Health
Breathe In, Breathe Out: 5 Breathing Methods That May Ease Dry Eyes, Heartburn, and Brain Fog, Science Shows

“Take a deep breath” — it’s advice you’ve probably both given and received. Slowing down and focusing on your breathing allows you to center yourself and reassess things; it helps you think more clearly and feel better mentally. But did you know that breathing exercises — or breathing in a way that requires certain steps — can help you feel better physically as well? See how breathing, the thing you’re doing all the time anyway, can be used as a tool for better health, according to science.
How can breathing exercises help me?
You already know breathing is important. We take about 17,000 breaths a day, yet never give it a second thought. For something we do so often, it’s important to know that how you breathe can make a difference on your body, too. For example: According to an animal study published in Science, breathing through your nose increases blood flow to your brain, triggering feelings of tranquility on a neurological level. Breath is the key to good health, and mastering certain breathing exercises can help in a wide variety of ways, from erasing stress to taming a heartburn flare.
For Dry Eyes: Try ‘Belly Breathing’
For the 61 percent of women over 50 with dry eye, help is here. Three minutes of “belly breathing” may boost women’s tear production significantly, as shown in a randomized controlled trial published in The Ocular Surface. The reason? Belly breathing calms the parasympathetic nervous system, which regulates tear-producing lacrimal glands. To do: Inhale through your nose for four seconds as your belly rises, then exhale through your nose for six seconds as your belly falls. Repeat for three minutes.
For Heartburn: Try the 4-7-8 Trick
You’re not just imagining it — you really may be getting heartburn more often when you’re stressed out. A study published in Digestive Diseases and Sciences found stress nearly doubles your odds of heartburn, since it slows digestion. When food stays in your stomach, it stretches the “plug” that blocks acid. The fix: Inhale for four seconds, hold for seven, then exhale for eight. Repeat for three minutes. Research from The American Journal of Gastroenterology suggests deep breathing like this may even cut the need for heartburn meds.
For Brain Fog: Practice Deep Breathing
Deep breathing may clear mental cobwebs, reveals research from Frontiers in Psychology. What’s more, a study published in PLoS One found that some soldiers practiced something called “tactical breathing” — during which they breathed deeply — were more focused, even when under pressure. (Note: More research is necessary, because not all soldiers experienced beneficial effects from tactical breathing.)
To do: Imagine a square in front of you. As you trace each side of the box in your mind, inhale for four seconds, hold for four, exhale for four, then keep your lungs empty for four to complete the box. Repeat four times.
For Anxiety: Try ‘Cyclical Sighing’
A Cell Reports Medicine study found “cyclical sighing” (exhaling as if giving a sigh of relief) may calm worries in five minutes. Why? It may signal the brain that an urgent event is over and it’s time to relax. To do: Inhale through your nose until your lungs are mostly full. Pause, then inhale again. Pause, then exhale slowly through your nose. Repeat for five minutes.
For Pain: Try a Pillow Squeeze
If pain flares, gently squeeze a pillow and breathe deeply. A study published in PLoS One shows that it may engage the diaphragm and slow your breathing rate to 10 breaths a minute — a pace proven to calm the nervous system. Research in The Journal of the International Association for the Study of Pain says 20 minutes of this type of breathing may block pain signals.
A version of this article originally appeared in our print magazine, Woman’s World.
ARNICARE FOR PAIN AND BRUISES!
Powered by Arnica montana, Arnicare® is designed to treat muscle pain, swelling, and discoloration from bruising. The unscented gel cools on contact and absorbs quickly into your skin, leaving no sticky or greasy residue, and provides you with the relief you seek. Learn more at Arnicare.com.

