Health
Is there a chicken coop in your future as egg costs rise? Know the health risks first
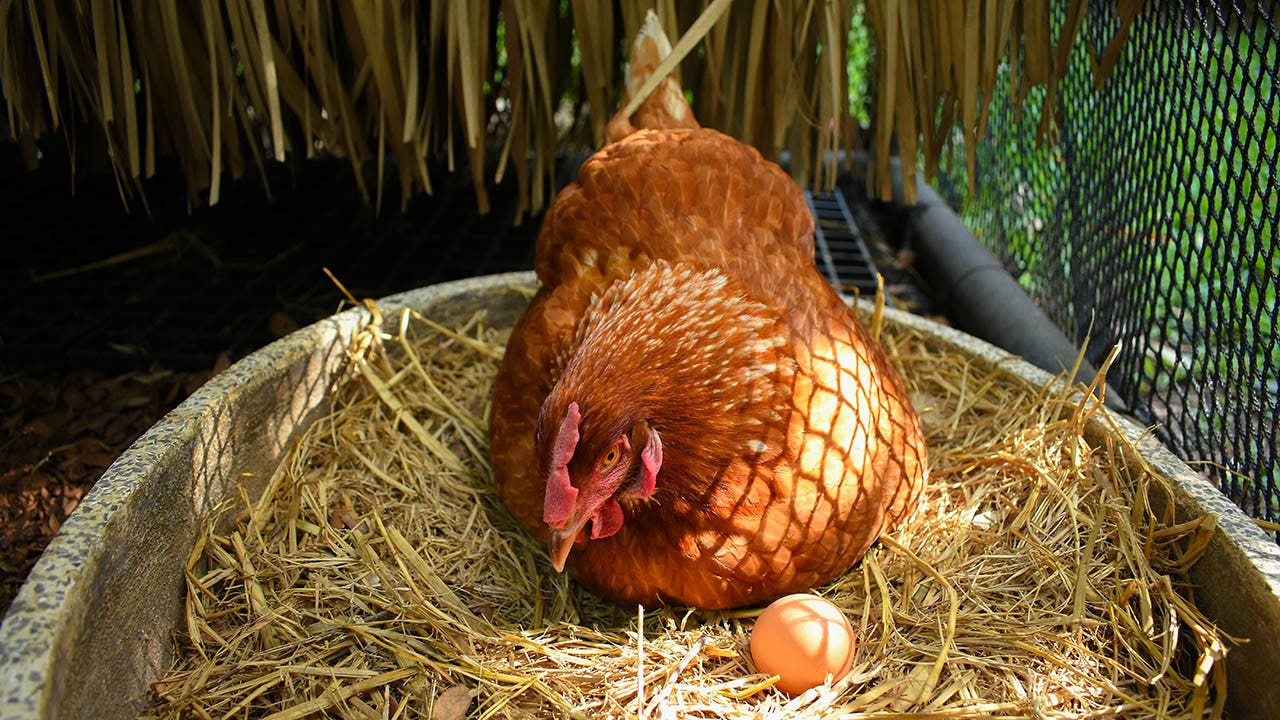

The hovering value of eggs could also be inspiring some folks so as to add a rooster coop or two to their yard or property.
The feathery pets, nonetheless, include critical well being dangers, based on the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention (CDC) — so folks ought to go into such an endeavor with eyes large open.
“Elevating any kind of animal or chicken is at all times doubtlessly fraught with communicable illness transmission,” Dr. Aaron Glatt, chief of infectious illnesses at Mount Sinai South Nassau Hospital on Lengthy Island, New York, informed Fox Information Digital this week.
PENNSYLVANIA COUPLE STARTS ‘RENT THE CHICKEN’ BUSINESS AMID HIGH EGG PRICES IN STORES
“Correct consideration must be given towards sustaining the great well being of those creatures, in addition to stopping the unfold of microbes they might harbor,” added Glatt. He’s additionally a spokesperson for the Infectious Illnesses Society of America.
Final 12 months, there have been 1,230 sicknesses, 225 hospitalizations and two deaths in 49 states and Puerto Rico as a part of a CDC investigation into outbreaks linked to yard poultry, based on its web site.
