Science
The Secret Behind Japan’s Wintry Strawberries

MINOH, Japan — Strawberry shortcake. Strawberry mochi. Strawberries à la mode.
These could sound like summertime delights. However in Japan, the strawberry crop peaks in wintertime — a cold season of picture-perfect berries, essentially the most immaculate ones promoting for lots of of {dollars} apiece to be given as particular presents.
Japan’s strawberries include an environmental toll. To recreate a synthetic spring within the winter months, farmers develop their out-of-season delicacies in big greenhouses heated with large, gas-guzzling heaters.
“We’ve come to some extent the place many individuals suppose it’s pure to have strawberries in winter,” stated Satoko Yoshimura, a strawberry farmer in Minoh, Japan, simply exterior Osaka, who till final season burned kerosene to warmth her greenhouse all winter lengthy, when temperatures can dip effectively bellow freezing.
However as she stored filling up her heater’s tank with gasoline, she stated, she began to suppose: “What are we doing?”
Fruits and veggies are grown in greenhouses everywhere in the world, after all. The Japan strawberry trade has carried it to such an excessive, nonetheless, that almost all farmers have stopped rising strawberries in the course of the far much less profitable hotter months, the precise rising season. As an alternative, in summertime Japan imports a lot of its strawberry provide.
It’s an instance of how trendy expectations of contemporary produce 12 months spherical can require shocking quantities of power, contributing to a warming local weather in return for having strawberries (or tomatoes or cucumbers) even when temperatures are plunging.
Up till a number of many years in the past, Japan’s strawberry season began within the spring and bumped into early summer time. However the Japanese market has historically positioned a excessive worth on first-of-the-season or “hatsumono” produce, from tuna to rice and tea. A crop claiming the hatsumono mantle can convey many instances regular costs, and even snags fevered media protection.
Because the nation’s shopper economic system took off, the hatsumono race spilled over into strawberries. Farms began to compete to convey their strawberries to market earlier and earlier within the 12 months. “Peak strawberry season went from April to March to February to January, and at last hit Christmas,” stated Daisuke Miyazaki, chief government at Ichigo Tech, a Tokyo-based strawberry consulting agency.
Now, strawberries are a serious Christmas staple in Japan, adorning Christmas truffles bought throughout the nation all December. Some farmers have began to ship first-of-the-season strawberries in November, Mr. Miyazaki stated. (Lately, one image excellent Japanese-branded strawberry, Oishii (which suggests “scrumptious”), has develop into TikTok-famous, however it’s grown by a U.S. firm in New Jersey.)
Japan’s swing towards cultivating strawberries in freezing climate has made strawberry farming considerably extra power intensive. Based on analyses of greenhouse gasoline emissions related to varied produce in Japan, the emissions footprint of strawberries is roughly eight instances that of grapes, and greater than 10 instances that of mandarin oranges.
“All of it comes right down to heating,” stated Naoki Yoshikawa, a researcher in environmental sciences on the College of Shiga Prefecture in western Japan, who led the produce emissions examine. “And we checked out all features, together with transport, or what it takes to supply fertilizer — even then, heating had the largest footprint.”
Examples like these complicate the concept of consuming native, particularly the concept embraced by some environmentally acutely aware consumers of shopping for meals that was produced comparatively shut by, partially to chop down on the gasoline and air pollution related to transport.
Transportation of meals usually has much less of a local weather impression than the best way by which it’s produced, stated Shelie Miller, a professor on the College of Michigan who focuses on local weather, meals and sustainability. One examine discovered, for instance, that tomatoes grown regionally in heated greenhouses within the Britain had the next carbon footprint in comparison with tomatoes grown in Spain (outdoor, and in-season), and shipped to British supermarkets.
Local weather-controlled greenhouses can have advantages: They will require much less land and fewer pesticide use, they usually can produce increased yields. However the backside line, Professor Miller stated, is that “it’s supreme should you can eat each in-season, and regionally, so your meals is produced with out having so as to add main power expenditures.”
In Japan, the power required to develop strawberries in winter hasn’t confirmed to be only a local weather burden. It has additionally made strawberry cultivation costly, significantly as gasoline prices have risen, hurting farmers’ backside traces.
Analysis and improvement of berry varieties, in addition to elaborate branding, has helped alleviate a few of these pressures by serving to farmers fetch increased costs. Strawberry varieties in Japan are bought with whimsical names like Beni Hoppe (“pink cheeks”), Koinoka (“scent of affection”), Bijin Hime (“lovely princess”). Together with different expensive fruit like watermelons, they are sometimes given as presents.
Tochigi, a prefecture north of Tokyo that produces extra strawberries than some other in Japan, has been working to sort out each local weather and price challenges with a brand new number of strawberry it’s calling Tochiaika, a shortened model of the phrase, “Tochigi’s beloved fruit.”
Seven years within the making by agricultural researchers at Tochigi’s Strawberry Analysis Institute, the brand new selection is bigger, extra immune to illness, and produces the next yield from the identical inputs, making rising them extra power environment friendly.
Tochiaika strawberries even have firmer pores and skin, reducing down on the variety of strawberries that get broken throughout transit, thereby decreasing meals waste, which additionally has local weather penalties. In america, the place strawberries are grown principally in hotter climates in California and Florida, strawberry patrons discard an estimated one-third of the crop, partly due to how fragile they’re.
And as a substitute of heaters, some farmers in Tochigi use one thing referred to as a “water curtain,” a trickle of water that envelopes the skin of greenhouses, protecting temperatures inside fixed, although that requires entry to ample groundwater. “Farmers can save on gasoline prices, and assist battle world warming,” stated Takayuki Matsumoto, a member of the workforce that helped develop the Tochiaika strawberry. “That’s the best.”
There are different efforts afoot. Researchers within the northeastern metropolis of Sendai have been exploring methods to harness solar energy to maintain the temperature inside strawberry greenhouses heat.
Ms. Yoshimura, the strawberry farmer in Minoh, labored in farming a decade earlier than deciding she wished to dispose of her large industrial heater within the winter of 2021.
A younger mom of 1, with one other on the best way, she had spent a lot of the lockdown days of the pandemic studying up on local weather change. A sequence of devastating floods in 2018 that wrecked the tomato patch on the farm she runs along with her husband additionally woke up her to the risks of a warming planet. “I spotted I wanted to vary the best way I farmed, for the sake of my youngsters,” she stated.
However in mountainous Minoh, temperatures can dip to beneath 20 levels Fahrenheit, or about minus 7 Celsius, ranges at which strawberry vegetation would usually go dormant. So she delved into agricultural research to attempt to discover one other method to ship her strawberries out in the course of the profitable winter months, whereas not utilizing fossil gasoline heating.
She learn that strawberries sense temperatures through part of the plant often called the crown, or the brief thickened stem on the plant’s base. If she might use groundwater, which typically stays at a continuing temperature, to guard the crown from freezing temperatures, she wouldn’t need to depend on industrial heating, she surmised.
Ms. Yoshimura fitted her strawberry beds with a easy irrigation system. For additional insulation at night time, she coated her strawberries with plastic.
She stresses that her cultivation strategies are a piece in progress. However after her berries survived a chilly snap in December, she took her industrial heater, which had remained on standby at one nook of her greenhouse, and bought it.
Now, she’s working to achieve native recognition for her “unheated” strawberries. “It could be good,” she stated, “if we might simply make strawberries when it’s pure to.”

