Health
Human Brain Cells Grow in Rats, and Feel What the Rats Feel

Scientists have efficiently transplanted clusters of human neurons into the brains of new child rats, a hanging feat of organic engineering that will present extra lifelike fashions for neurological circumstances corresponding to autism and function a technique to restore injured brains.
In a examine printed on Wednesday, researchers from Stanford reported that the clumps of human cells, generally known as “organoids,” grew into tens of millions of recent neurons and wired themselves into their new nervous programs. As soon as the organoids had plugged into the brains of the rats, the animals may obtain sensory indicators from their whiskers and assist generate command indicators to information their actions.
Dr. Sergiu Pasca, the neuroscientist who led the analysis, mentioned that he and his colleagues have been now utilizing the transplanted neurons to study in regards to the biology underlying autism, schizophrenia and different developmental problems.
“If we actually wish to deal with the biology of those circumstances, we’re going to want extra complicated fashions of the human mind,” Dr. Pasca mentioned.
In 2009, after coaching in medication in Romania, Dr. Pasca joined Stanford as a postdoctoral researcher to learn to create human neurons in a dish. He and his colleagues took pores and skin cells from volunteers and bathed them in chemical compounds that induced them to vary character. Now they have been extra like embryo cells, which might turn out to be any tissue within the physique.
With the addition of extra chemical compounds, the researchers coaxed the cells to turn into neurons. They may then observe pulses of voltage shoot down the size of the neurons as they lay in a dish.
Dr. Pasca and his colleagues carried out the identical experiment once more, this time utilizing pores and skin cells from folks with Timothy syndrome, a uncommon type of autism attributable to a single mutation that results in severe coronary heart issues in addition to impaired language and social expertise.
Rising Timothy syndrome neurons in a dish, Dr. Pasca may see quite a few variations between them and typical neurons. They produced additional quantities of signaling chemical compounds corresponding to dopamine, for instance.
However inspecting single cells may reveal solely a restricted variety of clues in regards to the situation. Dr. Pasca suspected that he may study extra by finding out 1000’s of neurons joined collectively in circuits known as mind organoids.
A brand new chemical recipe allowed Dr. Pasca to imitate the situation contained in the creating mind. Bathed on this broth, pores and skin cells was progenitor mind cells, which in flip grew to become tangles of neurons discovered within the mind’s outer layers, known as the cortex.
In a later examine, he and his colleagues linked three organoids: one fabricated from cortex, one other of spinal twine and a 3rd of muscle cells. Stimulating the cortex organoid induced the muscle cells to contract.
However organoids are removed from being miniature brains. For one factor, their neurons stay stunted. For one more, they aren’t as electrically energetic as atypical neurons in a residing mind. “It’s clear that there are a selection of limitations to those fashions,” Dr. Pasca mentioned.
Scientists started placing organoids in residing brains, theorizing {that a} petri dish restricted an organoid’s improvement. In 2018, the neuroscientist Fred Gage and his colleagues on the Salk Institute for Organic Research transplanted human mind organoids into the brains of grownup mice. The human neurons continued to mature because the mouse mind provided them with blood vessels.
Since then, Dr. Gage and different researchers have implanted organoids into the again of the mind, the place mice understand indicators from their eyes. When the animals noticed pulsing flashes of white gentle, the human-organoid neurons responded in a lot the identical means the mouse’s personal cells did, in keeping with a examine printed on-line in June that has not but been peer-reviewed.
Dr. Pasca and his crew have been additionally engaged on organoid transplants, however they selected to place them into younger rodents reasonably than adults. A day or two after a rat was born, the scientists injected an organoid the scale of a poppy seed right into a area of the mind known as the somatosensory cortex, which processes contact, ache and different indicators from throughout the physique. In rats, the area is particularly delicate to indicators from their whiskers.
The human neurons multiplied within the rat mind till they numbered about three million, making up a few third of the cortex on one aspect of the rat mind. Every cell within the organoid grew six occasions longer than it might have in a petri dish. The cells additionally grew to become about as energetic as neurons in human brains.
Much more strikingly, the human organoids spontaneously wired themselves into the rat mind. They linked not simply to close by neurons, however to distant ones as nicely.