“Elevating any kind of animal or chicken is at all times doubtlessly fraught with communicable illness transmission,” stated an infectious illness professional.
(iStock)
“In 2022, CDC investigated 13 multi-state outbreaks of salmonella infections linked to yard poultry,” Dr. Kathy Benedict, a veterinarian epidemiologist with the CDC, informed Fox Information Digital.
“Yard poultry could be a reservoir for a lot of illnesses, which might unfold illnesses to poultry and/or people,” added Maurice Pitesky, a cooperative extension specialist with College of California, Davis Faculty of Veterinary Medication in Davis, California.
“Yard poultry could be a reservoir for a lot of illnesses.”
“It’s our duty to boost the birds in such a way as to scale back the potential for illness transmission,” he added.
US FARM GROUP CALLS FOR PROBE OF HIGH EGG PRICES
The CDC offers recommendations on easy methods to keep protected from the dangerous germs that chickens can unfold.
Chickens carry germs
“Chickens can carry germs like campylobacter, E. coli and salmonella,” Benedict of the CDC informed Fox Information Digital.
These are all bacterial infections.

Chickens can look “clear and wholesome however nonetheless unfold germs to folks.”
(iStock)
Chickens don’t normally get sick from these germs, she stated — so “they’ll look clear and wholesome however nonetheless unfold the germs to folks.”
Individuals utilizing a rooster coop can even get an an infection often called histoplasmosis, stated Benedict.
Histoplasmosis is brought on by a fungus present in soil that is been contaminated with chicken poop.
It is brought on by a fungus present in soil that is contaminated with chicken poop.
Consultants emphasize the significance of figuring out the well being dangers of 1 bacterial an infection particularly — salmonella — related to having a rooster coop.
Know the information about salmonella
“You will get sick from touching your yard poultry or something of their atmosphere after which touching your mouth or meals and swallowing salmonella germs,” the CDC notes on its web site.
Sufferers who’re sick with salmonella usually have a fever and diarrheal signs with abdomen cramps, the CDC says.
The signs usually start as early as six hours as much as six days after swallowing the micro organism, however most individuals get higher on their very own in a single week.

Eggs that keep within the nest for a very long time can break or change into soiled — so accumulate freshly laid eggs as usually as you may, well being consultants advise.
(iStock)
Youngsters youthful than 5, adults who’re 65 and older, and people who find themselves immunocompromised usually tend to be in danger for extreme illness from salmonella and will require therapy, together with hospitalization.
Wash your palms
The company emphasizes that folks ought to at all times wash their palms with cleaning soap and water after the next: dealing with any chickens; touching their eggs; and touching something the place chickens stay and roam.
Children must also be supervised any time they’re round yard poultry.
However hand sanitizer is an efficient second-line possibility if cleaning soap and water will not be available.
MEET THE AMERICAN WHO INVENTED SLICED BREAD: OTTO ROHWEDDER, HARD-LUCK HAWKEYE
The company suggests folks have a prepared provide of hand sanitizer close to the rooster coop.
Don’t kiss chickens or snuggle with them
Kissing or snuggling chickens can unfold germs to the mouth — which is why the CDC recommends in opposition to doing this.
Additionally, do not eat or drink when round chickens, the CDC says.

It is best to not eat or drink something if you’re round chickens.
(iStock)
Maintain chickens, their care provides similar to feed containers, and the particular sneakers you put on to look after chickens outdoors the house.
“You must also clear the provides outdoors the home,” the CDC provides on its web site.
Supervise the children
Children must also be supervised any time they’re round yard poultry.
Dad and mom and caregivers ought to remind them to additionally wash their palms after dealing with chickens.
Youngsters below 5 years outdated mustn’t contact chickens. That is as a result of they’re at increased threat of getting sick from germs like salmonella.
Deal with eggs properly
Whereas “eggs are certainly one of nature’s most nutritious and economical meals,” the CDC factors out, “eggs could make you sick if you don’t deal with and cook dinner them correctly.”
Eggs that keep within the nest for a very long time can break or change into soiled — so accumulate eggs as usually as you may.
