Science
Arctic Summer Could Be Practically Sea-Ice-Free by the 2030s

The first summer on record that melts practically all of the Arctic’s floating sea ice could occur as early as the 2030s, according to a new scientific study — about a decade sooner than researchers previously predicted.
The peer-reviewed findings, published Tuesday, also show that this milestone of climate change could materialize even if nations manage to curb greenhouse gas emissions more decisively than they are currently doing. Earlier projections had found that stronger action to slow global warming might be enough to preserve the summer ice. The latest research suggests that, where Arctic sea ice is concerned, only steep, sharp emissions cuts might be able to reverse the effects of the warming already underway.
“We are very quickly about to lose the Arctic summer sea-ice cover, basically independent of what we are doing,” said Dirk Notz, a climate scientist at the University of Hamburg in Germany and one of the new study’s five authors. “We’ve been waiting too long now to do something about climate change to still protect the remaining ice.”
As sea ice has dwindled in recent decades, communities, ecosystems and economies across the roof of the world have been grappling with the consequences. But the effects extend far beyond the region.
Sea ice reflects solar radiation back into space, so the less ice there is, the faster the Arctic warms. This causes the Greenland ice sheet to melt more quickly, adding to sea-level rise globally.
The temperature difference between the North Pole and the Equator also influences storm tracks and wind speed in the mid-latitudes, which means Arctic warming could be affecting weather events like extreme rainfall and heat waves in temperate parts of North America, Europe and Asia.
Over the past four decades, the far north has already been warming four times as quickly as the global average, a phenomenon that scientists call Arctic amplification.
“Our result suggests that the Arctic amplification will be coming faster and stronger,” said Seung-Ki Min, a climate scientist at Pohang University of Science and Technology in South Korea and another author of the new paper. “That means the related impacts will be also coming faster.”
Over the course of every year, the surface water of the Arctic Ocean freezes and melts with the seasons. The amount of ice grows in winter, peaks around March, then declines toward an annual minimum, typically in September.
The September lows have been edging downward ever since continuous satellite measurements began in 1979, leading researchers to try to predict when the ocean might experience its first summer that melts effectively all of the floating ice.
This doesn’t mean there would be zero ice on the water — icy patches are expected to remain in certain corners of the Arctic for some time to come. Instead, the threshold scientists use is 1 million square kilometers of ice, or about 386,000 square miles. This is less than 15 percent of the Arctic’s seasonal minimum ice cover in the late 1970s.
Looking at both satellite measurements of ice cover and computer models of the global climate, researchers have projected that the September ice will likely dip below this level for the first time before 2050. But the exact timing has been hard to predict, partly because the computer models generally underestimate the sea-ice declines that satellites have been detecting.
The authors of the latest study, which was published in the journal Nature Communications, accounted for this issue by first adjusting the climate models to align more closely with the satellite observations. They then used the adjusted models to project future sea-ice changes under four possible scenarios for greenhouse gas emissions in the coming decades.
Under three of these scenarios, representing moderate to high increases in emissions, the September ice falls below the critical threshold for the first time as early as the 2030s, about a decade earlier than previously estimated.
But the study also found roughly similar timing under the fourth scenario, in which humanity stops pumping additional heat-trapping gases into the atmosphere around 2070, something nations’ policies are not on course to achieve. Earlier research had suggested that September might stay abundantly icy in this scenario.
The Arctic Ocean’s first unfrozen September, if and when it arrives, will be an important scientific benchmark, but it won’t be some kind of turning point, said Mark C. Serreze, the director of the National Snow and Ice Data Center at the University of Colorado Boulder. The Arctic started transforming into a bluer ocean decades ago, setting off vast changes to polar bear populations, shipping routes, access to natural resources and geopolitics.
“It’s already happening,” said Dr. Serreze, who was not involved in the new research. “And as the Arctic continues to lose its ice, those impacts will grow and grow and grow.”