Science
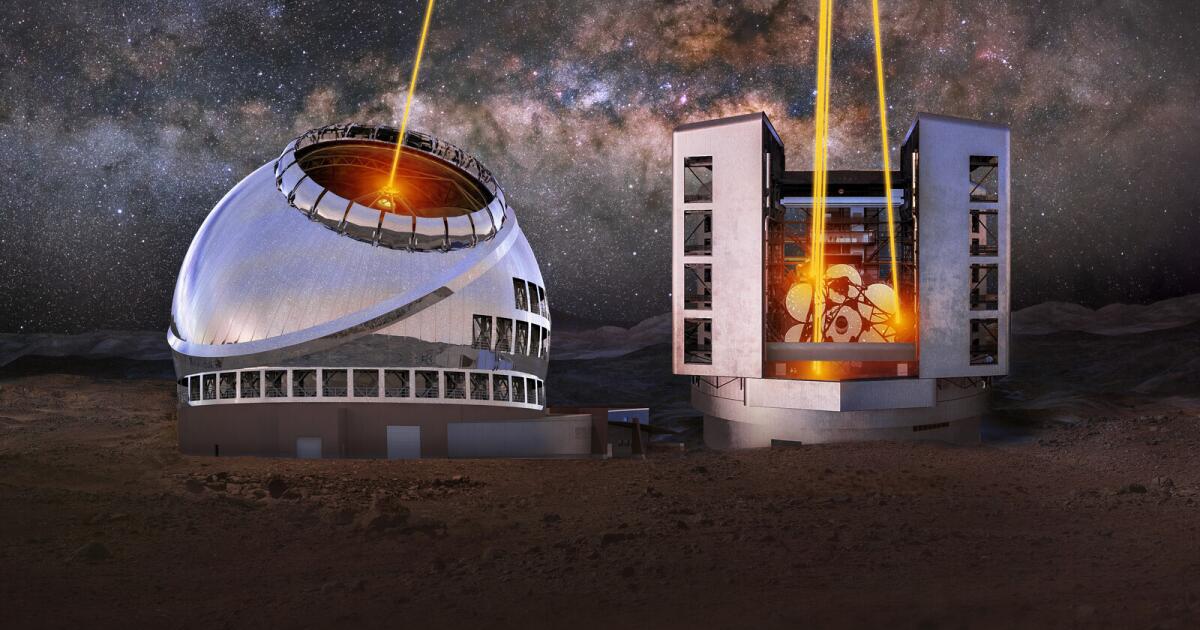
Opinion: America's 'big glass' dominance hangs on the fate of two powerful new telescopes
More than 100 years ago, astronomer George Ellery Hale brought our two Pasadena institutions together to build what was then the largest optical telescope in the world. The Mt. Wilson Observatory changed the conception of humankind’s place in the universe and revealed the mysteries of the heavens to generations of citizens and scientists alike. Ever since then, the United States has been at the forefront of “big glass.”
In fact, our institutions, Carnegie Science and Caltech, still help run some of the largest telescopes for visible-light astronomy ever built.
But that legacy is being threatened as the National Science Foundation, the federal agency that supports basic research in the U.S., considers whether to fund two giant telescope projects. What’s at stake is falling behind in astronomy and cosmology, potentially for half a century, and surrendering the scientific and technological agenda to Europe and China.
In 2021, the National Academy of Sciences released Astro2020. This report, a road map of national priorities, recommended funding the $2.5-billion Giant Magellan Telescope at the peak of Cerro Las Campanas in Chile and the $3.9-billion Thirty Meter Telescope at Mauna Kea in Hawaii. According to those plans, the telescopes would be up and running sometime in the 2030s.
NASA and the Department of Energy backed the plan. Still, the National Science Foundation’s governing board on Feb. 27 said it should limit its contribution to $1.6 billion, enough to move ahead with just one telescope. The NSF intends to present their process for making a final decision in early May, when it will also ask for an update on nongovernmental funding for the two telescopes. The ultimate arbiter is Congress, which sets the agency’s budget.
America has learned the hard way that falling behind in science and technology can be costly. Beginning in the 1970s, the U.S. ceded its powerful manufacturing base, once the nation’s pride, to Asia. Fast forward to 2022, the U.S. government marshaled a genuine effort toward rebuilding and restarting its factories — for advanced manufacturing, clean energy and more — with the Inflation Reduction Act, which is expected to cost more than $1 trillion.
President Biden also signed into law the $280-billion CHIPS and Science Act two years ago to revive domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors — which the U.S. used to dominate — and narrow the gap with China.
As of 2024, America is the unquestioned leader in astronomy, building powerful telescopes and making significant discoveries. A failure to step up now would cede our dominance in ways that would be difficult to remedy.
The National Science Foundation’s decision will be highly consequential. Europe, which is on the cusp of overtaking the U.S. in astronomy, is building the aptly named Extremely Large Telescope, and the United States hasn’t been invited to partner in the project. Russia aims to create a new space station and link up with China to build an automated nuclear reactor on the moon.
Although we welcome any sizable grant for new telescope projects, it’s crucial to understand that allocating funds sufficient for just one of the two planned telescopes won’t suffice. The Giant Magellan and the Thirty Meter telescopes are designed to work together to create capabilities far greater than the sum of their parts. They are complementary ground stations. The GMT would have an expansive view of the southern hemisphere heavens, and the TMT would do the same for the northern hemisphere.
The goal is “all-sky” observation, a wide-angle view into deep space. Europe’s Extremely Large Telescope won’t have that capability. Besides boosting America’s competitive edge in astronomy, the powerful dual telescopes, with full coverage of both hemispheres, would allow researchers to gain a better understanding of phenomena that come and go quickly, such as colliding black holes and the massive stellar explosions known as supernovas. They would put us on a path to explore Earth-like planets orbiting other suns and address the question: “Are we alone?”
Funding both the GMT and TMT is an investment in basic science research, the kind of fundamental work that typically has led to economic growth and innovation in our uniquely American ecosystem of scientists, investors and entrepreneurs.
Elon Musk’s SpaceX is the most recent example, but the synergy goes back decades. Basic science at the vaunted Bell Labs, in part supported by taxpayer contributions, was responsible for the transistor, the discovery of cosmic microwave background and establishing the basis of modern quantum computing. The internet, in large part, started as a military communications project during the Cold War.
Beyond its economic ripple effect, basic research in space and about the cosmos has played an outsized role in the imagination of Americans. In the 1960s, Dutch-born American astronomer Maarten Schmidt was the first scientist to identify a quasar, a star-like object that emits radio waves, a discovery that supported a new understanding of the creation of the universe: the Big Bang. The first picture of a black hole, seen with the Event Horizon Telescope, was front-page news in 2019.
We understand that competing in astronomy has only gotten more expensive, and there’s a need to concentrate on a limited number of critical projects. But what could get lost in the shuffle are the kind of ambitious projects that have made America the scientific envy of the world, inspiring new generations of researchers and attracting the best minds in math and science to our colleges and universities.
Do we really want to pay that price?
Eric D. Isaacs is the president of Carnegie Science, prime backer of the Giant Magellan Telescope. Thomas F. Rosenbaum is president of Caltech, key developer of the Thirty Meter Telescope.
Science
Mosquito season is upon us. So why are Southern California officials releasing more of them?
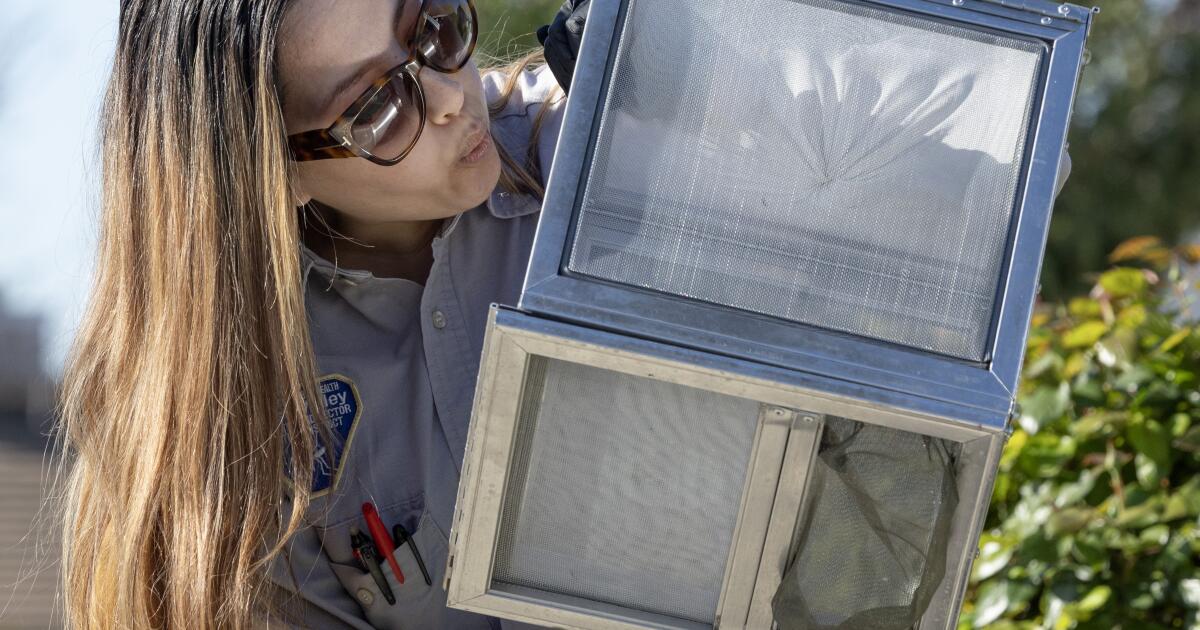

Jennifer Castellon shook, tapped and blew on a box to shoo out more than 1,000 mosquitoes in a quiet, upscale Inland Empire neighborhood.