‘SKY-HIGH’ EGG PRICES: HISTORICAL LOOK AT EGG COSTS SINCE 1980
Damaged eggs permit germs to enter the egg extra simply via the cracked shell. Any eggs with damaged shells ought to be thrown away.
For unbroken eggs, “rub off grime on [these] eggs with effective sandpaper, a brush or a fabric,” the CDC notes on its web site.

As soon as you’ve got cleaned the eggs, it is wisest to refrigerate them to maintain them contemporary and to gradual bacterial development, the CDC says.
(iStock)
For heat, contemporary eggs, keep away from washing them with water, “as a result of colder water can pull germs into the egg.”
As soon as you’ve got cleaned the eggs, it is wisest to refrigerate them to maintain them contemporary and to gradual bacterial development.
Whereas some folks consider that contemporary, unwashed eggs might be saved safely at room temperature, refrigerating them will assist them last more.
The CDC provides, “Prepare dinner eggs till each the yolk and white are agency, and cook dinner egg dishes to an inner temperature of 160°F to kill all germs.”
Benedict informed Fox Information Digital, “CDC’s web site has details about easy methods to keep wholesome round yard chickens and easy methods to hold your chickens wholesome.”
She famous that the company additionally contains FAQs and “a printable infographic for individuals who have rooster coops.”

Health
Horoscope: What’s in Store for You April 22 — April 28, 2024?

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
With whooping cough cases on the rise, do you need a booster vaccine?

As whooping cough cases are surging globally, some may wonder if it’s necessary to get a booster.
Cases of the childhood respiratory disease also known as pertussis are surging internationally and in parts of the U.S., according to a recent report.
Bordetella pertussis is a type of bacteria that causes a very contagious respiratory infection that spreads from person to person through small respiratory droplets, per the CDC.
NEW YORK HEALTH OFFICIALS WARN OF WHOOPING COUGH OUTBREAK AMONG CHILDREN
“Reports indicate that whooping cough outbreaks are surging across Europe, Asia and parts of the United States, including Northern California, marking the largest uptick since 2012, with cases rising sharply since December,” Maggie Rae, president of the Royal Society of Medicine’s epidemiological and public health section in London, told Fox News Digital.
Bordetella pertussis is a type of bacteria that causes a contagious respiratory infection that spreads from person to person through small respiratory droplets, per the CDC. (iStock)
Prevalence of cases
In the U.K., there were an estimated 555 cases in January of this year and 913 cases in February — compared to 858 cases for all of 2023, according to the UK Health Security Agency.
Cases in China totaled more than 15,000 this January. That’s 15 times higher than the same time period last year, reports stated.
AMID CHILDHOOD PNEUMONIA OUTBREAKS, INFECTIOUS DISEASES EXPERT REVEALS KEY FACTS ABOUT ‘WHITE LUNG SYNDROME’
“Concerns are mounting in Europe, especially in the Netherlands, where 1,800 cases were reported in the first two weeks of April, leading to four deaths, with declining childhood vaccination rates cited as a possible cause by public health officials,” Rae said.
“This is a very important public health issue, and I would urge those members of the public who require a vaccine for pertussis to take this up.”
Whooping cough is mostly controlled in the United States, although “breakthrough cases” can occur in people who are fully vaccinated.

Cases of the childhood respiratory disease known as whooping cough or pertussis are surging internationally and in parts of the U.S., according to a recent report. (iStock)
Clusters of cases in certain parts of the U.S. are expected for this time of year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
There have been small “clusters” of cases of whooping cough in the U.S., extending from San Francisco to New York City.
CDC RECOMMENDS ADDITIONAL COVID VACCINE FOR ADULTS 65 AND OVER
A Catholic high school in San Francisco, California, has reported more than 12 cases since January, according to local reports.
The New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene estimated 244 cases from Oct. 1, 2023, to Jan. 31, 2024.
That’s a 200% increase compared to the same time period in the prior year, a recent health advisory stated.
“This is a very important public health issue.”
Most unvaccinated cases involved infants, while most vaccinated individuals were school-aged children.
A majority of adults had an unknown vaccination history, the advisory noted.