These connections made the human neurons delicate to the rat’s senses. When the researchers blew puffs of air over the rat’s whiskers, its human organoid crackled in response.
Dr. Pasca and his colleagues additionally ran experiments to see how the organoids affected the conduct of the rats, utilizing a water fountain of their chambers.
After 15 days of coaching, the rats realized they may get a drink from the fountain when their organoid was stimulated. The human organoids have been apparently sending messages to the reward-seeking areas of the rats’ brains.
These species-blending experiments elevate provocative moral questions. Earlier than beginning the work, Dr. Pasca consulted with consultants on the Heart for Regulation and the Biosciences at Stanford, who urged him to pay particular consideration to the animals’ ache and well-being.
“You’re not simply nervous about what number of mice are in a cage, or how nicely they’re fed,” mentioned Henry Greely, a Stanford legislation professor. “It is a new form of factor. You don’t know what you may see.”
Dr. Pasca’s crew discovered no proof that the rats skilled ache, grew to become liable to seizures or suffered a lack of reminiscence or management of their actions. “It seems that the rats tolerate the human graft very well,” Dr. Pasca mentioned.
Giorgia Quadrato, a neurobiologist on the College of Southern California who was not concerned within the new examine, famous that the human organoids didn’t make the rats extra human. On studying checks, for instance, they scored no higher than different rats.
“They’re rats, they usually keep rats,” Dr. Quadrato mentioned. “This needs to be reassuring from an moral perspective.”
However that may not maintain true if scientists have been to place human organoids in an in depth relative of people, like a monkey or a chimpanzee. “It might be alternative to set pointers to function in the suitable moral framework sooner or later,” she mentioned.
Dr. Pasca mentioned that the similarity between primates and people may permit the organoids to develop extra and tackle a much bigger function within the animal’s psychological processes. “It’s not one thing that we’d do, or would encourage doing,” he mentioned.
As a substitute, he’s utilizing the implanted organoids to review neurological problems. In a single experiment, Dr. Pasca’s crew implanted an organoid from a affected person with Timothy syndrome on one aspect of a rat’s mind and implanted one other organoid with out the mutation on the opposite aspect.
Each organoids grew within the rats. However the Timothy syndrome neurons developed twice as many branches for receiving incoming indicators, known as dendrites. What’s extra, the dendrites have been shorter.
Dr. Pasca hopes that he’ll be capable to observe variations in the way in which rats behave once they carry mind organoids from folks with autism and different neurological circumstances. Such experiments may assist reveal how sure mutations alter the way in which the mind works.
Dr. Isaac Chen, a neurosurgeon and organoid researcher on the College of Pennsylvania who was not concerned within the analysis, noticed one other risk within the new examine: the restore of accidents to human brains.
Dr. Chen envisioned rising mind organoids from the pores and skin of a affected person with a broken cortex. As soon as injected into the mind of the affected person, the organoid may develop and wire up with wholesome neurons.
“This concept is certainly on the market,” he mentioned. “It’s only a matter of, How can we make the most of it, and take it to the subsequent degree?”

Health
How a Company Makes Millions Off a Hospital Program Meant to Help the Poor

Soon after being diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer, Virginia King sat in an outpatient clinic in Santa Fe, N.M, while a nurse injected her with a powerful drug to slow damage to her spine, where the disease had spread.
Even though the drug had a list price of about $2,700, the hospital that owned the cancer center billed Mrs. King’s insurance company $22,700. Her insurer paid $10,000, but the hospital wanted more.
She got a bill for over $2,500 — “more than half my take-home salary for a month,” said Mrs. King, 65.
She had unknowingly sought care from a hospital that participates in a federal program allowing it to buy drugs at a steep discount and charge patients and insurers a higher amount, keeping the difference.
The intention behind the program was for a small number of safety-net providers to have access to affordable drugs and be able to expand their care for needy patients. But instead, the program has exploded: Now, more than half of nonprofit hospitals in the United States take part. While some providers say it has helped keep their doors open, others — especially large nonprofit health systems — have been accused of maximizing payouts and swallowing the profits.
The program’s escalation has driven up health care costs for employers, patients and taxpayers, studies show.
In 2023, for instance, New York changed the way it administers drug benefits for Medicaid patients, in part because the state had discovered the cost of the federal program had increased by more than 200 percent over three years, said Amir Bassiri, the state’s Medicaid director.