The insects had a job to do, and the pest scientist wanted every last one out.
Aggressive and impactful reporting on climate change, the environment, health and science.
Their task? Find lady mosquitoes and mate.
But these were no ordinary mosquitoes. Technicians had zapped the insects, all males, with radiation in a nearby lab to make them sterile. If they achieve their amorous quest, there will be fewer baby mosquitoes than there would be if nature ran its course. That means fewer mouths to feed — mouths that thirst for human blood.
“I believe, fingers crossed, that we can drop the population size,” said Solomon Birhanie, scientific director for the West Valley Mosquito and Vector Control District, which released the mosquitoes in several San Bernardino County neighborhoods this month.
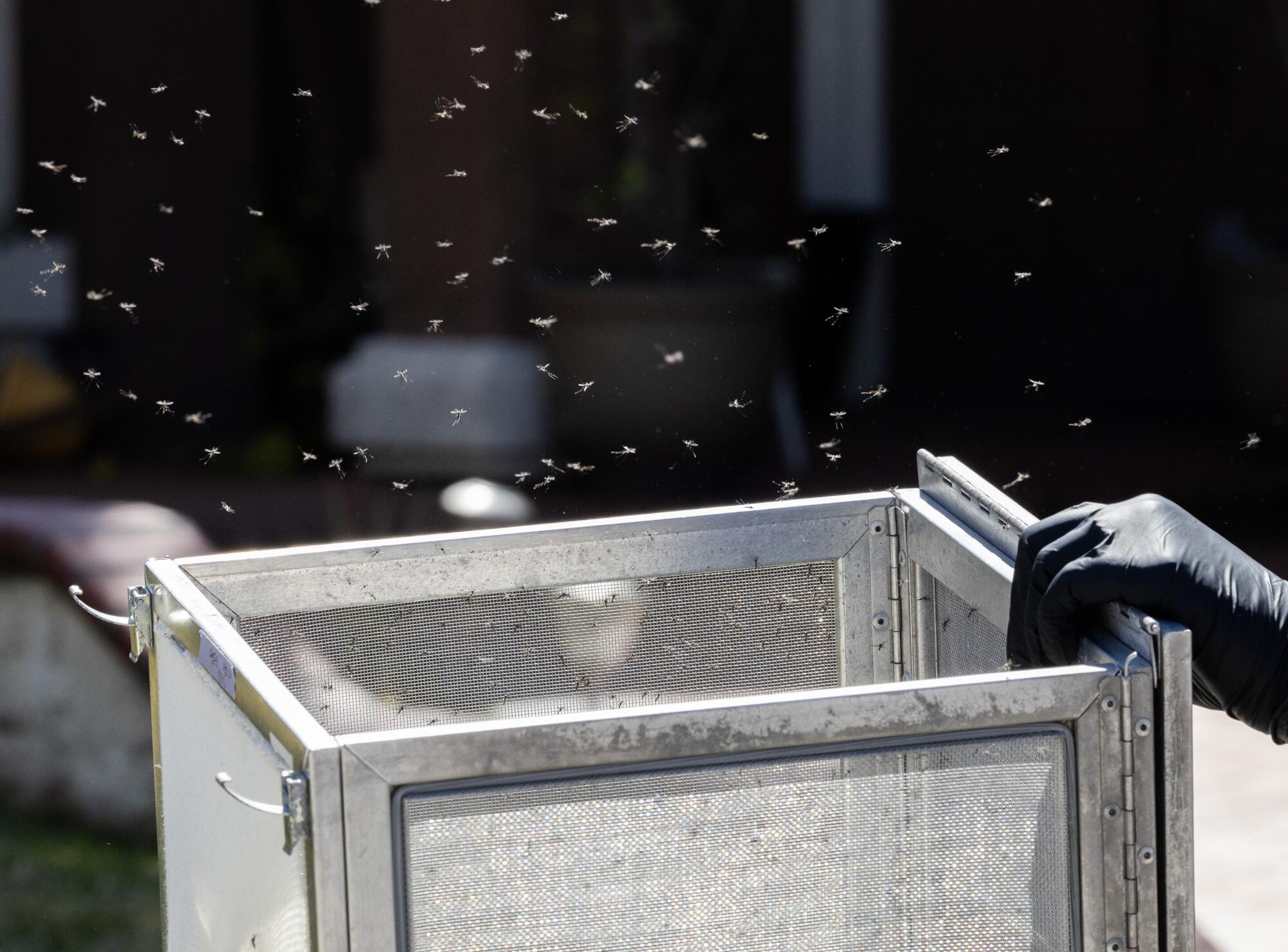

Sterilized male Aedes mosquitoes are released from a box in Rancho Cucamonga.
(Myung J. Chun / Los Angeles Times)
Controlling mosquitoes with mosquitoes
Mosquito control agencies in Southern California are desperate to tamp down an invasive mosquito — called Aedes aegypti — that has exploded in recent years. Itchy, unhappy residents are demanding it. And the mosquitoes known for fierce ankle biting aren’t just putting a damper on outdoor hangouts — they also spread disease.
The low-flying, day-biting mosquitoes can lay eggs in tiny water sources. A bottle cap is fair game. And they might lay a few, say, in a plant tray and others, perhaps, in a drain. Tackling the invaders isn’t easy when it can be hard to even locate all the reproduction spots. So public health agencies increasingly are trying to use the insects’ own biology against them by releasing sterilized males.
The West Valley district, which covers six cities in San Bernardino County, rolled out the first program of this kind in California last year. Now they’re expanding it. Next month, a vector district covering a large swath of Los Angeles County will launch its own pilot, followed by Orange County in the near future. Other districts are considering using the sterile insect technique, as the method is known, or watching early adopters closely.
On the plus side, it’s an approach that doesn’t rely on pesticides, which mosquitoes become resistant to, but it requires significant resources and triggers conspiracy theories.
“People are complaining that they can’t go into their backyard or barbecue in the summer,” Birhanie said at his Ontario lab. “So we needed something to strengthen our Aedes control.” Of particular concern is the Aedes aegypti, which love to bite people — often multiple times in rapid succession.
Releasing sterilized male insects to combat pests is a proven scientific technique, but using it to control invasive mosquitoes is relatively new.
Vector control experts often point to the success of a decades-long effort in California to fight Mediterranean fruit flies by dropping enormous quantities of sterile males from small planes. That program, run by the U.S. Department of Agriculture and the California Department of Food and Agriculture, costs about $16 million a year. That’s nearly four times West Valley’s annual budget.
So rather than try to tackle every nook and cranny of the district, encompassing roughly 650,000 residents, West Valley decided to use a more targeted approach. If a problem area reaches a certain threshold — over 50 mosquitoes counted in an overnight trap — it becomes a candidate.