The U.S. typically has approximately 20,000 cases of pertussis per year. Yet as people donned masks and practiced physical distancing during the pandemic, annual cases dropped to 6,124 in 2020 and 2,116 in 2021, according to the CDC.
Symptoms and risk factors
Clusters of cases often occur where there are large groups of young people, such as child care centers and schools.
“The symptoms of pertussis are initially like a cold, with a runny nose, and progress to a cough,” Jennifer Duchon, M.D., hospital epidemiologist and director of antimicrobial stewardship at Mount Sinai Kravis Children’s Hospital in New York, told Fox News Digital.
Patients tend to develop a cough that can become severe — sometimes to the point of vomiting, Duchon said.

Health care providers typically test for the disease with a nasal swab. (iStock)
“The characteristic ‘whooping’ sound is a gasp that is made when trying to breathe after a long episode of coughing,” she added.
The cough can linger for weeks after a person catches pertussis.
When outbreaks occur, babies are at a high risk of getting sick and dying from the infection, health officials warn.
AS NEW JERSEY INVESTIGATES MUMPS OUTBREAK, EXPERTS SHARE WHAT TO KNOW ABOUT SYMPTOMS, PROTECTION
“Pertussis is most severe in infants 6 months of age or less, especially in infants who were born preterm or are not immunized,” Duchon said.
“Young infants can have a severe cough that impairs their ability to breathe, and can lead to episodes where they vomit, struggle to breathe or even cease breathing after bouts of coughing.”
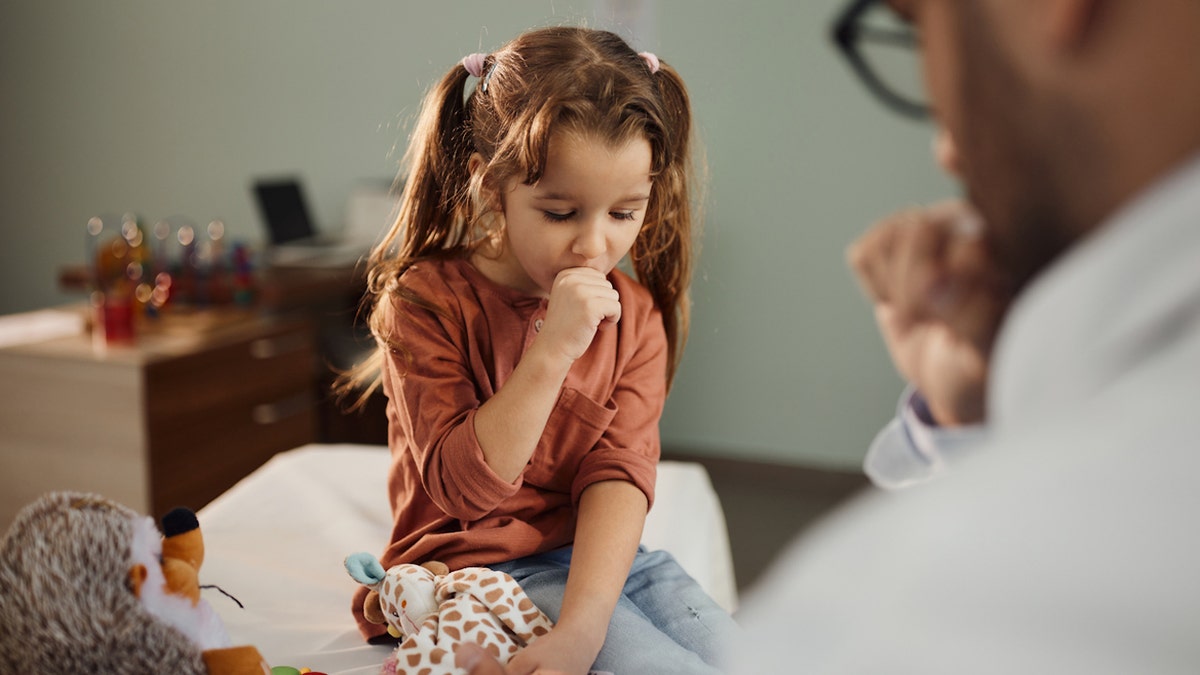

Patients tend to develop a cough that can become severe — sometimes to the point of vomiting, a doctor said. “The characteristic ‘whooping’ sound is a gasp that is made when trying to breathe after a long episode of coughing.” (iStock)
Babies often won’t make that whooping sound, so a warning sign is when their face turns blue as they struggle to breathe, the CDC noted.