“The numbers and the growth were staggering,” he said. “We all bear the cost.”
Along the way, one little-known middleman has been cashing in, The New York Times found.
The company, Apexus, has worked behind the scenes to supercharge the program, according to interviews with current and former employees and emails, internal reports and other documents.
Twenty years ago, the federal government chose Apexus to manage what was then a small program, negotiating with drug distributors and manufacturers to secure better prices and access to medications. But Apexus is allowed to collect a fee for almost every drug sold under the program, giving the company an incentive to help hospitals and clinics capture as many prescriptions as possible:
-
Its “purchasing optimization team” shows hospitals how they can make more money by buying different drugs.
-
A certification program and an Apexus-run “university” trains providers in boosting earnings.
-
Apexus employees give advice that broadly interprets the rules of the program so hospitals can claim additional patients and drugs.
Apexus was on track to double its revenue from 2018 to 2022, projecting $227 million that year, according to a 2022 internal memo written for the directors of Apexus’ parent corporation and reviewed by The Times. The company costs relatively little to operate and has enjoyed profit margins above 80 percent, according to that memo and three former employees.
In a statement, Apexus said it simply executed its government contract and did not contribute to the growth of the program, called the 340B Drug Pricing Program. “The drivers of growth are multifaceted,” the statement said.
But in the 2022 memo, the president of Apexus, Chris Hatwig, posed a question: “Are there other areas for program expansion within 340B that we are not thinking about?”
Government officials have told Apexus to focus solely on administering the program and not to influence drug purchases. But Apexus leaders have sometimes ignored that request, according to two complaints filed with a government watchdog and six current and former employees, speaking on the condition of anonymity because they feared professional or legal retribution.
In its statement, Apexus said it was “fully transparent” with the Department of Health and Human Services and had never breached its contractual obligations.
The Health Resources and Services Administration, an agency within H.H.S. that oversees the program, declined to answer detailed questions from The Times. But in a statement, a spokeswoman said the agency “conducts rigorous oversight of all contracts,” and “to our knowledge, Apexus has not violated” its contract. Regulators and leaders of the company meet frequently to discuss the company’s work and prevent conflicts of interest, the spokeswoman said.
The growth of 340B has drawn criticism for years from Congress, drugmakers and employers, who say it has added to ballooning health care costs. But the role of Apexus has largely gone unexamined.
“They’ve got a license to hunt,” said Marsha Simon, who as a staff member of a congressional committee helped write the bill that authorized the program.
$66 Billion in Sales
Established in 1992, the 340B program essentially requires pharmaceutical manufacturers to offer discounts on outpatient drugs to hospitals and clinics that treat a greater share of low-income and uninsured patients.
The hospitals then can charge insurers and patients the standard price and keep the profits. Although the money is supposed to encourage care for impoverished patients, there are few rules to enforce that.
Patients rarely know they are part of this system. Their prescriptions can be counted as 340B when they get outpatient treatment at a hospital or clinic that qualifies for the program, regardless of the patients’ own income or insurance status. The provider can continue to make money off the patients’ future outpatient prescriptions, even if they get them somewhere else.
Apexus has had contracts to handle the program since the early 2000s. The government does not pay Apexus — instead, drugmakers and distributors pay the company a small percentage of sales.
Based in Irving, Texas, it is a subsidiary of Vizient, a private business owned by hospitals that negotiates a range of health care discounts. Apexus was established as a small nonprofit in 2007 but became a for-profit company in 2014.
Around the same time, 340B began to explode for a number of reasons. More hospitals qualified for the program after the Affordable Care Act expanded the number of people on Medicaid. Other health care systems qualified after acquiring hospitals and clinics in poor areas. Some, already eligible for 340B, bought up practices that used high-margin drugs, like oncology clinics. And a government rule change meant hospitals could make money from prescriptions filled at a greater number of pharmacies.
A decade ago, sales of 340B drugs were $12 billion. In 2023, they reached a high of $66 billion.
Fighting the program’s growth has become a top priority for drugmakers, as well as some employers and insurers.