1
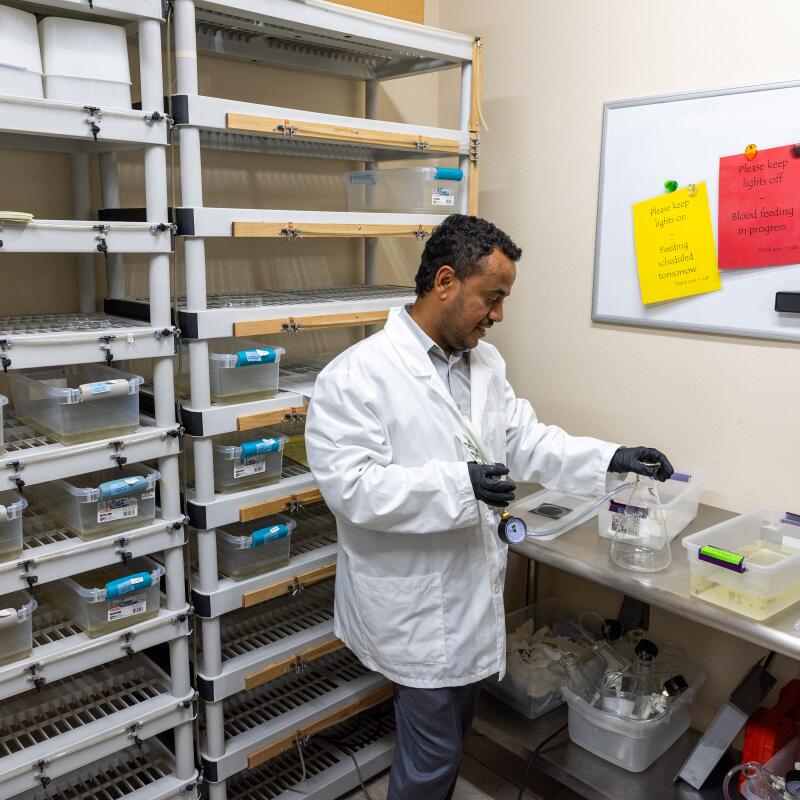

2

3

4
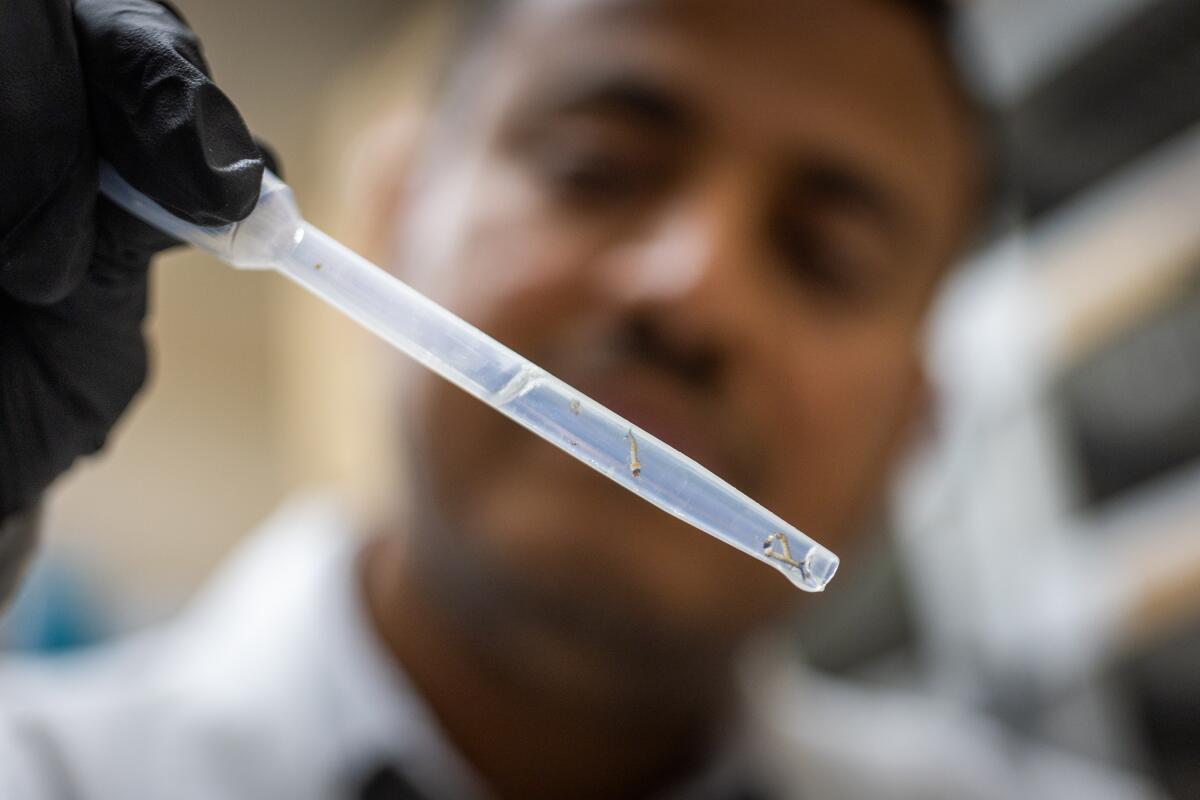
5
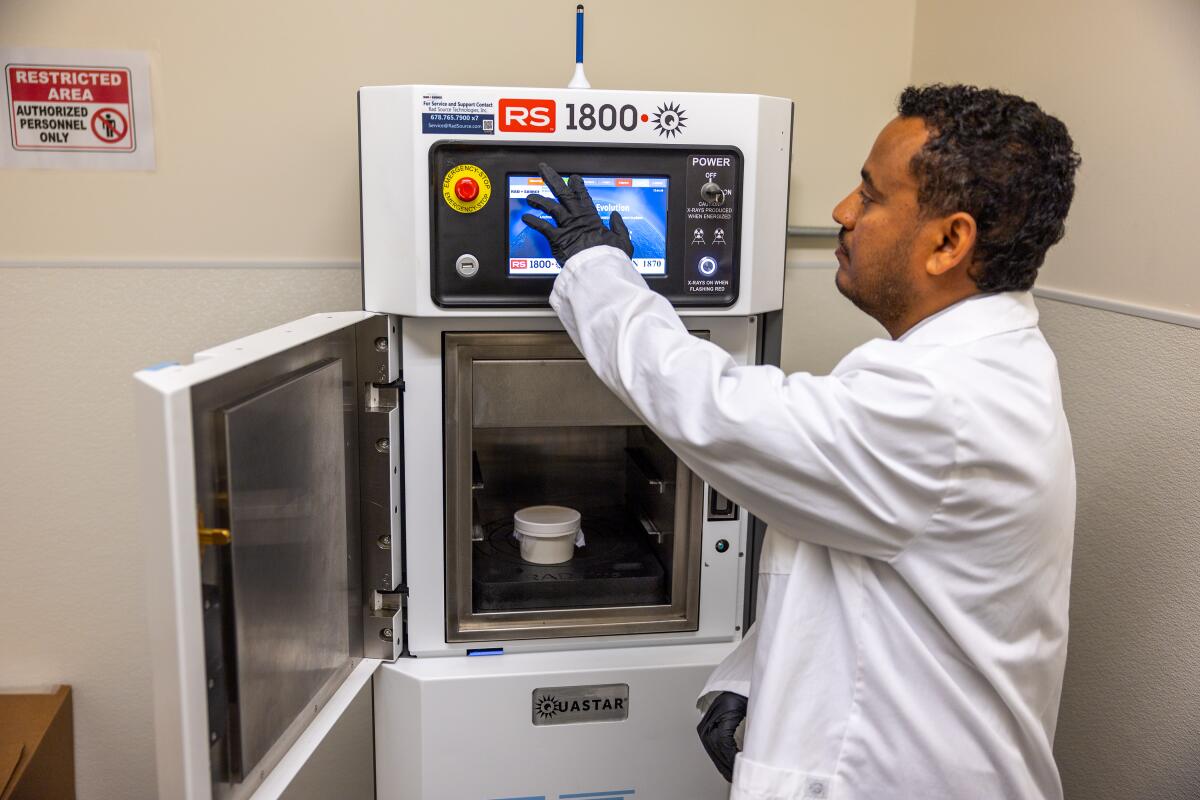

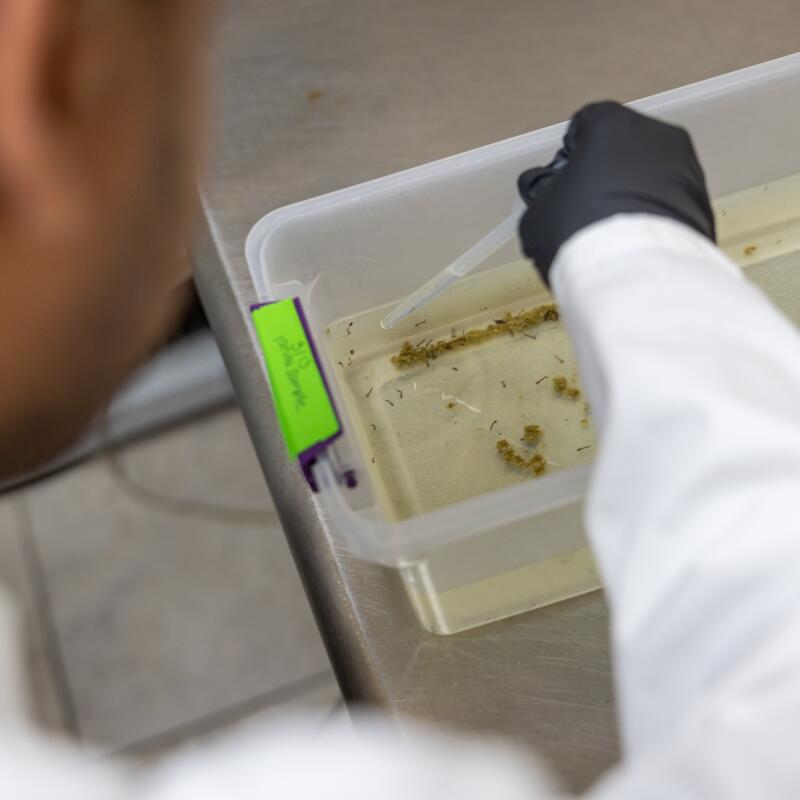
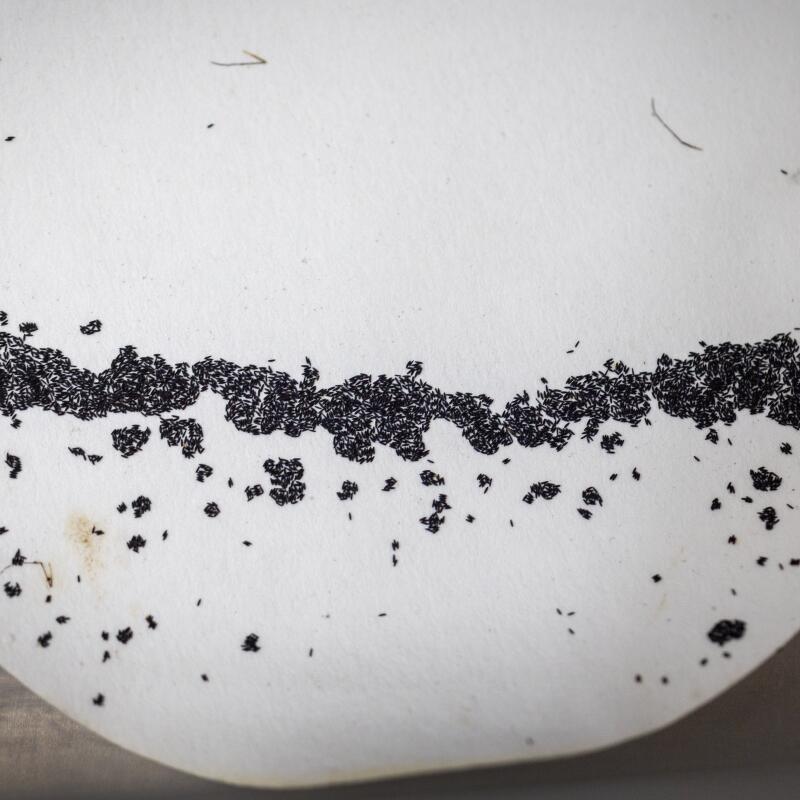
1. Solomon Birhanie inspects a container of mosquito larvae in the lab at the West Valley Mosquito and Vector Control District in Ontario. 2. Birhanie and his team raise mosquitoes in the lab, separating them by sex, because only the males, which don’t bite humans, will eventually be released. 3. Mosquito eggs in the West Valley lab. 4. The lab can grow about 10,000 mosquitoes at a time. 5. Before the male mosquitoes are released, an X-ray machine sterilizes them. If the zapped males mate with a female, her eggs won’t hatch. (Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times)
And it’s still a big lift. About 10,000 mosquitoes are reared at a time at West Valley’s facility, about half of which will be males. The males are separated out, packed into cups and placed into an X-ray machine that looks like a small refrigerator. The sterilizing process isn’t that different from microwaving a frozen dinner. Zap them on a particular setting for four to five minutes and they’re good to go.
Equipment purchased for the program costs roughly $200,000, said Brian Reisinger, spokesperson for the district. He said it was too early to pin down a cost estimate for the program, which is expanding.
Some districts serving more people are going bigger.
The Greater Los Angeles County Vector Control District plans to unleash up to 60,000 mosquitoes a week in two neighborhoods in Sunland-Tujunga from mid-May through November.
With the sterile-insect program, “the biggest hurdle we’re up against really is scalability,” said Susanne Kluh, general manager of the L.A. County district, which is responsible for nearly 6 million residents across 36 cities.
In part to save money, Kluh’s district has partnered with the Orange County Mosquito and Vector Control District. They’re sharing equipment and collaborating on studies, but L.A. County’s releases will move forward first, said Brian Brannon, spokesperson for the O.C. district. Orange County expects to release its “ankle biter fighters,” as Brannon called them, in Mission Viejo this fall or next spring.