The infection can progress to bacterial pneumonia or a condition called pulmonary hypertension, in which heart function is affected by the disease, Duchon warned.
Treatment and prevention
Health care providers typically test for the disease with a nasal swab.
“If pertussis is caught early, patients can take an antibiotic called azithromycin, but this only helps make the disease less severe and does not cure the disease,” Duchon noted.
MEASLES VACCINATIONS GIVEN IN ’70S AND ’80S MAY HAVE WORN OFF BY NOW, DOCTOR WARNS
“If someone is exposed to pertussis and is at risk for severe disease or had a lot of contact with the ill person, doctors will sometimes recommend a short course of an antibiotic to act as a ‘prophylaxis’ against the disease.”
Currently, there are two kinds of vaccines for whooping cough available in the U.S., according to the CDC.
“The best way to prevent the disease is to make sure that all family members and health care workers are up-to-date on their vaccinations — not only for pertussis, but also other vaccine-preventable diseases,” Duchon told Fox News Digital.
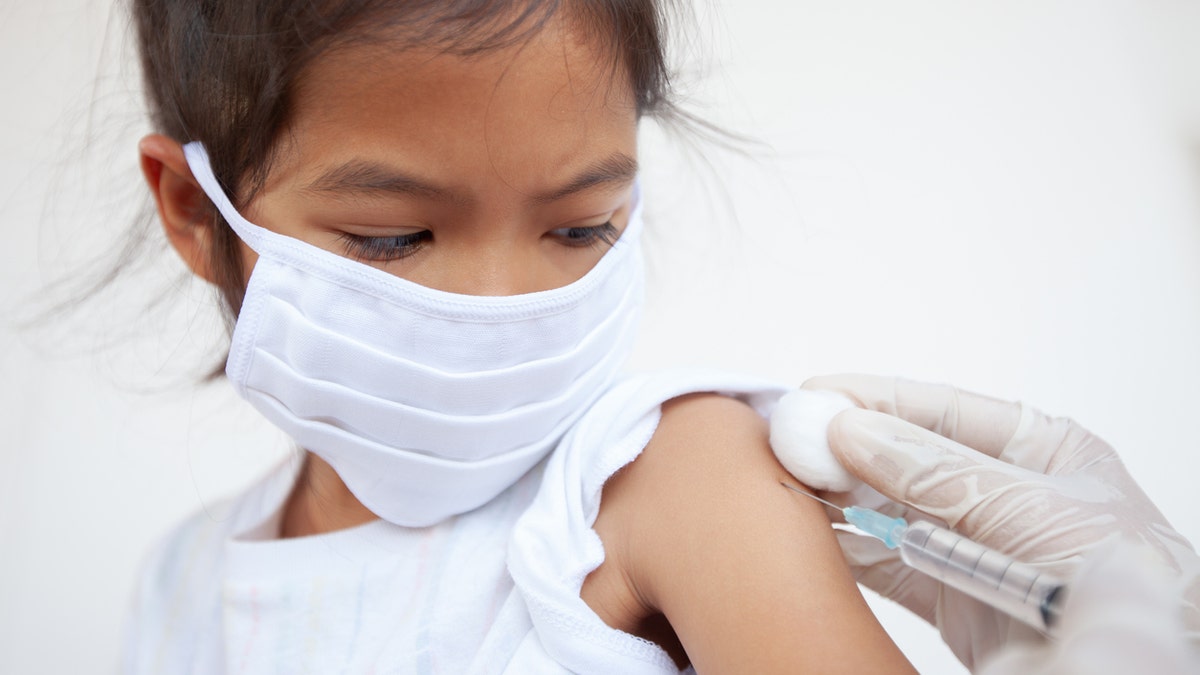
“Children should get their primary series of vaccines at 2 months, 4 months and 6 months, and then at 15 months through 18 months, and at 4 years through 6 years,” a doctor advised. (iStock)
The DTaP vaccine protects against diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis.
