Health
When He Stood Up Quickly, He Sometimes Fainted. What Was It?

Years earlier than, the affected person had fallen within the bathtub, damaged his ribs and punctured a lung. Blood crammed his chest and collapsed the lung. He needed to be rushed to the hospital. Sufferers who’re caught in mattress whereas within the hospital are liable to creating blood clots within the veins of their legs as a result of they’re immobilized. Clots kind when blood isn’t shifting. These sufferers are often began on blood thinners to scale back that threat. As a result of this man had bled into his chest, blood thinners weren’t a great possibility for him. Clots that kind due to immobility block veins and trigger swelling and ache, however they may also be lethal in the event that they journey by the physique and find yourself within the lungs or mind. So his docs had chosen to place a filter in the principle vein that introduced blood from his legs again to his coronary heart — a vessel referred to as the inferior vena cava — to catch any clots that shaped and broke free.
These filters are presupposed to be eliminated a number of months later when the danger of clotting goes down, however many should not eliminated on schedule. This one had been left in place for greater than 15 years. What if, Slief urged after explaining this historical past, the filter had executed its job and captured clots and so they have been now blocking all the vessel? May that trigger his positional hypotension? Centor listened thoughtfully. He’d been a health care provider for 45 years and had by no means seen this. And but it was an fascinating concept. Definitely value contemplating.
One of many many benefits of the V.A. Hospital system is that it has computerized medical information going again a long time. Slief did a deep dive into this man’s medical historical past and hit what seemed like some promising outcomes. Seven years earlier, the person had a CT scan that confirmed an virtually whole blockage of his vena cava. Was it potential that the additional blood that was presupposed to go from the legs to the mind when the person stood up didn’t get there quick sufficient due to the narrowed vena cava?
The Daddy-Longlegs Machine
There was actually no option to take a look at this speculation, but it surely made sense. They defined to the affected person that the subsequent step was to get the filter out. The affected person was desirous to attempt. The staff reached out to Dr. Invoice Parkhurst on the College of Alabama at Birmingham Hospital, who specialised in this type of process.
The affected person was sedated for the operation. Parkhurst put a tiny tube by an incision into the affected person’s jugular vein in his neck and slowly superior it down previous the guts into the vena cava the place the filter was situated. These contraptions appear to be daddy longlegs with tiny hooks at every foot to carry them in place within the vein. The place the physique of the insect can be situated was a small hook. Parkhurst used a tiny gripping device to know the hook and pull the filter up by the vena cava and out by the small incision within the affected person’s neck. Subsequent Parkhurst inserted tiny balloons that he inflated to reopen the threadlike stream by the narrowed vena cava. He then positioned a stent to carry the vessel open. He continued this course of down the first vein of every leg. The process took six hours and required 9 stents, however lastly there was good blood move between the legs and the guts.
The primary time the affected person stood up after this process, he was amazed. The dizziness was gone. It has been 4 months and it hasn’t come again. No weak legs, no lightheadedness, no falls. His toes are nonetheless numb, however he can dwell with that as long as they continue to be on the bottom and he stays upright.
Slief is modest about making this obscure analysis. There are solely a handful of case experiences within the medical literature. Nonetheless, Slief advised me, it does make you marvel if possibly that is occurring extra usually than reported. He’s definitely going to be searching for it.
Lisa Sanders, M.D., is a contributing author for the journal. Her newest e book is “Analysis: Fixing the Most Baffling Medical Mysteries.” If in case you have a solved case to share, write her at Lisa.Sandersmdnyt@gmail.com.

Health
The Bangles Members: A Look at the Cool '80s Girl Group Then and Now

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
Horoscope: What’s in Store for You April 22 — April 28, 2024?

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
With whooping cough cases on the rise, do you need a booster vaccine?

As whooping cough cases are surging globally, some may wonder if it’s necessary to get a booster.
Cases of the childhood respiratory disease also known as pertussis are surging internationally and in parts of the U.S., according to a recent report.
Bordetella pertussis is a type of bacteria that causes a very contagious respiratory infection that spreads from person to person through small respiratory droplets, per the CDC.
NEW YORK HEALTH OFFICIALS WARN OF WHOOPING COUGH OUTBREAK AMONG CHILDREN
“Reports indicate that whooping cough outbreaks are surging across Europe, Asia and parts of the United States, including Northern California, marking the largest uptick since 2012, with cases rising sharply since December,” Maggie Rae, president of the Royal Society of Medicine’s epidemiological and public health section in London, told Fox News Digital.
Bordetella pertussis is a type of bacteria that causes a contagious respiratory infection that spreads from person to person through small respiratory droplets, per the CDC. (iStock)
Prevalence of cases
In the U.K., there were an estimated 555 cases in January of this year and 913 cases in February — compared to 858 cases for all of 2023, according to the UK Health Security Agency.
Cases in China totaled more than 15,000 this January. That’s 15 times higher than the same time period last year, reports stated.
AMID CHILDHOOD PNEUMONIA OUTBREAKS, INFECTIOUS DISEASES EXPERT REVEALS KEY FACTS ABOUT ‘WHITE LUNG SYNDROME’
“Concerns are mounting in Europe, especially in the Netherlands, where 1,800 cases were reported in the first two weeks of April, leading to four deaths, with declining childhood vaccination rates cited as a possible cause by public health officials,” Rae said.
“This is a very important public health issue, and I would urge those members of the public who require a vaccine for pertussis to take this up.”
Whooping cough is mostly controlled in the United States, although “breakthrough cases” can occur in people who are fully vaccinated.