So far, the L.A. County district has shelled out about $255,000 for its pilot, while O.C. has spent around $160,000. It’s a relatively small portion of their annual budgets: L.A. at nearly $25 million and O.C. at $17 million. But the area they’re targeting is modest.
Mosquito control experts tout sterilization for being environmentally friendly because it doesn’t involve spraying chemicals, and it may have a longer-lasting effectiveness than pesticides. It can also be done now. Other methods involving genetically modified mosquitoes and ones infected with bacteria are stuck in an approval process that spans federal and state agencies. One technique, involving the bacteria Wolbachia was recently approved by the Environmental Protection Agency and is now heading to the California Department of Pesticide Regulation to review, said Jeremy Wittie, general manager for the Coachella Valley Mosquito and Vector Control District.
“Using pesticides or insecticides, resistance crops up very quickly,” said Nathan Grubaugh, associate professor of epidemiology at the Yale School of Public Health.
Vector control experts hope the fact that the sterilization technique doesn’t involve genetic modification will tamp down conspiracy theories that have cropped up around mosquito releases. One erroneous claim is that a Bill Gates-backed effort to release mosquitoes was tied to malaria cases in Florida and Texas. Reputable outlets debunked the conspiracy theory, pointing out that Gates’ foundation didn’t fund the Florida project and that the type of mosquito released (Aedes) does not transmit malaria.
To get ahead of concerns, districts carrying out the releases say they’ve engaged in extensive outreach and education campaigns. Residents’ desire to rid themselves of a scourge may overcome any anxieties.
“I think if you have the choice of getting eaten alive by ankle biters or having a DayGlo male X-rayed mosquito come by looking for a female to not have babies with, you’d probably go for the latter,” Brannon said. (“DayGlo” is a riff on the fluorescent pigment product of the same name — the sterilized mosquitoes were dusted with bright colors to help identify them.)
