’s very bad and has only been getting worse,” said Susanna Visser of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
TICK BITES AND LYME DISEASE: WHAT TO DO IF A TICK BITES YOU OR YOUR PET
An increasing variety of ticks are pushing into new geographical areas, bringing unusual diseases. Exotic southern species like the Gulf Coast tick and the lone star tick are being detected in New York and other northern states, for example.
But the tick that experts warn of the most is a common blacklegged tick, which is found mainly in forests and spreads Lyme disease. Infection rates begin to peak in May, and U.S. health officials estimate nearly half a million Lyme disease infections happen annually.
Here’s a look at what’s expected this year and how you can protect yourself.
An adult deer tick, also known as the blacklegged tick, crawls on a fingernail at Connetquot State Park in Oakdale, New York on Dec. 27, 2011. (Bill Davis/Newsday RM via Getty Images)
TICK FACTS
Ticks are small, eight-legged bloodsucking parasites — arachnids, not insects — that feed on animals and sometimes people. Some ticks are infected with germs that can cause illness, and they spread those germs when they bite.
There is no widely accepted estimate of how many ticks there are from one year to the next, but there is a scientific consensus that they are an increasingly common health hazard in large portions of the United States.
Blacklegged ticks — also known as deer ticks, since they feed on deer — are among the most common ticks in the eastern half of the U.S. They were plentiful centuries ago, then diminished when forests were cut down and deer were hunted, and rebounded alongside deer and wooded suburbs. The ticks have spread out from pockets in New England and the Midwest over a wider range.
Tick populations cycle throughout the year and their numbers depend on a few factors. They like warm, humid weather, and more can be seen after a mild winter. The more deer and mice available to feed matters, too.
Overall, the blacklegged tick population has been expanding for at least four decades, researchers say.
“This is an epidemic in slow motion,” said Rebecca Eisen, a CDC research biologist and tick expert.
2024 TICK SEASON FORECAST
Weather can play a role in the severity of a tick season.
Very cold, dry winters can whittle down tick populations, but recent winters have been mild — a trend some attribute to climate change.
As Scott Williams, a tick researcher at the Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station, said: “Winters are no longer limiting the tick population.”
Ticks can withstand the heat but tend to almost hibernate when it’s a dry summer. That happened in Maine in 2020 through 2022, said Chuck Lubelczyk, a vector ecologist at the MaineHealth Institute for Research.
But last year was a very wet year, and tick activity multiplied in Maine — the state with the highest incidence of Lyme disease in the country. Weather service predictions call for higher temperatures and precipitation, so “on paper, at least, it could be a very good year for the ticks,” Lubelczyk said.
In Wisconsin, adult ticks were out longer than usual due to a mild winter. The tick nymphs are starting to emerge, and a wet spring is setting the stage for the possibility that the population will be robust, said Xia Lee, an entomologist at the Wisconsin Department of Health Services.
Ditto New York.
“It will be as bad as last year, or worse,” said Saravanan Thangamani, who studies ticks and tickborne diseases at SUNY Upstate Medical University in Syracuse.
WHAT IS LYME DISEASE?
Not all ticks are infected with disease-causing germs — about 20% to 30% of the blacklegged tick nymphs that emerge in the Northeast and Midwest this spring and into summer will be carrying the bacteria that causes Lyme disease, experts estimate.
Lyme disease symptoms tend to start between three and 30 days after a bite occurs and can include fever, headache, fatigue and a bull’s-eye-like rash. If you get bitten and develop symptoms, see a doctor to get treated with antibiotics.
HOW TO KEEP TICKS OFF OF YOU
Experts say the best thing to do is take steps to avoid a tick bite in the first place.
If you go outdoors, make note of wooded areas and where grassy properties start bleeding into wooded areas. Ticks tend to perch on ankle-level vegetation with their upper legs outstretched, waiting to latch on to an unsuspecting dog or human.
Try to walk in the middle of paths, wear light-colored and permethrin-treated clothing and use Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)-registered insect repellents.
HOW TO CHECK FOR TICKS
When you come inside, check for ticks. They can be found anywhere on the human body, but common spots include around the waist, behind the knees, between fingers and toes, on underarms, in the belly button and around the neck or hairline.
They are harder to see when they are young, so look carefully and immediately pull them off with tweezers.
The CDC does not recommend sending individual ticks to testing services for analysis, because a person might get more than one tick bite and the results from the tested tick may not be sufficient information.
Health
Pizza for Weight Loss? Top MD Says This Dough Makes It Possible

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPentagon chief confirms US pause on weapons shipment to Israel
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoRFK Jr said a worm ate part of his brain and died in his head
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoOhio AG defends letter warning 'woke' masked anti-Israel protesters they face prison time: 'We have a society'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoNine Things We Learned From TikTok’s Lawsuit Against The US Government
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoBiden’s decision to pull Israel weapons shipment kept quiet until after Holocaust remembrance address: report
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: Police Use Pepper Spray on Protesters on G.W.U.’s Campus
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoA look at Chinese investment within Hungary
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoThe Major Supreme Court Cases of 2024