Cases of the childhood respiratory disease known as whooping cough or pertussis are surging internationally and in parts of the U.S., according to a recent report. (iStock)
Clusters of cases in certain parts of the U.S. are expected for this time of year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
There have been small “clusters” of cases of whooping cough in the U.S., extending from San Francisco to New York City.
CDC RECOMMENDS ADDITIONAL COVID VACCINE FOR ADULTS 65 AND OVER
A Catholic high school in San Francisco, California, has reported more than 12 cases since January, according to local reports.
The New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene estimated 244 cases from Oct. 1, 2023, to Jan. 31, 2024.
That’s a 200% increase compared to the same time period in the prior year, a recent health advisory stated.
“This is a very important public health issue.”
Most unvaccinated cases involved infants, while most vaccinated individuals were school-aged children.
A majority of adults had an unknown vaccination history, the advisory noted.
The U.S. typically has approximately 20,000 cases of pertussis per year. Yet as people donned masks and practiced physical distancing during the pandemic, annual cases dropped to 6,124 in 2020 and 2,116 in 2021, according to the CDC.
Symptoms and risk factors
Clusters of cases often occur where there are large groups of young people, such as child care centers and schools.
“The symptoms of pertussis are initially like a cold, with a runny nose, and progress to a cough,” Jennifer Duchon, M.D., hospital epidemiologist and director of antimicrobial stewardship at Mount Sinai Kravis Children’s Hospital in New York, told Fox News Digital.
Patients tend to develop a cough that can become severe — sometimes to the point of vomiting, Duchon said.

Health care providers typically test for the disease with a nasal swab. (iStock)
“The characteristic ‘whooping’ sound is a gasp that is made when trying to breathe after a long episode of coughing,” she added.
The cough can linger for weeks after a person catches pertussis.
When outbreaks occur, babies are at a high risk of getting sick and dying from the infection, health officials warn.
AS NEW JERSEY INVESTIGATES MUMPS OUTBREAK, EXPERTS SHARE WHAT TO KNOW ABOUT SYMPTOMS, PROTECTION
“Pertussis is most severe in infants 6 months of age or less, especially in infants who were born preterm or are not immunized,” Duchon said.
“Young infants can have a severe cough that impairs their ability to breathe, and can lead to episodes where they vomit, struggle to breathe or even cease breathing after bouts of coughing.”