The Tdap vaccine protects against tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis.
The DTaP vaccine is for babies, while the Tdap “booster” vaccine is for pre-teens, teenagers and adults, per the CDC.
“Before vaccination became available, the disease used to be a major cause of mortality in young children,” Duchon noted.
Specific vaccine recommendations
Due to the high risk to babies, the CDC recommends that pregnant women receive the Tdap vaccine during the 27th and 36th week of pregnancy, regardless of their prior vaccination status.
This prevents 78% of cases in infants younger than 2 months old and decreases hospitalization by 90% for infants younger than 2 months old who are infected with pertussis, according to the CDC.
“Everyone in close contact with a very young infant should be vaccinated against pertussis.”
It is recommended that babies get immunized with the DTaP vaccine series, which provides immunity for three separate infectious diseases — diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis.
“Children should get their primary series of vaccines at 2 months, 4 months and 6 months, and then at 15 months through 18 months, and at 4 years through 6 years,” Duchon advised.
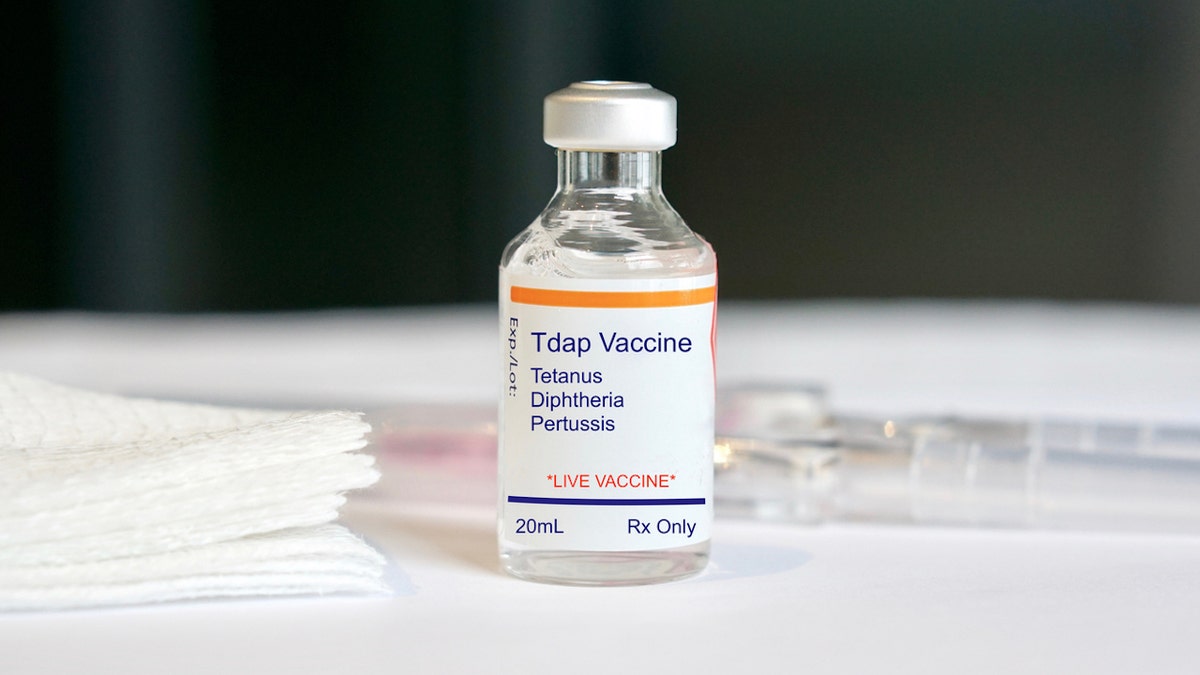
The Tdap vaccine protects against tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis. (iStock)
Adolescents should receive the Tdap vaccine at 11 to 12 years old to boost their immunity, the CDC recommends.