Science
After months of silence, Voyager 1 has returned NASA's calls

For the last five months, it seemed very possible that a 46-year-old conversation had finally reached its end.
Since its launch from Kennedy Space Center on Sept. 5, 1977, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has diligently sent regular updates to Earth on the health of its systems and data collected from its onboard instruments.
But in November, the craft went quiet.
Voyager 1 is now some 15 billion miles away from Earth. Somewhere in the cold interstellar space between our sun and the closest stars, its flight data system stopped communicating with the part of the probe that allows it to send signals back to Earth. Engineers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in La Cañada Flintridge could tell that Voyager 1 was getting its messages, but nothing was coming back.
“We’re to the point where the hardware is starting to age,” said Linda Spilker, the project scientist for Voyager mission. “It’s like working on an antique car, from 15 billion miles away.”
Week after week, engineers sent troubleshooting commands to the spacecraft, each time patiently waiting the 45 hours it takes to get a response here on Earth — 22.5 hours traveling at the speed of light to reach the probe, and 22.5 hours back.
By March, the team had figured out that a memory chip that stored some of the flight data system’s software code had failed, turning the craft’s outgoing communications into gibberish.
A long-distance repair wasn’t possible. There wasn’t enough space anywhere in the system to shift the code in its entirety. So after manually reviewing the code line by line, engineers broke it up and tucked the pieces into the available slots of memory.
They sent a command to Voyager on Thursday. In the early morning hours Saturday, the team gathered around a conference table at JPL: laptops open, coffee and boxes of doughnuts in reach.
At 6:41 a.m., data from the craft showed up on their screens. The fix had worked.
“We went from very quiet and just waiting patiently to cheers and high-fives and big smiles and sighs of relief,” Spilker said. “I’m very happy to once again have a meaningful conversation with Voyager 1.”
Voyager 1 is one of two identical space probes. Voyager 2, launched two weeks before Voyager 1, is now about 13 billion miles from Earth, the two crafts’ trajectories having diverged somewhere around Saturn. (Voyager 2 continued its weekly communications uninterrupted during Voyager 1’s outage.)
They are the farthest-flung human-made objects in the universe, having traveled farther from their home planet than anything else this species has built. The task of keeping communications going grows harder with each passing day. Every 24 hours, Voyager 1 travels 912,000 miles farther away from us. As that distance grows, the signal becomes slower and weaker.
When the probe visited Jupiter in 1979, it was sending back data at a rate of 115.2 kilobits per second, Spilker said. Today, 45 years and more than 14 billion miles later, data comes back at a rate of 40 bits per second.
The team is cautiously optimistic that the probes will stay in contact for three more years, long enough to celebrate the mission’s 50th anniversary in 2027, Spilker said. They could conceivably last until the 2030s.
The conversation can’t last forever. Microscopic bits of silica keep clogging up the thrusters that keep the probes’ antennas pointed toward Earth, which could end communications. The power is running low. Eventually, the day will come when both Voyagers stop transmitting data to Earth, and the first part of their mission ends.
But on the day each craft goes quiet, they begin a new era, one that could potentially last far longer. Each probe is equipped with a metallic album cover containing a Golden Record, a gold-plated copper disk inscribed with sounds and images meant to describe the species that built the Voyagers and the planet they came from.
Erosion in space is negligible; the images could be readable for another billion years or more. Should any other intelligent life form encounter one of the Voyager probes and have a means of retrieving the data from the record, they will at the very least have a chance to figure out who sent them — even if our species is by that time long gone.
Science
How L.A. County is trying to remake addiction treatment — no more 'business as usual'