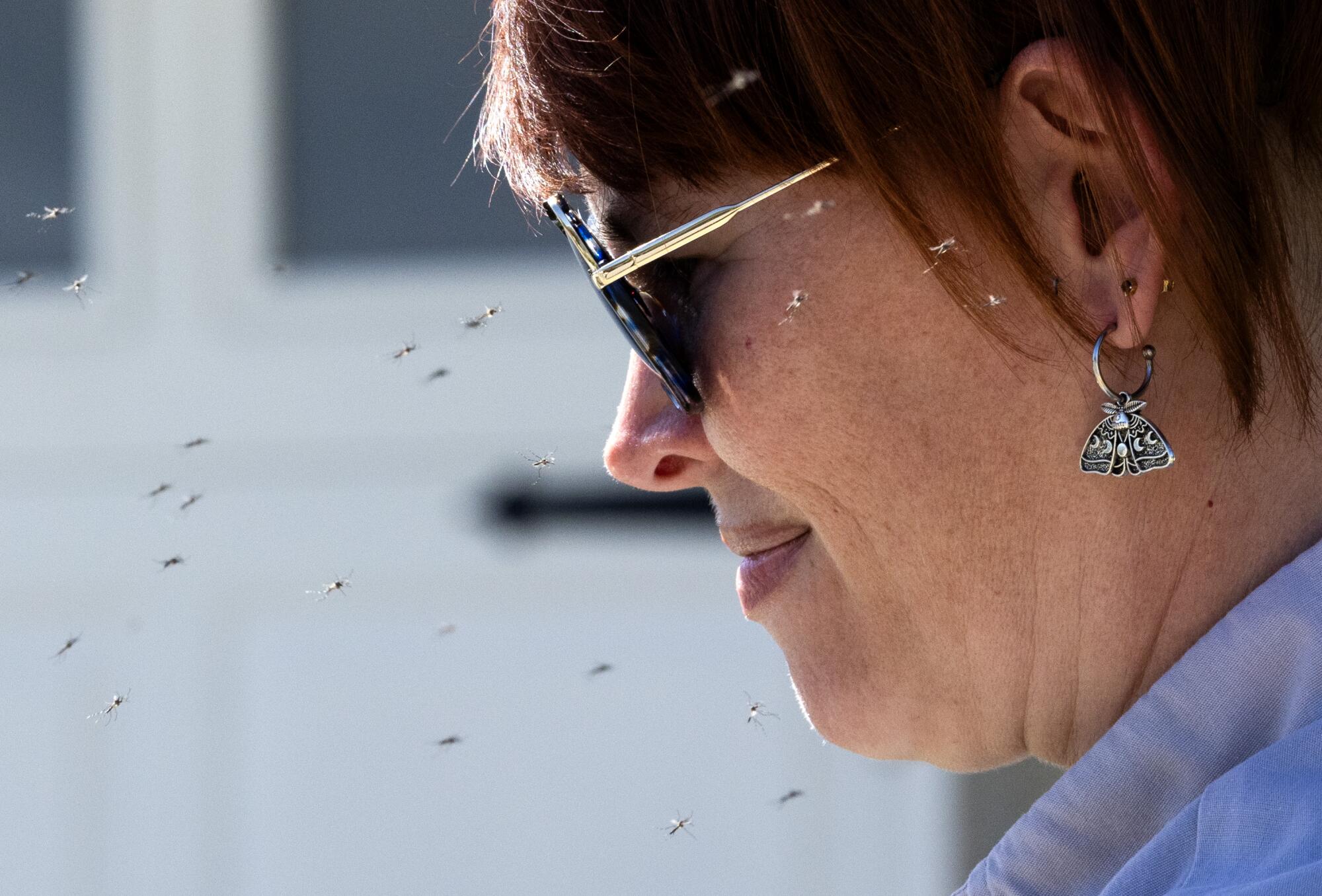

Sterilized male mosquitoes buzz around vector ecologist Jennifer Castellon as they are released in Rancho Cucamonga earlier this month.
(Myung J. Chun / Los Angeles Times)
Disease at our doorstep
As the climate warms and some regions become wetter, dengue is expanding to areas it’s never been seen before — and surging in areas where it’s established. Florida has seen alarming spikes in the viral infection in recent years, and Brazil and Puerto Rico are currently battling severe outbreaks. While most people infected with dengue have no symptoms, it can cause severe body aches and fever and, in rare cases, death. Its alias, “breakbone fever,” provides a grim glimpse into what it can feel like.
In October of last year, the city of Pasadena announced the Golden State’s first documented locally transmitted case of dengue, describing it as “extremely rare” in a news release. That same month, a second case was confirmed in Long Beach. Local transmission means the patient hadn’t traveled to a region where dengue is common; they may have been bitten by a mosquito carrying the disease in their own neighborhood.
Surging dengue abroad means there’s more opportunity for travelers to bring it home. However, Grubaugh said it doesn’t seem that California is imminently poised for a “Florida-like situation,” where there were nearly 1,000 cases in 2022, including 60 that were locally acquired. Southern California in particular lacks heavy rainfall that mosquitoes like, he said. But some vector experts believe more locally acquired cases are inevitable.
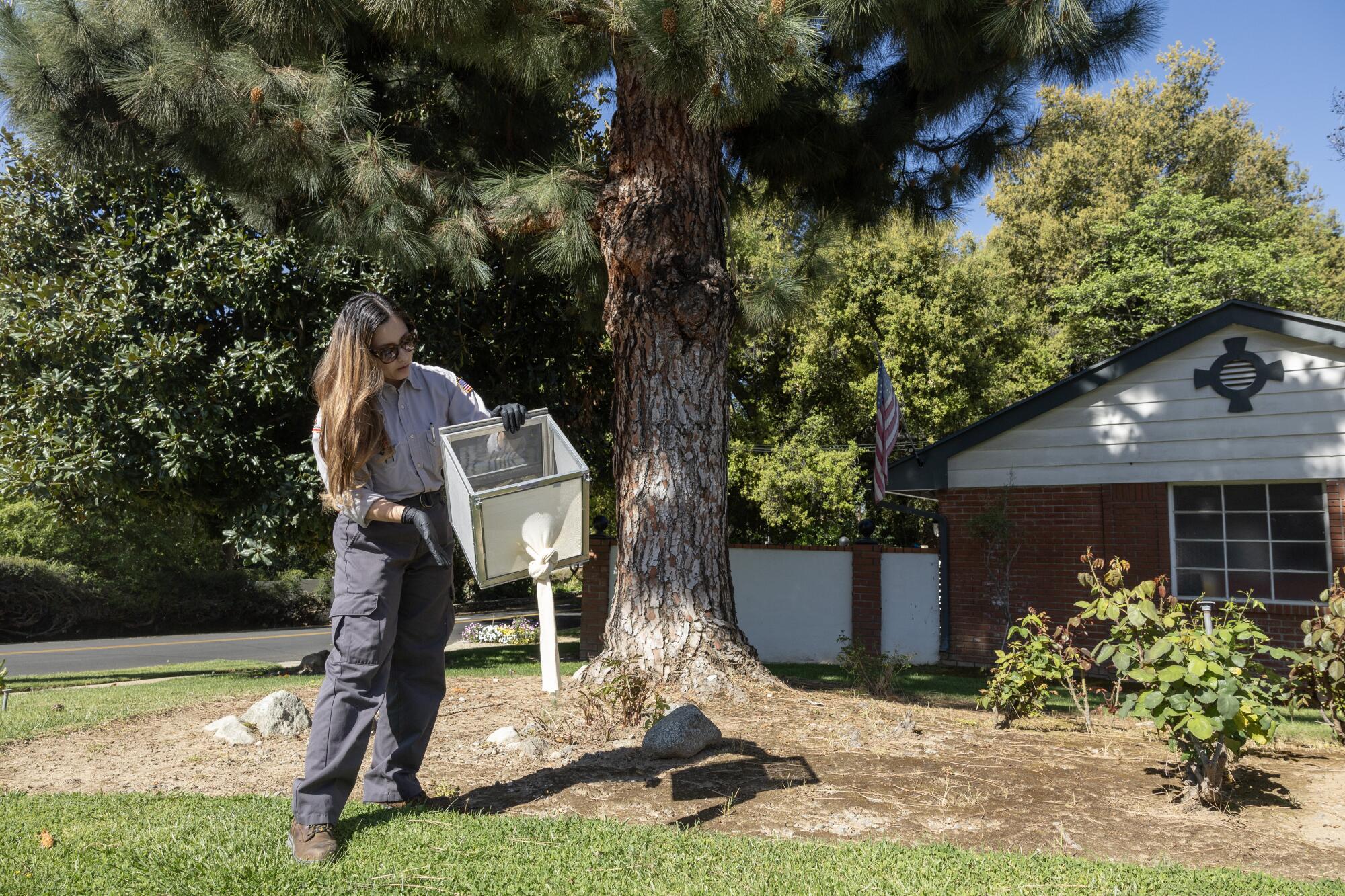

Ale Macias releases sterilized male mosquitoes in Upland this month.