In North Carolina, prescription drug spending for state employees jumped almost 50 percent from 2018 to 2022. A report in May from the state treasurer’s office found that 340B was partly to blame: Hospitals that participated in the program billed the state health plan far more than hospitals that did not — almost 85 percent more for certain cancer drugs. In one example, hospitals bought a drug commonly used to treat melanoma for an average of $8,000 but billed the state $21,512.
In some cases, costs are passed along to patients.
Mrs. King, the cancer patient in New Mexico, refused to pay her $2,500 bill, and the hospital, Christus St. Vincent, sent it to collections in July.
After The Times asked about the bill last month, a spokeswoman for Christus St. Vincent said the charge was “a misunderstanding and has been resolved,” adding that the drug program helped the hospital provide charity care and reinvest in cancer treatment and primary care.
Mrs. King switched to a free-standing oncology clinic that does not qualify for the federal drug program. That clinic billed her insurance $8,000 for the injection, about a third of what Christus St. Vincent had charged. Her responsibility was nothing.
An Ever-Growing Portfolio
Ms. Simon, who helped draft the legislation creating 340B, said the government chose an outside contractor like Apexus in order to negotiate with distributors and drugmakers on behalf of small hospitals and clinics without a lot of buying power.
But regulators and Apexus have expanded that role, allowing the company to build a highly profitable business off the program and the loosely written statute that authorized it. The company has been “aggressive” in helping health care facilities maximize their revenue from the program, said Shawn Gremminger, chief executive of the National Alliance of Healthcare Purchaser Coalitions, which represents employers who buy health insurance for more than 45 million people in the United States.
“This is a government contractor, and the goal of the government should not be, ‘How do we make more money for 340B providers?’” said Mr. Gremminger, whose organization has pushed for the program to be overhauled.
Over the past two decades, Apexus has adapted its business model to harness 340B’s tremendous growth. A 2022 PowerPoint presentation obtained by The Times showed that Apexus employees received bonuses if the company increased its revenue each year.
With exclusive access to sales data, Apexus’ “purchasing optimization team” will analyze a hospital system’s drug-buying habits and compare them with those of their competitors, according to four current and former employees. In some cases, Apexus will suggest that a hospital buy more 340B drugs or tweak its inventory in ways that can churn more cash.
Apexus declined to answer detailed questions about its optimization team, but said in a statement that the company “only provides technical assistance” in keeping with regulations.
Apexus also holds “340B University” events to help providers and others in the health care industry understand the program, and it fields questions through a national call center. But the rules governing the program are ambiguous, and Apexus offers broad interpretations, according to four current and former employees.
For instance, one of the thorniest issues is which patients can be claimed by hospitals for discounted drugs. The further a hospital casts its net, the more patients and drugs it can include under the program, and the more money it can make. Apexus has advised hospitals that they can mine records as far back as 36 months for eligible patients they may have missed, two of those employees said.
Similarly, Apexus employees have showed hospitals how to maximize the number of pharmacies they work with, boosting the number of prescriptions that can qualify for discounts, those employees said.
In its statement, Apexus said those examples were inaccurate but would not say how. It added that the company encouraged “conservative and responsible stewardship” of the 340B program, and that all information it provided was approved by regulators.
A spokeswoman for H.R.S.A. said it reviewed materials prepared by Apexus but declined to comment on that specific advice.
The company has developed other ventures that have brought in revenue:
-
About eight years ago, Apexus began selling a $750 course for people to become “certified experts” in 340B.
-
It started a business to give hospitals better access to specialty drugs — for conditions like cancer, H.I.V. and autoimmune diseases — which are major drivers of 340B’s growth. That company, Acentrus, helped hospitals and clinics provide data to manufacturers in exchange for deeper discounts and access to those drugs. It was sold last year.
-
The company charges 3 percent in fees for a line of generic drugs that are managed and provided by drug distributors, according to former employees. Apexus simply provides access to the health systems.
For the last decade, Apexus has earned millions of dollars on drug purchases made outside the 340B program: Because not all outpatient drugs qualify for 340B discounts, hospitals must stock their pharmacies with medication purchased through different channels. Apexus acts as a middleman, making fees off those transactions.
That has frustrated drugmakers and competitors. In 2021, the drug manufacturer Baxter wanted to sell non-340B drugs to hospitals without going through Apexus, according to emails obtained under public-records laws. But government regulators would not allow it, a spokeswoman for Baxter said.