Health
Young girl survives cancer thanks to little sister’s lifesaving donation: 'A perfect match'
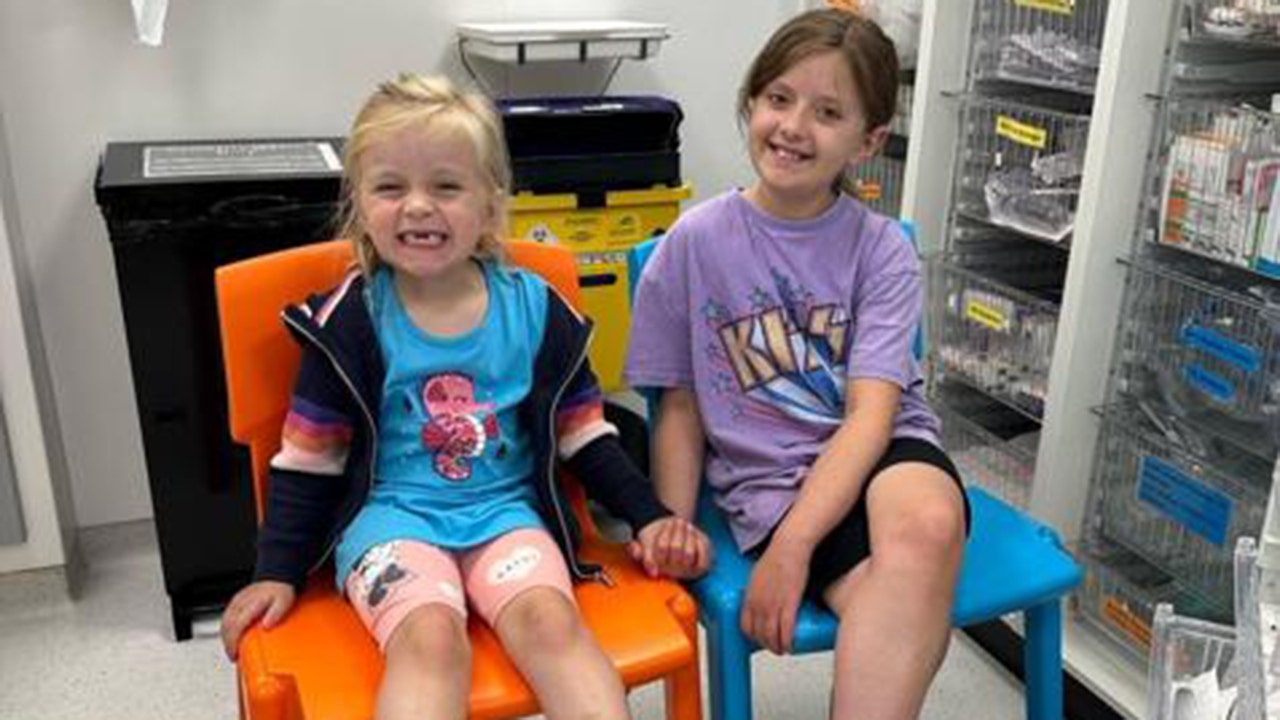

A young girl in the U.K. is in cancer remission thanks to her sister’s lifesaving bone marrow donation.
Ruby Leaning, 10, was diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia after collapsing on the school playground in Jan. 2020, according to SWNS, the British news service.
The rare blood cancer required an urgent bone marrow transplant to keep the 6-year-old alive.
AI COULD PREDICT WHETHER CANCER TREATMENTS WILL WORK, EXPERTS SAY
After several tests, Leaning’s then 2-year-old sister, Mabel Leaning, came up as a “perfect match.”
The Leaning sisters’ grandmother, Amanda Fawcett, confirmed to SWNS that Ruby Leaning received treatment with Mabel Leaning’s stem cells.
Sisters Mabel Leaning, left, and Ruby Leaning hold hands in the hospital. The younger sister saved the older one with a bone marrow transplant. (Amanda Fawcett via SWNS)
Ruby Leaning was declared cancer-free in 2022 — meaning Mabel Leaning “saved Ruby’s life for sure,” Fawcett said.
“She’s a happy, normal and healthy 10-year-old who loves swimming, dancing and piano lessons.”
“We [weren’t] expecting her to be a match at first, but thankfully she was, so we just couldn’t believe our luck,” she said.
“It was amazing – we were so thankful.”
SOME BREAST CANCER PATIENTS COULD BE AT RISK OF ANOTHER TYPE OF CANCER, STUDY REVEALS
Fawcett recalled the moment her granddaughter was diagnosed with cancer at Sheffield Children’s Hospital.
“It’s just every parent and grandparent’s nightmare,” she said to SWNS.