Patients tend to develop a cough that can become severe — sometimes to the point of vomiting, a doctor said. “The characteristic ‘whooping’ sound is a gasp that is made when trying to breathe after a long episode of coughing.” (iStock)
Babies often won’t make that whooping sound, so a warning sign is when their face turns blue as they struggle to breathe, the CDC noted.
The infection can progress to bacterial pneumonia or a condition called pulmonary hypertension, in which heart function is affected by the disease, Duchon warned.
Treatment and prevention
Health care providers typically test for the disease with a nasal swab.
“If pertussis is caught early, patients can take an antibiotic called azithromycin, but this only helps make the disease less severe and does not cure the disease,” Duchon noted.
MEASLES VACCINATIONS GIVEN IN ’70S AND ’80S MAY HAVE WORN OFF BY NOW, DOCTOR WARNS
“If someone is exposed to pertussis and is at risk for severe disease or had a lot of contact with the ill person, doctors will sometimes recommend a short course of an antibiotic to act as a ‘prophylaxis’ against the disease.”
Currently, there are two kinds of vaccines for whooping cough available in the U.S., according to the CDC.
“The best way to prevent the disease is to make sure that all family members and health care workers are up-to-date on their vaccinations — not only for pertussis, but also other vaccine-preventable diseases,” Duchon told Fox News Digital.
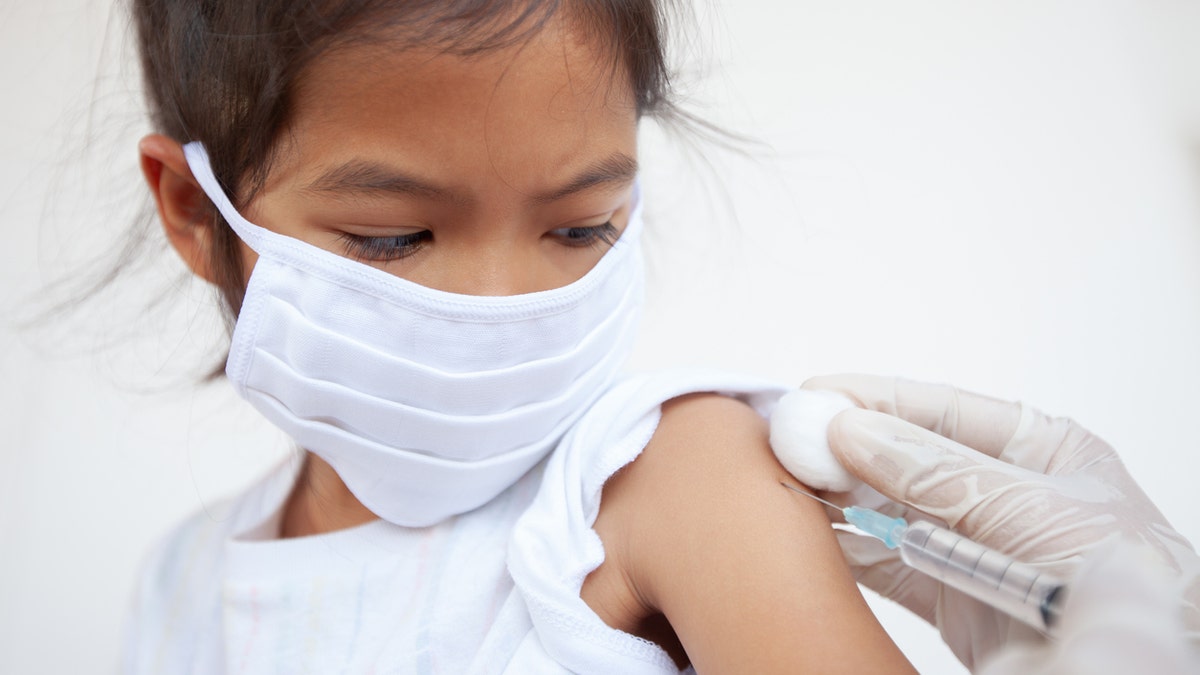
“Children should get their primary series of vaccines at 2 months, 4 months and 6 months, and then at 15 months through 18 months, and at 4 years through 6 years,” a doctor advised. (iStock)
The DTaP vaccine protects against diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis.
The Tdap vaccine protects against tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis.
The DTaP vaccine is for babies, while the Tdap “booster” vaccine is for pre-teens, teenagers and adults, per the CDC.
“Before vaccination became available, the disease used to be a major cause of mortality in young children,” Duchon noted.
Specific vaccine recommendations
Due to the high risk to babies, the CDC recommends that pregnant women receive the Tdap vaccine during the 27th and 36th week of pregnancy, regardless of their prior vaccination status.
This prevents 78% of cases in infants younger than 2 months old and decreases hospitalization by 90% for infants younger than 2 months old who are infected with pertussis, according to the CDC.
“Everyone in close contact with a very young infant should be vaccinated against pertussis.”
It is recommended that babies get immunized with the DTaP vaccine series, which provides immunity for three separate infectious diseases — diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis.