In early November, Premier, the main competitor to Apexus’s parent company, Vizient, sued the federal government over these sales. The setup, the suit argued, forces hospitals to pay higher prices for those non-340B drugs and drives revenue to drug manufacturers and Apexus.
In its statement, Apexus said its federal contract did not preclude it from developing other businesses, as long as they were not in conflict with the terms of the agreement.
Regulators were aware of these ventures, the company said, noting that its specialty drug business, Acentrus, was in “no way associated with” the 340B program. The 2022 company memo, however, said Acentrus “resulted in an additional $20 million” in revenue within the 340B program.
H.R.S.A. declined to comment on the scope of its authority over Apexus and whether it knew about all the company’s revenue-generating arms.
Criticized, but Pushing Ahead
About six years ago, Krista Pedley, then the director of the H.H.S. office in charge of 340B, reprimanded Apexus leaders in a Skype meeting, saying it was acting more like a sales-driven business than a program administrator. She reminded them that Apexus’ role was not to help 340B grow, according to five former or current employees familiar with the meeting.
For about a month afterward, regulators reviewed any communication Apexus had with health care facilities to make sure the company didn’t overstep, the employees said.
But that did not seem to dampen the company’s pursuits. (In an email, Ms. Pedley said she did not recall that meeting, and noted that her former office met regularly with Apexus.)
In 2021, an unnamed Apexus employee filed a complaint with H.H.S.’s Office of Inspector General, an internal watchdog, saying the company was “always trying to grow the program.” The company, the employee wrote, had hired “sales-type” staff to influence hospitals’ drug-purchasing decisions.
The complaint said that regulators did not understand Apexus’ business, and that employees had been told by company leaders to describe its work as “education.”
Another anonymous complaint, filed in 2022, echoed the allegation that Apexus had hired staff to help shape hospitals’ purchasing decisions, and said it was using “data in ways to drive revenue for itself, without asking (or asking and disregarding) the government’s opinion.”
Apexus declined to answer specific questions about the meeting with Ms. Pedley, but said The Times’s account was a “mischaracterization of our day-to-day, collaborative discussions” with the agency.
Apexus rejected the allegations in the anonymous complaints and said it had been unaware of them until The Times provided it with copies. The spokeswoman for H.R.S.A. said that it, too, had been unaware of the complaints.
In interviews, four current and former employees said that for years, Mr. Hatwig, Apexus’ president, acknowledged that regulators did not want the company to develop sales-focused arms of the business but encouraged his staff to do so anyway, saying that the government would not know.
Apexus denied that, saying that “everyone at Apexus understands the expectation that they conduct themselves and perform their work in an ethical and compliant manner.”
Julie Tate and Carson Kessler contributed research.
Health
3 signs your aging loved one may be ready for assisted living

As Mom and Dad grow older, the big question might be looming in the background: When is the right time to provide living support?
Dr. Macie P. Smith, a licensed social worker and gerontologist based in South Carolina, shared with Fox News Digital that there may be a few telltale signs that it’s time to make a move, whether it’s hiring an at-home aide or seeking out a living facility.
1. They’re at risk of harming themselves
Most importantly, Smith noted that if a senior is at risk of hurting themselves or getting into dangerous situations, it’s most likely time to call in help.
DEMENTIA REPORT REVEALS ‘SHOCKING’ SIGNS AT AGE 60 THAT YOU’LL DEVELOP THE DISEASE BY AGE 80
Smith, who specializes in seniors living with Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive impairment, recommended starting with enlisting at-home aid before pulling a loved one out of their home.
Memory loss can cause dangerous environments and behaviors for aging adults, experts warn. (iStock)
“The last thing anybody wants to lose is their independence,” she said. “The last thing anybody wants is to live in a space with 50 other strangers.”
At-home support can help lower the risk of self-inflicted danger from incidents like leaving the stove on, or mobility issues that could lead to falls.
2. The person is having memory issues
As people age, their capacity to remember things begins to naturally slow down.
DEMENTIA RISK FOR PEOPLE 55 AND OLDER HAS DOUBLED, NEW STUDY FINDS
Sometimes, this presents in the form of diseases like Alzheimer’s or dementia. The severity of memory loss in seniors dictates whether living support is necessary, according to experts.