In children who receive the full series, 98% have full protection against the infection within a year after the last dose, but the response decreases to 71% after five years, the agency states.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
As pertussis immunity wanes from the original vaccination series in childhood, adults should get regular boosters, Monica Gandhi, M.D., professor of medicine and an infectious disease specialist at UCSF/ San Francisco General Hospital, told Fox News Digital.
“Although the exact frequency of the need for booster vaccination has not been precisely worked out, we recommend a tetanus vaccine every 10 years,” she said.
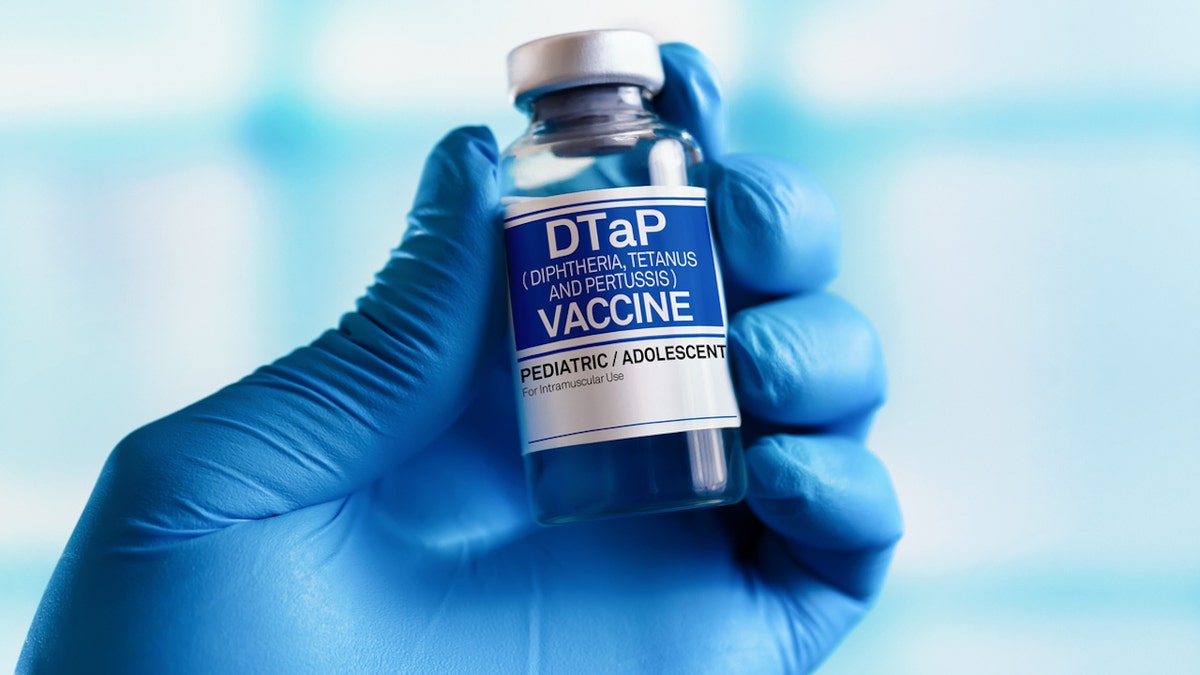
The DTaP vaccine protects against diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis. (iStock)
As the pertussis vaccine comes formulated with tetanus immunization in the form of the Tdap vaccine, many practitioners recommend a pertussis vaccine every 10 years when the booster for tetanus is provided, according to Gandhi.
Other providers may only recommend routine pertussis boosters in certain circumstances, such as for pregnant women or adults who have never been vaccinated, Duchon added.
“Everyone in close contact with a very young infant should be vaccinated against pertussis,” she said.
“We call this strategy ‘cocooning,’ where those around the baby form a protective wall against the disease.”
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.