Gary Horejsi wrestled with the decision before him, knowing a life could be in his hands.
It was the third time that the woman had used drugs or alcohol since coming to CRI-Help, which runs a 135-bed residential facility in North Hollywood where people are treated for substance use disorder.
CRI-Help needed to be a safe place for people grappling with their addictions. In the past, others had been removed for less. Horejsi, the clinical director, had the final say on whether she should be discharged.
He perused her file on his computer. The woman was still trying, CRI-Help staffers told him. She hadn’t shared drugs with anyone. And if she were to leave, the risks of an overdose were graver than before.
Horejsi decided to let her stay.
“Things can’t be business as usual anymore,” their chief executive, Brandon Fernandez, later said at a CRI-Help staff meeting. If someone leaves treatment and resumes using drugs the same way they were before, “that could very well look like them dying.”
“So are we going to be willing to do something different?”
“Things can’t be business as usual anymore,” CRI-Help Chief Executive Brandon Fernandez told his staff at a meeting in North Hollywood on April 10.
(Myung J. Chun / Los Angeles Times)
Fernandez had gathered CRI-Help staff in their North Hollywood conference room to talk about a Los Angeles County initiative that could reshape such decisions. It’s called Reaching the 95% — or R95 — and its goal is to engage with more people than the fraction of Angelenos already getting addiction treatment.
Across the country, more than 48 million people had a drug or alcohol use disorder, according to the latest results from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health. Only 13 million received treatment in the previous year. Among those who did not get treatment, roughly 95% said they did not think that they should.
Those numbers have collided with the grim toll of fentanyl, an especially potent opioid that has driven up deaths across the country. In Los Angeles County, the number of overdose deaths tied to fentanyl skyrocketed between 2016 and 2022, soaring from 109 to 1,910, according to a county report.
“We can’t just take the approach that we’ve been taking and kind of assume that everyone wants the services that we offer,” said Dr. Gary Tsai, director of the Substance Abuse Prevention and Control division at the L.A. County Department of Public Health. “That’s just not the reality.”
His department is trying to nudge addiction treatment facilities to change their approach, by offering financial incentives for those that meet R95 requirements. Among them: changing their rules to not automatically eject people who have a “lapse” of drug use.
Fernandez, whose organization is participating in R95, said abstinence is still its aspirational goal — and “we still have the ability to use our own clinical judgment on a case-by-case basis,” such as if people endanger other participants. But “we shouldn’t have blanket policies.”
To get R95 funding, they also cannot require people to be totally abstinent before being admitted. And under R95, treatment programs are also being encouraged to partner with syringe programs rooted in “harm reduction” — a philosophy focused on minimizing the harmful effects of drug use — to address the needs of people who may not want to enter or remain in treatment.
Some treatment providers “view us as the enemy instead of as allies,” said Soma Snakeoil, executive director of the Sidewalk Project, which provides Narcan spray to reverse overdoses and other services on L.A.’s Skid Row.
With R95, she said, “the biggest change is that harm reduction organizations and treatment providers are talking to each other in a way that was not happening before.”

Soma Snakeoil, executive director of the Sidewalk Project, gives first aid to a woman with an open wound on her foot last year in Los Angeles.
(Francine Orr / Los Angeles Times)
The county is also prodding addiction treatment facilities to reexamine whether the way they operate could be turning people away, and look more closely at the “customer experience.” Tsai compared the situation to a restaurant drawing few customers: “How do we get more people in the door?”
Too often, “the drug dealers do a much better job of delivering their product to our patients than we do,” said Dr. Randolph Holmes, chair of government affairs for the California Society of Addiction Medicine.
When Johnny Guerrero decided to get off Skid Row and go into residential treatment in Los Angeles, he was initially turned away because he had arrived “late — maybe 10 minutes late,” the 35-year-old said.
He was only able to get in, he said, because the harm reduction worker who had taken him to the facility let him stay the night at her home, then brought him back the next morning. Even then, “there was so much paperwork. I was so dopesick. There was just hurdle after hurdle after hurdle.”
“They did not make it easy for an addict to get help,” Guerrero said.
In many cases, “the biggest barrier is just being able to get somebody on the phone” with a treatment provider, said Amanda Cowan, executive director of Community Health Project LA, which provides clean syringes and other services to people who use drugs. “When people are ready, they are ready in that moment.”
As of late March, roughly half of the addiction treatment providers that contract with L.A. County were on track to become “R95 Champions,” which could yield hundreds of thousands of dollars each in additional funding.