Smith mentioned how forgetting familiar tasks and activities, like eating, can pose a danger to someone’s health.

“Respect them enough to have the conversation, because they still have the ability to make decisions about their life.” (iStock)
“If their nutrition is poor, it may be because they are dealing with some pain that they are not expressing to anyone else,” she said. “They may be dealing with some depression and, frankly, they just don’t have the motivation.”
“Respect them enough to have the conversation, because they still have the ability to make decisions about their life.”
The expert advised watching out for signs of spoiled food in the refrigerator.
The person may also forget how to do simple tasks like making a bed, doing laundry, washing the dishes or following cooking instructions.
AGING ‘HOTSPOT’ FOUND IN BRAIN, RESEARCHERS SAY: ‘MAJOR CHANGES’
“If they’re having trouble cognitively, they’re having trouble making decisions, and that’s going to ultimately impact … how they live independently,” Smith said.
3. They repeat themselves
Repetition of thoughts is also common in individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
Smith noted that if your loved one is repeating themselves more frequently, it’s a good idea to bring in some support not only for help with day-to-day living, but also for attention and friendship.

The repetition of thoughts is common in individuals who suffer from Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. (iStock)
“In some cases, it’s because they’re lonely,” she said. “It’s because they’re living by themselves, and they don’t have any type of engagement or motivation.”
‘Very difficult’ decision
Smith emphasized how difficult it can be to make the decision to place a loved one into care, especially if it means removing them from their home.
The senior should “always be a part of the conversation” when it comes to deciding the next steps, she urged.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“The last thing you want to do is come in and uproot them from the place where they feel the most comfortable and safe, just because you feel they shouldn’t be there,” Smith said.
“Always include them in the conversation, even if they’re in the early stages of dementia,” she encouraged. “They still have a lucidity … to be able to participate in the decision-making process.”
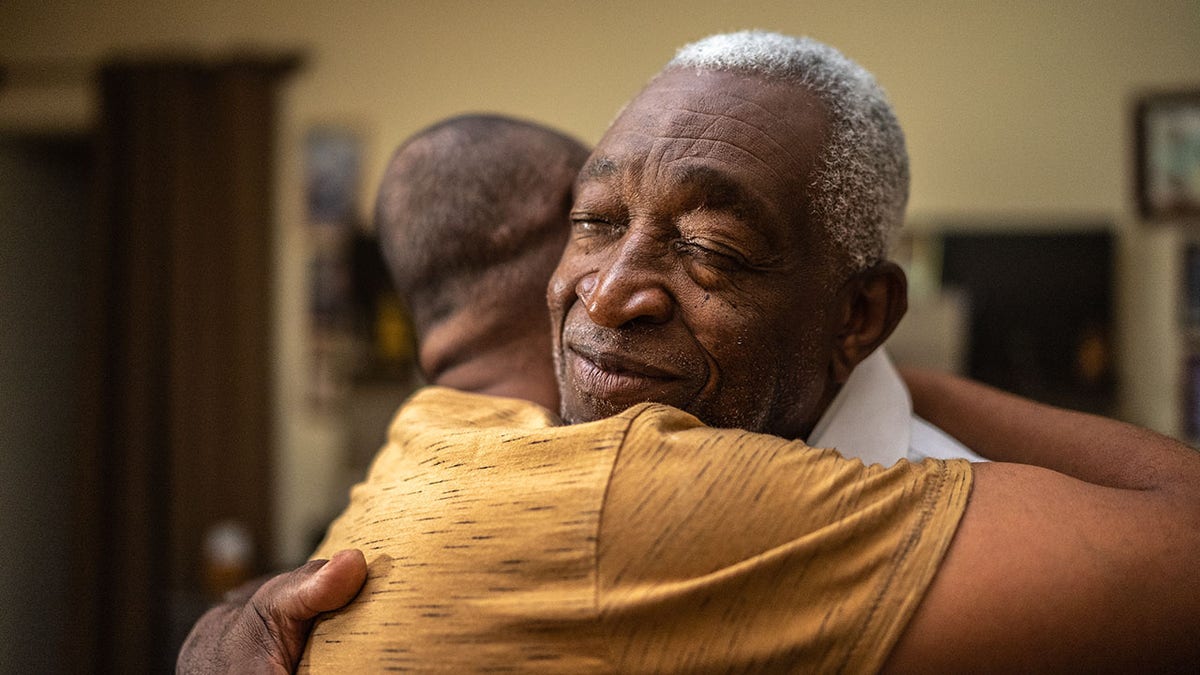
Taking away your loved one’s control and independence can cause issues, the expert warned. Instead, “we need to be there to support them and wrap services around them.” (iStock)
Whether the decision is to bring in care or move somewhere new, Smith said the senior should never be made to feel unsafe or unfamiliar, as this can increase dangerous behaviors, cause agitation and lead to health decline.