(Myung J. Chun / Los Angeles Times)
Set them free
In mid-April, a caravan of staffers from the West Valley district traveled to five mosquito “hot spots” in Chino, Upland and Rancho Cucamonga — where data showed mosquito levels were particularly high — to release their first batches of sterilized male mosquitoes for the year. Peak Aedes season is months away, typically August to October in the district, and Birhanie said that’s the point. The goal is to force down the numbers to prevent an itchy tsunami later.
Males don’t bite, so the releases won’t lead to more inflamed welts. But residents might notice more insects in the air. Sterilized males released by West Valley will outnumber females in the wild by at least 100 to 1 to increase their chances of beating out unaltered males, spokeperson Reisinger said.
“They’re not going to be contributing to the biting pressure; they’re just going to be looking for love,” as Reisinger put it.
Eggs produced by a female after a romp with a sterile male don’t hatch. And female mosquitoes typically mate only once, meaning all her eggs are spoiled, so to speak. Vector experts say the process drives down the population over time.
Interestingly, the hot spots were fairly spread out across the district, indicative of the bloodsuckers’ widespread presence and adaptive nature. A picturesque foothills community in Upland was “especially interesting” because of its relatively high elevation, Birhanie said.
It was once inhabited primarily by another invasive mosquito that prefers colder, mountainous climates. Construction and deforestation in the area has literally paved the way for its humidity- and heat-loving brethren to move in.
Another neighborhood, in Rancho Cucamonga, posed a mystery. For the last two years, mosquito levels were consistently high. Door-to-door inspections, confoundingly, didn’t reveal the source.
“That’s one of the things about invasive Aedes mosquitoes — you can’t find them,” he said.
Next steps
Some vector control experts want to see a regional approach to sterile mosquito releases, similar to the state Medfly program.
Jason Farned, district manager for the San Gabriel Valley Mosquito and Vector Control District, believes a widespread effort “would be much more effective” and thinks that will come in time.
There are no talks underway to make it happen, and it’s not yet clear how it would work. Vector control agencies are set up to serve their local communities.
Fears of a bad mosquito year ahead are bubbling as the weather warms. Rain — which there was plenty of this spring — can quickly transform into real estate for mosquito reproduction.
When the swarms come, mosquito haters can take typical precautions: dump standing water and wear repellent. And they can root for the sterile males to get lucky.
Science
After months of silence, Voyager 1 has returned NASA's calls

For the last five months, it seemed very possible that a 46-year-old conversation had finally reached its end.
Since its launch from Kennedy Space Center on Sept. 5, 1977, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has diligently sent regular updates to Earth on the health of its systems and data collected from its onboard instruments.
But in November, the craft went quiet.
Voyager 1 is now some 15 billion miles away from Earth. Somewhere in the cold interstellar space between our sun and the closest stars, its flight data system stopped communicating with the part of the probe that allows it to send signals back to Earth. Engineers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in La Cañada Flintridge could tell that Voyager 1 was getting its messages, but nothing was coming back.
“We’re to the point where the hardware is starting to age,” said Linda Spilker, the project scientist for Voyager mission. “It’s like working on an antique car, from 15 billion miles away.”
Week after week, engineers sent troubleshooting commands to the spacecraft, each time patiently waiting the 45 hours it takes to get a response here on Earth — 22.5 hours traveling at the speed of light to reach the probe, and 22.5 hours back.
By March, the team had figured out that a memory chip that stored some of the flight data system’s software code had failed, turning the craft’s outgoing communications into gibberish.
A long-distance repair wasn’t possible. There wasn’t enough space anywhere in the system to shift the code in its entirety. So after manually reviewing the code line by line, engineers broke it up and tucked the pieces into the available slots of memory.
They sent a command to Voyager on Thursday. In the early morning hours Saturday, the team gathered around a conference table at JPL: laptops open, coffee and boxes of doughnuts in reach.
At 6:41 a.m., data from the craft showed up on their screens. The fix had worked.
“We went from very quiet and just waiting patiently to cheers and high-fives and big smiles and sighs of relief,” Spilker said. “I’m very happy to once again have a meaningful conversation with Voyager 1.”
Voyager 1 is one of two identical space probes. Voyager 2, launched two weeks before Voyager 1, is now about 13 billion miles from Earth, the two crafts’ trajectories having diverged somewhere around Saturn. (Voyager 2 continued its weekly communications uninterrupted during Voyager 1’s outage.)
They are the farthest-flung human-made objects in the universe, having traveled farther from their home planet than anything else this species has built. The task of keeping communications going grows harder with each passing day. Every 24 hours, Voyager 1 travels 912,000 miles farther away from us. As that distance grows, the signal becomes slower and weaker.
When the probe visited Jupiter in 1979, it was sending back data at a rate of 115.2 kilobits per second, Spilker said. Today, 45 years and more than 14 billion miles later, data comes back at a rate of 40 bits per second.
The team is cautiously optimistic that the probes will stay in contact for three more years, long enough to celebrate the mission’s 50th anniversary in 2027, Spilker said. They could conceivably last until the 2030s.
The conversation can’t last forever. Microscopic bits of silica keep clogging up the thrusters that keep the probes’ antennas pointed toward Earth, which could end communications. The power is running low. Eventually, the day will come when both Voyagers stop transmitting data to Earth, and the first part of their mission ends.
But on the day each craft goes quiet, they begin a new era, one that could potentially last far longer. Each probe is equipped with a metallic album cover containing a Golden Record, a gold-plated copper disk inscribed with sounds and images meant to describe the species that built the Voyagers and the planet they came from.