Health
'Battle of the Diets' Study Reveals the Healthy + Fastest Way to Lose Weight

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
-
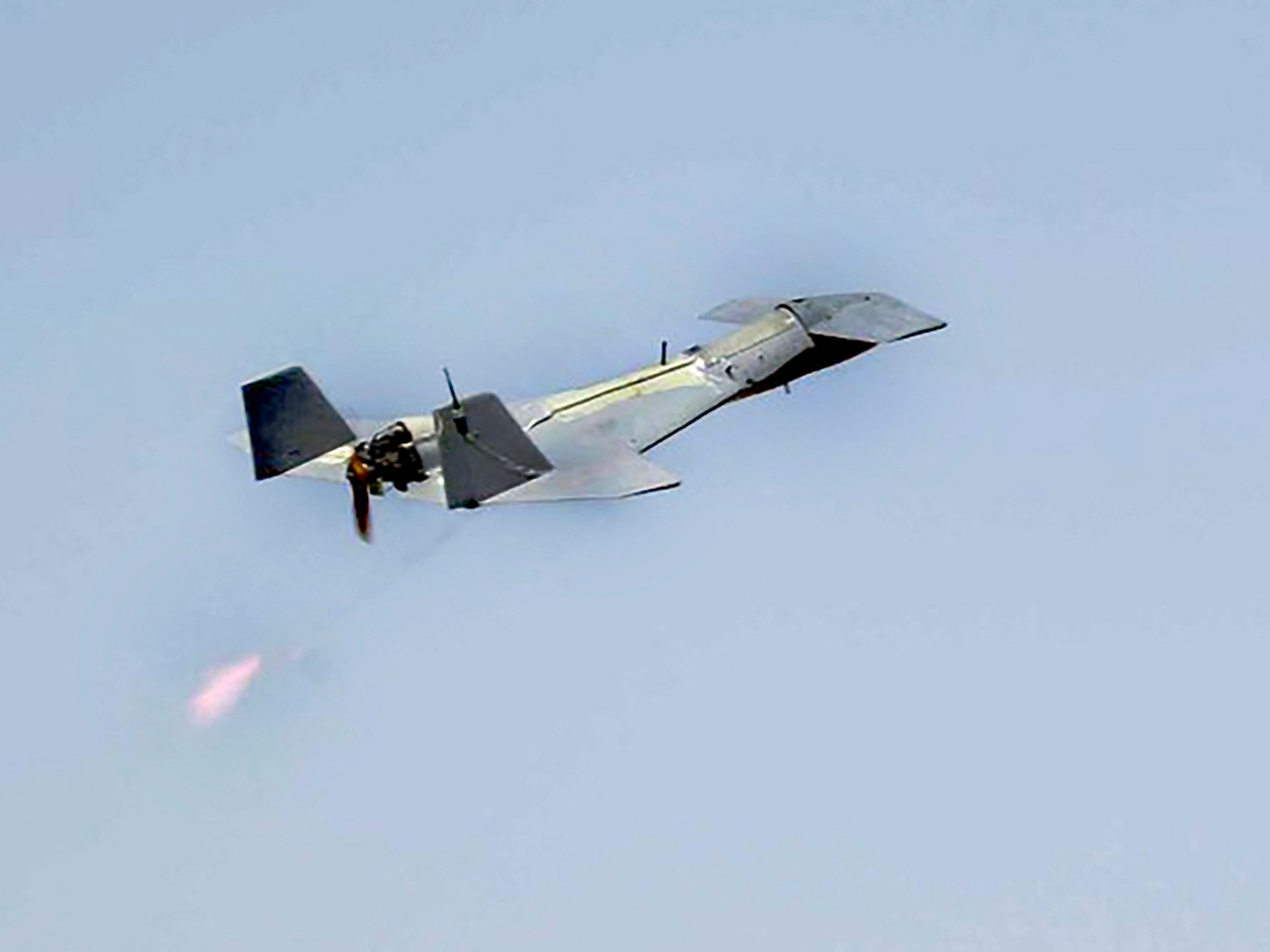

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIran launches dozens of drones at Israel
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoCross-Tabs: April 2024 Times/Siena Poll of Registered Voters Nationwide
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTrump defense challenges jury selection in criminal hush money trial
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoWhite House says US support for Israel is 'ironclad,' will 'support their defense' amid Iran attack
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoWyoming Democratic Caucus Results
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoCross-Tabs: April 2024 Times/Siena Poll of the Likely Electorate
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNine questions about the Trump trial, answered
-

 World5 days ago
World5 days agoIf not Ursula, then who? Seven in the wings for Commission top job