The conversation also should not start with the assumption that the senior will not accommodate your request or suggestion.
“Don’t assume they’re not going to remember,” Smith said. “Don’t assume they’re going to be irritable and combative.”
“Respect them enough to have the conversation, because they still have the ability to make decisions about their life.”
Health
Cancer Remission Like Catherine’s Does Not Always Mean the Illness Is Cured

Princess Catherine, wife of Prince William, reported on Tuesday that her cancer was in remission. But what does it mean to be in remission from cancer?
Doctors discovered her cancer unexpectedly last March when she had abdominal surgery. She has not revealed the type of cancer she has, nor how advanced it was when it was discovered.
But she did say she had chemotherapy, which she said had been completed in September. She told the British news agency PA Media that she had a port, a small device that is implanted under the skin and attached to a catheter that goes into a large vein. It allows medicines like chemotherapy drugs to be delivered directly to veins in the chest, avoiding needle sticks.
Catherine told PA Media that chemotherapy was “really tough.”
“It is a relief to now be in remission and I remain focused on recovery,” she wrote on Instagram.
Her announcement “certainly is good news and is reassuring,” said Dr. Kimmie Ng, associate chief of the division of gastrointestinal oncology at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston.
But cancer experts like Dr. Ng say that the meaning of remission in a patient can vary.
In general, when doctors and patients talk about remission, they mean there is no evidence of cancer in blood tests or scans.
The problem is that a complete remission does not mean the cancer is gone. Even when a cancer is “cured” — defined as no evidence of cancer for five years — it may not be vanquished.
That makes life emotionally difficult for patients, who have to have frequent visits with oncologists for physical exams, blood tests and imaging.
“It’s really scary,” Dr. Ng said. “The amount of uncertainty is very very hard,” she added.
But that ongoing surveillance is necessary, despite the toll it takes on patients.
“Different cancers have different propensities of returning or not returning,” said Dr. Elena Ratner, a gynecologic oncologist at the Yale Cancer Center.
As many as 75 to 80 percent of ovarian cancers, she noted, can come back in an average of 14 to 16 months after a remission, depending on the stage the cancer had reached when it was found and on the cancer’s biology.
“Once the cancer returns, it becomes a chronic disease,” Dr. Ratner said. She tells her patients: “You will live with this cancer. You will be on and off chemotherapy for the rest of your life.”
Dr. Ratner’s gynecological cancer patients have to come back every three months for CT scans to keep an eye out for evidence that the cancer has returned.
“The women live CT scan to CT scan,” she said. “They say that for two and a half months, they have a wonderful life, but then, in time for the next CT scan, the fear returns.”
“It costs them — it costs them a lot,” she said.
“It’s awful, yet I am amazed every day by their strength,” she said of her patients.
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoOzempic ‘microdosing’ is the new weight-loss trend: Should you try it?
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg) Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoMeta is highlighting a splintering global approach to online speech
-

 Science4 days ago
Science4 days agoMetro will offer free rides in L.A. through Sunday due to fires
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoLas Vegas police release ChatGPT logs from the suspect in the Cybertruck explosion
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week ago‘How to Make Millions Before Grandma Dies’ Review: Thai Oscar Entry Is a Disarmingly Sentimental Tear-Jerker
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoMichael J. Fox honored with Presidential Medal of Freedom for Parkinson’s research efforts
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: Millennials try to buy-in or opt-out of the “American Meltdown”
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoPhotos: Pacific Palisades Wildfire Engulfs Homes in an L.A. Neighborhood