Erosion in space is negligible; the images could be readable for another billion years or more. Should any other intelligent life form encounter one of the Voyager probes and have a means of retrieving the data from the record, they will at the very least have a chance to figure out who sent them — even if our species is by that time long gone.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIf not Ursula, then who? Seven in the wings for Commission top job
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoFilm Review: Season of Terror (1969) by Koji Wakamatsu
-
 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: The American Society of Magical Negroes
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoGOP senators demand full trial in Mayorkas impeachment
-
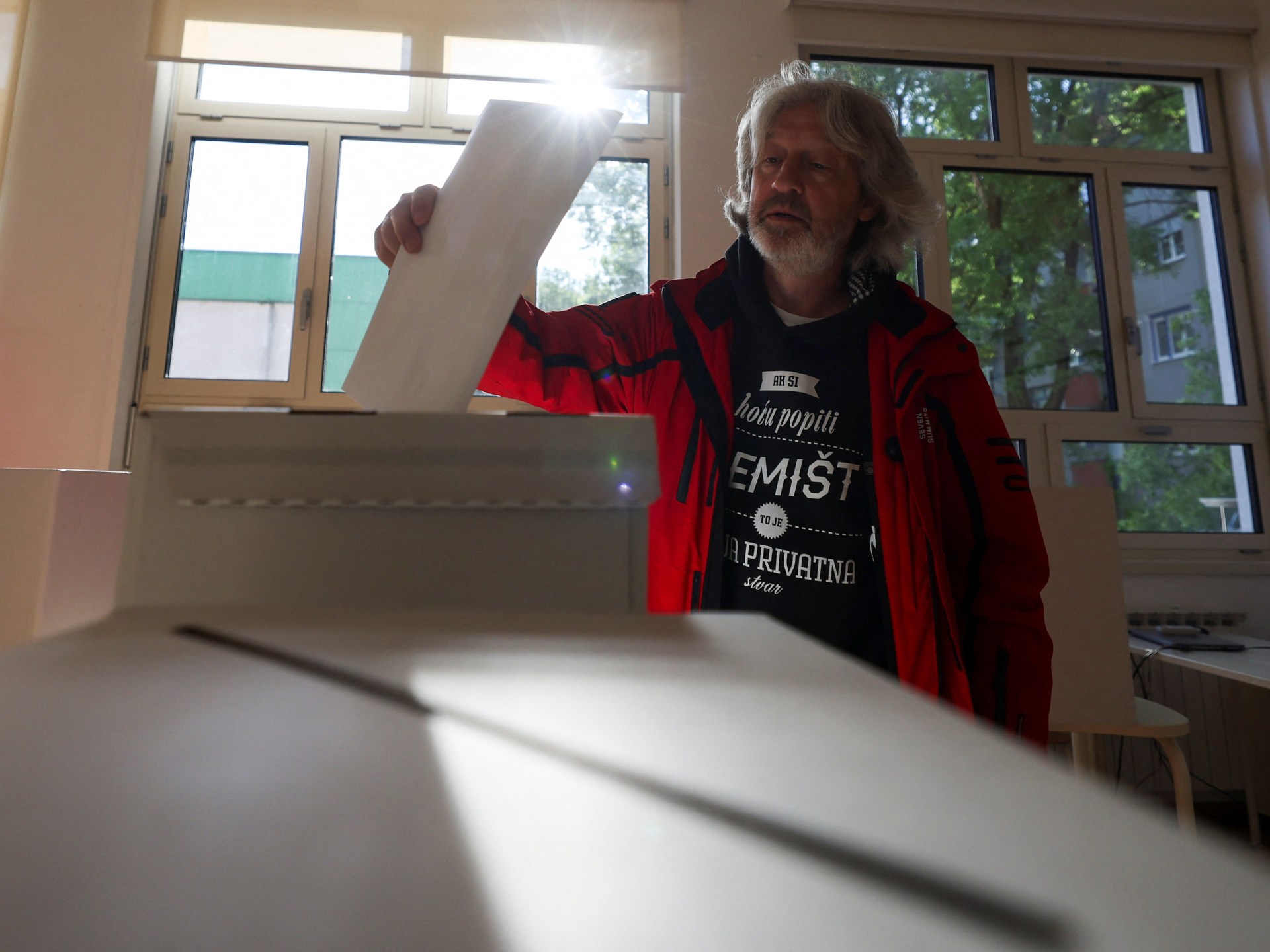

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCroatians vote in election pitting the PM against the country’s president
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoShort Film Review: For the Damaged Right Eye (1968) by Toshio Matsumoto
-
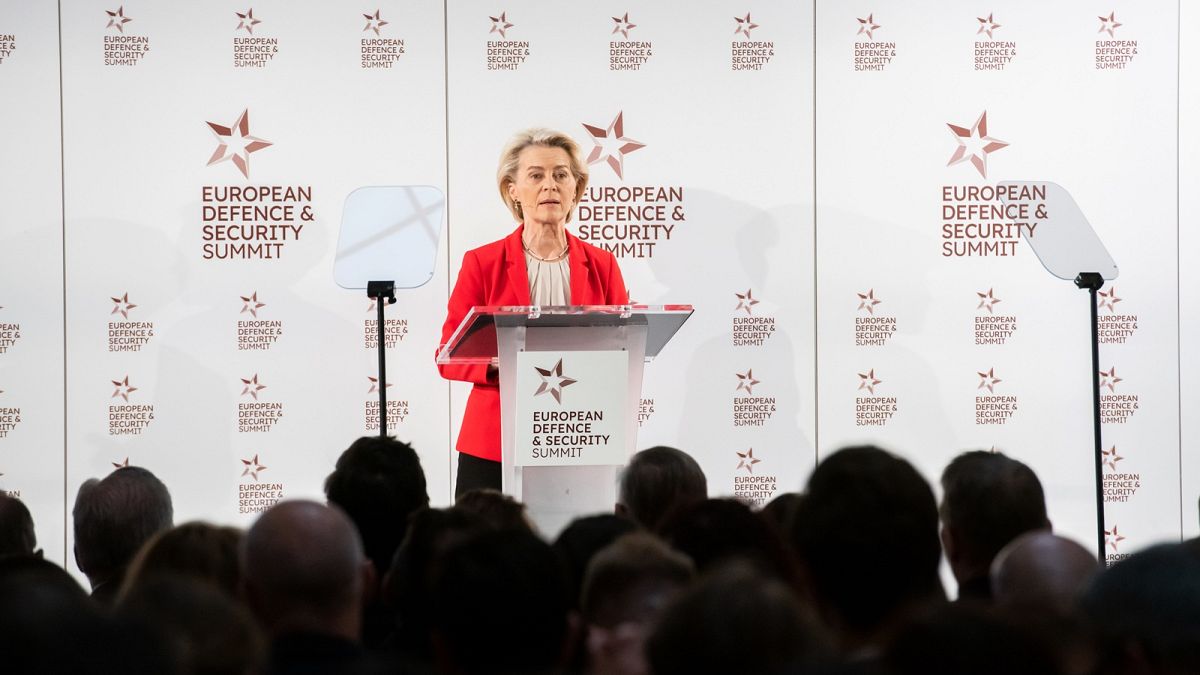

 World1 week ago
World1 week ago'You are a criminal!' Heckler blasts von der Leyen's stance on Israel
-
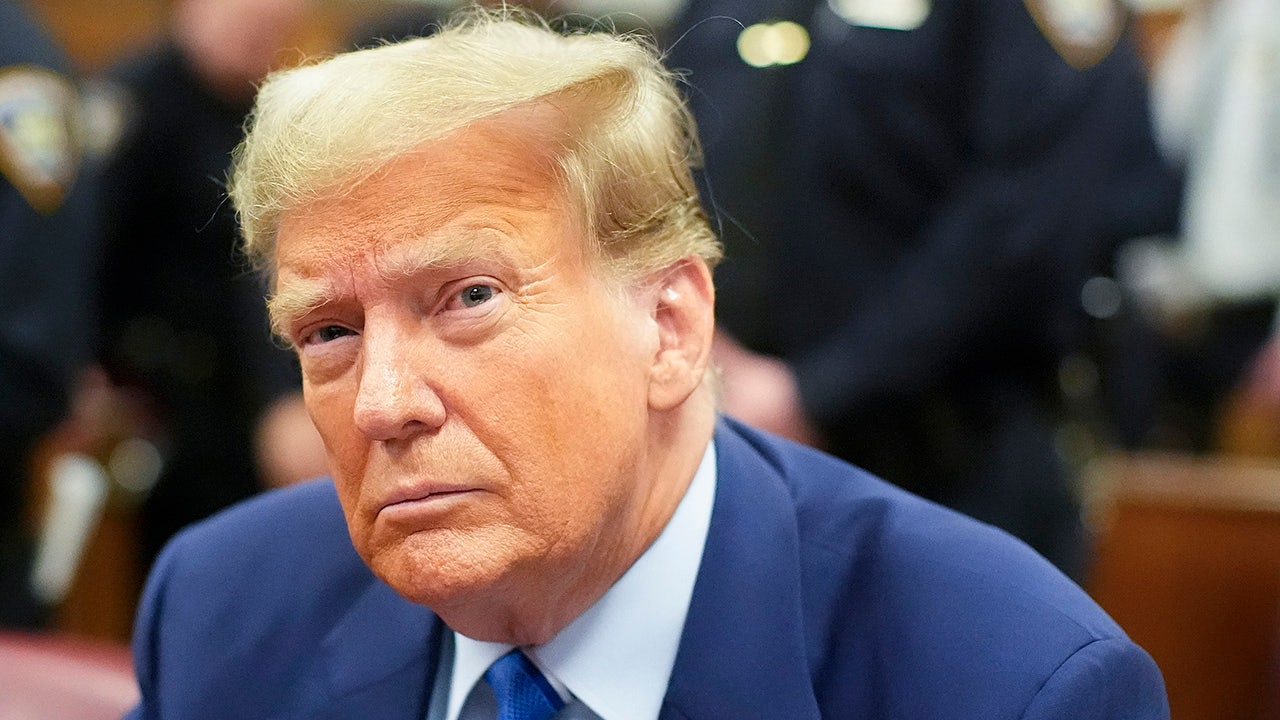

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTrump trial: Jury selection to resume in New York City for 3rd day in former president's trial