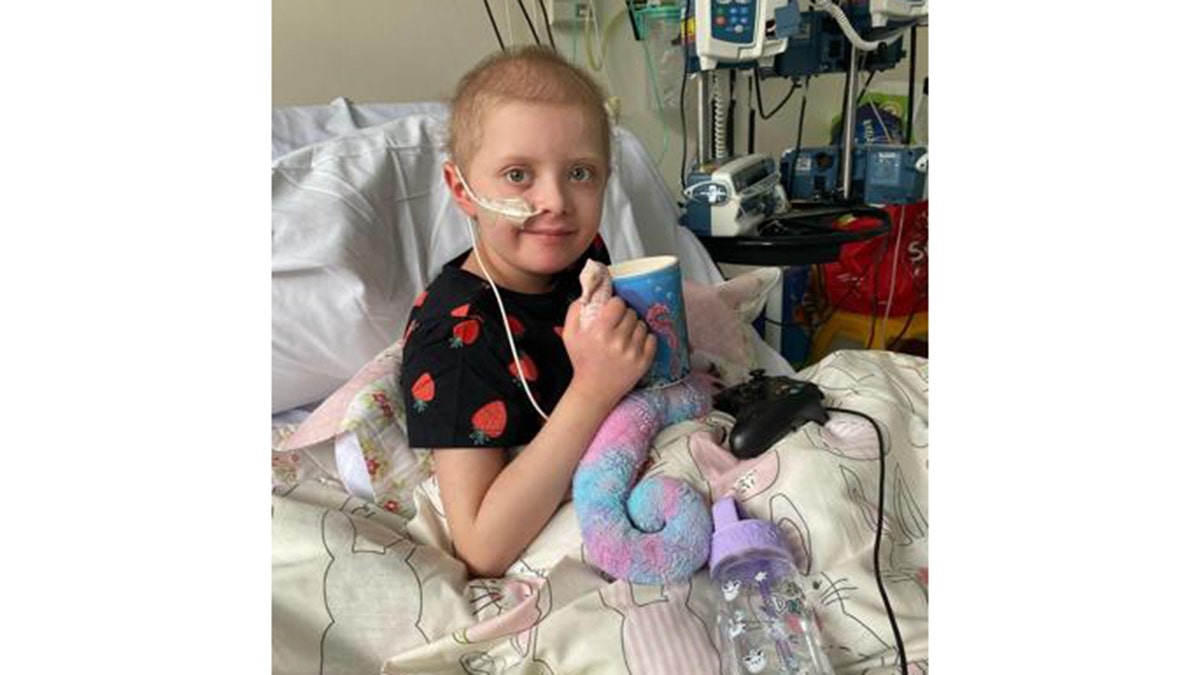
Ruby Leaning, pictured in the hospital, was diagnosed with acute leukemia in 2020. (Amanda Fawcett via SWNS)
“I was in the room with her mom when we found out, and you just can’t take anything in at all. It was all just heart-shattering.”
Fawcett described her granddaughters as “so close,” telling SWNS that they are “amazing girls.”
“They’ve got a great relationship between them,” she said.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“But Mabel will be asking to borrow Ruby’s shoes when she realizes [she saved her life] – and we do laugh about how it will be fun and games.”
Fawcett said Ruby Leaning has been “doing fantastic” in remission and is “back to her normal self.”
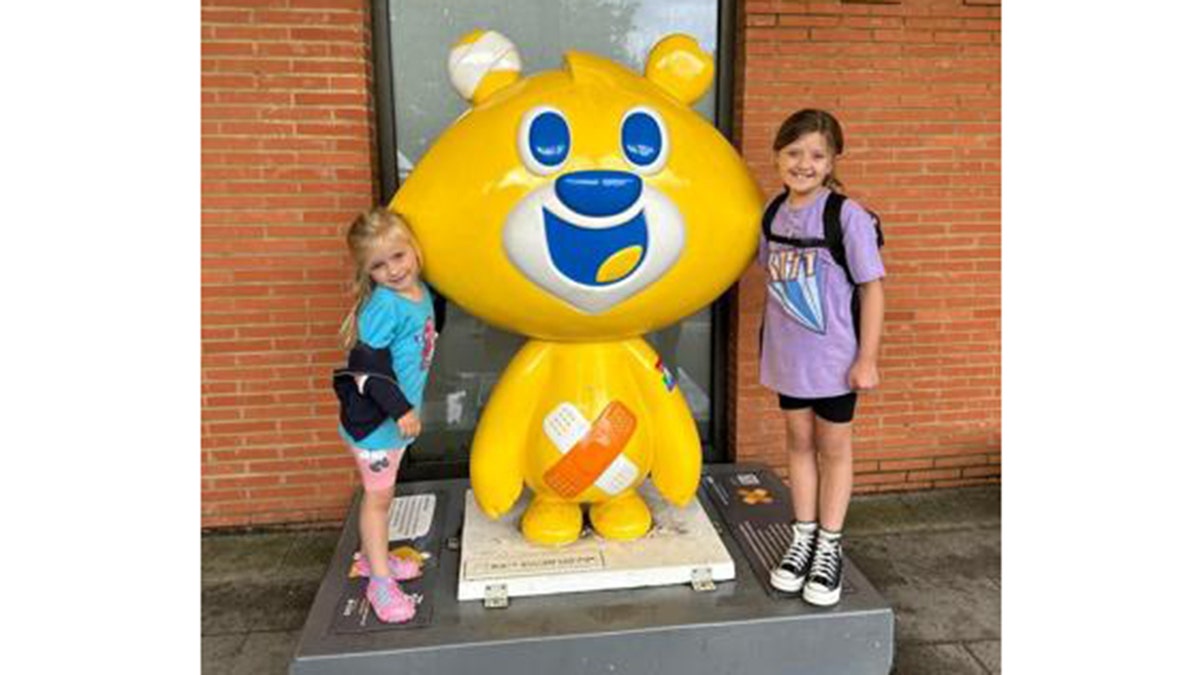

Ruby and Mabel Leaning have “a great relationship between them,” grandmother Amanda Fawcett said. (Amanda Fawcett via SWNS)
“She’s a happy, normal and healthy 10-year-old who loves swimming, dancing and piano lessons,” she said.