“Children should get their primary series of vaccines at 2 months, 4 months and 6 months, and then at 15 months through 18 months, and at 4 years through 6 years,” Duchon advised.
The Tdap vaccine protects against tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis. (iStock)
Adolescents should receive the Tdap vaccine at 11 to 12 years old to boost their immunity, the CDC recommends.
In children who receive the full series, 98% have full protection against the infection within a year after the last dose, but the response decreases to 71% after five years, the agency states.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
As pertussis immunity wanes from the original vaccination series in childhood, adults should get regular boosters, Monica Gandhi, M.D., professor of medicine and an infectious disease specialist at UCSF/ San Francisco General Hospital, told Fox News Digital.
“Although the exact frequency of the need for booster vaccination has not been precisely worked out, we recommend a tetanus vaccine every 10 years,” she said.
The DTaP vaccine protects against diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis. (iStock)
As the pertussis vaccine comes formulated with tetanus immunization in the form of the Tdap vaccine, many practitioners recommend a pertussis vaccine every 10 years when the booster for tetanus is provided, according to Gandhi.
Other providers may only recommend routine pertussis boosters in certain circumstances, such as for pregnant women or adults who have never been vaccinated, Duchon added.
“Everyone in close contact with a very young infant should be vaccinated against pertussis,” she said.
“We call this strategy ‘cocooning,’ where those around the baby form a protective wall against the disease.”
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoCross-Tabs: April 2024 Times/Siena Poll of Registered Voters Nationwide
-
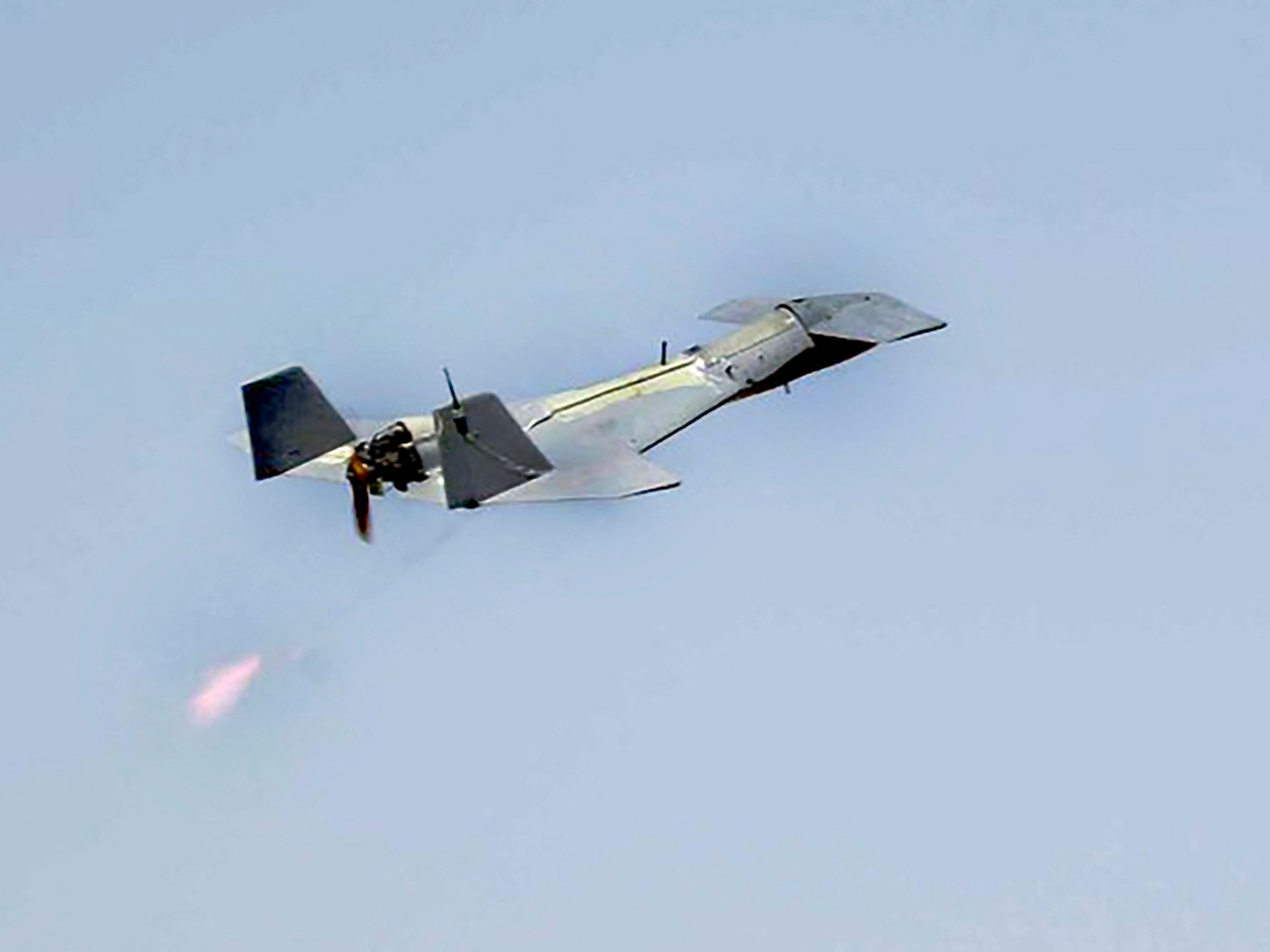

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIran launches dozens of drones at Israel
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoWhite House says US support for Israel is 'ironclad,' will 'support their defense' amid Iran attack
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoWyoming Democratic Caucus Results
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoCross-Tabs: April 2024 Times/Siena Poll of the Likely Electorate
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNine questions about the Trump trial, answered
-

 World5 days ago
World5 days agoIf not Ursula, then who? Seven in the wings for Commission top job
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoWhat biologists see from the shores of the drying Great Salt Lake