CRI-Help’s George T. Pfleger center in North Hollywood.
(Myung J. Chun / Los Angeles Times)
To get those funds, they must turn in admissions and discharge policies that adhere to the R95 guidelines, as well as an “engagement policy.” They are also supposed to meet R95 requirements in one other area of their choice, which could include a “customer walkthrough” to see what might turn away clients.
CRI-Help, for instance, had decided to change how it asks newcomers to undergo a search. “The last thing we want to do is trigger someone’s trauma history and potentially have them walk out the door,” Fernandez said.
To ensure it was consistently done with sensitivity, CRI-Help drew up a script for staffers, emphasizing that consenting to a search would help maintain a safe facility. The hope is that “they feel they’re doing something as a part of a community — versus being forced to undergo something that’s uncomfortable.”
Staffers also tell them that if they have any drugs to hand over, “there’s not going to be any consequence, you can still come into treatment,” Fernandez said. “And if we find them on you, there still won’t be any negative consequences.”
The L.A. County push comes as state and federal officials have stressed the need for “low barrier” approaches to addiction care. Even cutting back on drug use can have positive results, researchers have found.
But some of the changes can be at odds with long-standing beliefs among treatment providers, many of whom got into the field after successfully battling their own addictions in programs firmly focused on abstinence.
Many in the field think “this is what works” because it did work for them, said Vitka Eisen, chief executive of HealthRight 360, another R95 participant. But “we’re the survivors, and we don’t talk to those who didn’t survive.”
Addiction researchers have long called to reexamine how people are treated for substance use disorders. More than a decade ago, a Columbia University center found that “much of what passes for ‘treatment’ of addiction bears little resemblance to the treatment of other health conditions.”
“This is inexcusable given decades of accumulated scientific evidence attesting to the fact that addiction is a brain disease,” the National Center on Addiction and Substance Abuse lamented in its report.
Experts argue that part of the problem is that addiction treatment has long been separated from the rest of the healthcare system. Richard Rawson, senior advisor to UCLA Integrated Substance Abuse Programs, said a major shift was the emergence of buprenorphine, a medication for opioid addiction that could be prescribed in ordinary clinics just like medicines for other chronic conditions.
But some Southern California treatment providers have viewed using buprenorphine and other such medications as short of sobriety, UC San Diego researchers found — even as California has ushered in requirements for licensed treatment facilities to either offer or help people access such medications.
Addiction is now much more widely understood as a medical condition, but “how much of that philosophy actually gets down to the level of the counselor?” Rawson said. “I think that’s still a work in progress.”
Tsai said a challenge in rolling out R95 is the ingrained idea that “you’re ready or not” for substance use treatment. But “we don’t actually treat any other health condition that way,” he said. “You don’t tell someone with diabetes, ‘Your blood sugar has to be completely under control, and then you’ll be ready for treatment.’”
In North Hollywood, counselors and other CRI-Help employees seated around the conference table studied the R95 goals printed on an L.A. County handout. One staffer said she was struggling with a specific statement, particularly for people in a residential setting: “Requiring abstinence is too high of a bar” for treatment.
Fernandez decided to share his own story. More than a decade ago, he was struggling with drug use, which had worsened after the death of his father. He was unemployed and didn’t have a stable place to live. When an outpatient counselor suggested residential treatment, he initially brushed off the suggestion.