The grandmother is currently raising money for the Parents Association of Children with Tumors and Leukemia (PACT), which supported the Leaning family, according to SWNS.
“None of us could be there for Ruby, which was horrendous for us, because of the pandemic,” Fawcett shared.
“But they were an amazing support.”
Fox News Digital reached out to Sheffield Children’s Hospital for additional comment.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.
Health
Alan Hale Jr: 16 Facts About the Skipper from 'Gilligan's Island'

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
Alzheimer's drug embrace slows down as US doctors' reluctance grows

Nine months into the U.S. launch of the first drug proven to slow the advance of Alzheimer’s, Eisai and Biogen’s Leqembi is facing an unexpected hurdle to widespread use: an entrenched belief among some doctors that treating the memory-robbing disease is futile.
Alzheimer’s experts had anticipated bottlenecks due to Leqembi’s requirements, which include additional diagnostic tests, twice-monthly infusions and regular brain scans to guard against potentially lethal side effects.
And those issues have played a role in slow adoption since the drug was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, according to interviews with 20 neurologists and geriatricians from rural, urban, academic and community practices in 19 states.
FDA FULLY APPROVES ‘NOVEL’ ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE DRUG LEQEMBI, WILL BE COVERED BY MEDICARE
In interviews with Reuters, seven doctors treating patients for Alzheimer’s attributed their own reluctance to prescribe Leqembi to concerns about the drug’s efficacy, cost and risks.
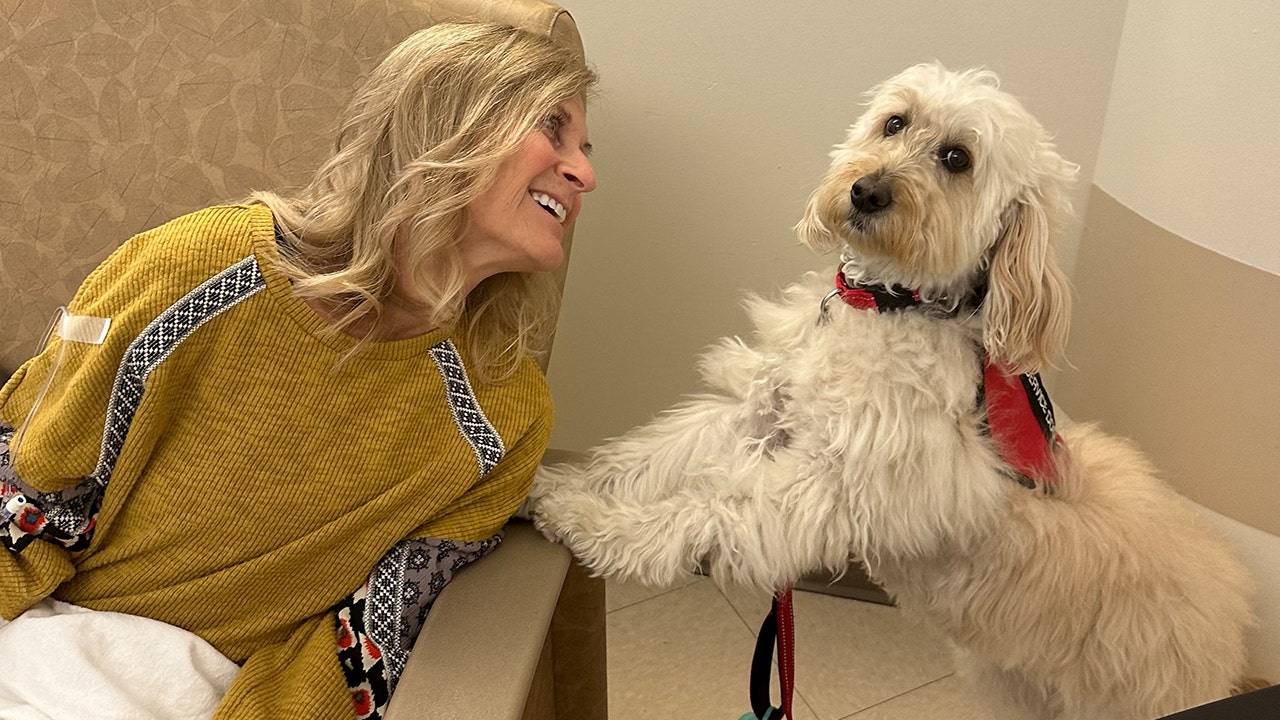
The use of the FDA-approved Alzheimer’s drug, Leqembi, has slowed down as doctor’s skepticism increases, while patients like Lyn Castellano in St. Louis continue to use the drug as it offers a sense of hope for her future. (Joe Castellano/Handout via REUTERS)
“I don’t think it’s a good Alzheimer’s drug. I think that’s the problem,” said Dr. James Burke, a neurologist at the Ohio State University who has been an outspoken critic of Leqembi. “It’s certainly nothing like the home run that we’re looking for.”