CRI-Help’s staffers had questions and concerns about the changing approach to addiction treatment but ultimately seemed supportive.
(Myung J. Chun / Los Angeles Times)
He changed his mind after a “tough weekend,” but had no intention of abstaining from all drugs in the long term. Fernandez said he was nonetheless welcomed at CRI-Help: “Let’s just help you out for now.”
“I came here begrudgingly with a total attitude that I was going to continue smoking weed when I left treatment. I definitely wasn’t going to stop drinking,” even as he recognized that other things he was doing might be a problem, Fernandez told the CRI-Help employees.
Among those who had gone to treatment, he asked the group, “were you ready for total abstinence on Day One?”
“No. That wasn’t even my plan,” the same staffer replied with a rueful laugh.
Still, she and others were anxious about how they would keep everyone safe if clients used drugs, especially if they tried to bring them into the facility. “That worries me a little bit,” she said.
“It worries me too,” Fernandez said.
What preoccupies CRI-Help staff is how to balance the needs of people who have had a “lapse” into drug use with maintaining a safe environment for other clients grappling with addiction.
Horejsi said in an interview that whenever someone uses — even if they don’t share their drugs — “everyone knows, and that in itself does have an effect on people. Sometimes people will feel less safe.”
But Horejsi stressed to the group that “we’re already not discharging people for using” alone.
When people have relapsed, the North Hollywood center has monitored them one-on-one in its television room until staff are sure they are safe, then decided on their next steps. Some have ultimately been moved to another CRI-Help residential facility to continue getting treatment and have a “fresh start,” he said.
The clinical director also urged his co-workers to look back at the many changes CRI-Help had already undergone, such as starting to offer medication for addiction treatment. He reminded them that years ago, CRI-Help clients could be discharged if a doctor had given them an opioid pill at the hospital.

Mary Grayson, a longtime staff member at CRI-Help, spoke positively of the organizations changes over the years.
(Myung J. Chun / Los Angeles Times)
“What about when we discharged people because they talked about getting — they glorified drugs?” said Mary Grayson, a longtime CRI-Help employee.
Leaning forward in her seat, Grayson reminded her co-workers that “CRI-Help is not what it was when I walked through those doors 25 years ago — thank God!”
It started with “two shacks on this property. Two raggedy shacks. And look at where we are now,” she said. “Without us changing and growing, we won’t be able to be who we are.”
Science
FDA approves bladder cancer treatment by Culver City company

The Food and Drug Administration on Monday approved a new treatment for a type of bladder cancer.
The treatment, which will be sold under the brand name Anktiva, is intended for some patients suffering from certain types of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer, according to an FDA statement announcing the approval.
News of the FDA action was first reported by Reuters, which said, “The therapy works by activating types of disease fighting white blood cells called natural killer (NK) cells and T-cells to create long-term immunity in the body.”
The drug is now being developed by ImmunityBio of Culver City after its initial development by Altor BioScience of Miramar, Fla.
Dr. Patrick Soon-Shiong, whose family owns the Los Angeles Times, is executive chairman of ImmunityBio.
In a statement, Soon-Shiong heralded the FDA action and called Anktiva “a next-generation immunotherapy.”
The FDA approval was based on the results of a clinical trial led by Dr. Karim Chamie, an associate professor of urology at UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine. In a statement released by UCLA Health, Chamie said the treatment offers “a compelling alternative for patients who have exhausted conventional treatment options.”
Anktiva is intended for bladder cancer patients who did not respond to prior treatments, the FDA said. It is delivered via a catheter and prompts the patient’s own immune system “to mount a targeted attack against cancer cells,” Chamie said.
He noted that the treatment could spare some patients from invasive procedures, such as surgery to remove all or part of the bladder.
Most of the new bladder cancer diagnoses are non-muscle invasive — cancer found in the tissue that lines the inner surface of the bladder and hasn’t spread into the bladder wall, according to the UCLA statement. Patients with this type of cancer usually undergo surgery and a bacteria-based immunotherapy, which is placed directly into the bladder.
However, even with this treatment, the cancer can come back, and many patients don’t respond well to further treatment, leaving some patients with limited options.
Last May, according to Reuters, the FDA declined to approve the new therapy “due to deficiencies in the company’s application.” The FDA cited problems in its inspections and offered the firm suggestions for how to resolve the manufacturing issues that were raised, according to the wire service.
-

 World6 days ago
World6 days agoIf not Ursula, then who? Seven in the wings for Commission top job
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNine questions about the Trump trial, answered
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoHungary won't rule out using veto during EU Council presidency
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoFilm Review: Season of Terror (1969) by Koji Wakamatsu
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCroatians vote in election pitting the PM against the country’s president
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoGroup of EU states should recognise Palestine together, Michel says
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoTrump trial: Jury selection to resume in New York City for 3rd day in former president's trial
-
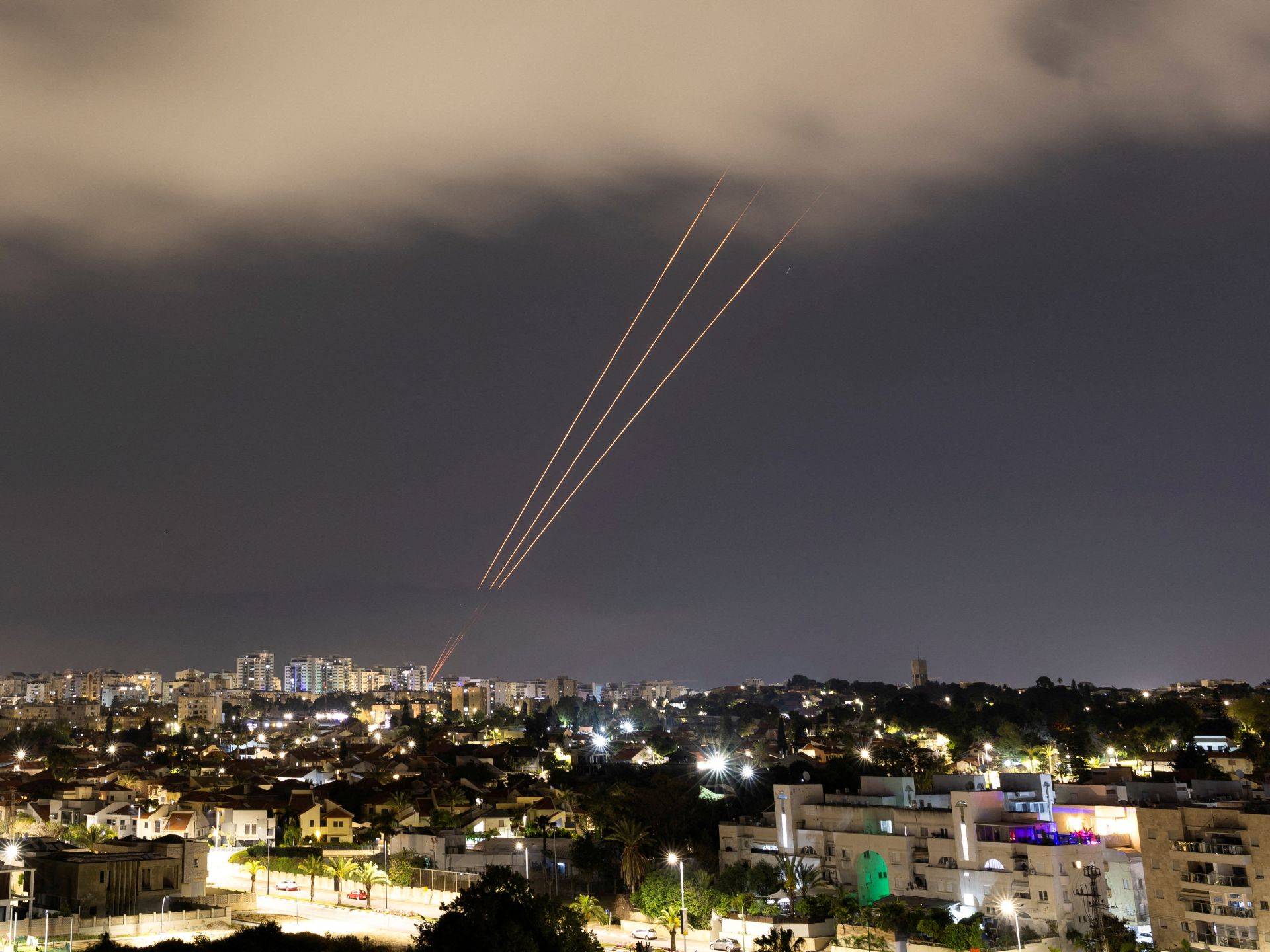

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoThe Take: How Iran’s attack on Israel unfolded