Another six scientists, all leaders in the field, said “therapeutic nihilism” – the belief that Alzheimer’s is a hopelessly intractable disease – was playing a bigger role than anticipated in suppressing demand from primary care doctors, geriatricians and neurologists who could be sending patients to memory specialists for treatment.
Dr. Reisa Sperling, a neurologist and Alzheimer’s researcher at Mass General Brigham in Boston, likens some doctors’ skepticism to Leqembi to fatalistic attitudes about cancer treatment 30 years ago: “You can’t really do anything about it, so why would you even want to get tested?”
Alex Scott, Eisai’s chief administrative officer, acknowledged that skepticism has weighed on the launch along with slower-than-expected adoption by large health systems.
He suggested that some of the doctors’ hesitancy could be a holdover from the decades-long journey to prove that removing the Alzheimer’s protein beta amyloid from the brain could slow the course of the disease. Before Esai released the promising results of its Leqembi trial, some thought that area of research “a fool’s errand,” Scott said.
“We are beginning to make more and more progress every single month. So we’re still quite encouraged,” Scott said. “This is a new journey, and I think it takes some time for providers to figure it out.”
‘SIGNIFICANT RISKS, MARGINAL BENEFIT’
Leqembi was the first amyloid-targeting drug granted full FDA approval after it slowed the decline in cognition in people in the early stages of Alzheimer’s by 27% in a clinical trial.
Of the 10,000 Americans the companies hoped to treat by the end of March, Eisai announced only a couple thousand had begun treatment as of the end of January. An Eisai spokeswoman declined to provide updated numbers.
Even for treatments that do not require dramatic changes to medical practice, adoption of new drugs is notoriously slow. Several studies have estimated that it can take 17 years on average for clinical research to be translated into routine practice.
The disease is estimated to affect more than 6 million Americans, according to the Alzheimer’s Association.
NEW DEMENTIA DRUG ‘HAS GIVEN ME HOPE’: ALZHEIMER’S PATIENTS REVEAL THEIR STORIES
Fewer than half of U.S. neurologists recommend Leqembi to patients, according to a January survey by life sciences market researcher Spherix Global Insights.
Dr. Michael Greicius, a professor at Stanford University’s Center for Memory Disorders, said there is little evidence that Leqembi benefits patients in a meaningful way.
“If we take the trial result at face value, the differences between placebo and treatment are likely small enough as to be undetectable by patients and family members or physicians,” said Greicius, who does not recommend Leqembi to patients.
He said the long wait for an Alzheimer’s drug has put doctors in the position of feeling obligated to offer a treatment “even if the evidence for it is very slim.”
Other doctors have raised concerns about the risk of brain swelling and bleeding associated with Leqembi as well as the costs associated with the $26,500 annual drug, frequent MRIs and twice-monthly infusions.
“There are significant risks associated with these drugs, there are significant costs, and I would say there is marginal benefit,” said Dr. Eric Widera, a geriatrician and professor at University of California San Francisco, referring to amyloid-lowering treatments.
In an editorial published in November in the Journal of Gerontological Nursing, Donna Fick, president of the American Geriatrics Society, advised doctors that the group recommends caution in the use of lecanemab, which is sold under the brand name of Leqembi.
“It is not yet clear whether treatments such as lecanemab that remove amyloid from the brain produce clinically important slowing of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease.”
‘YOUR ENEMY IS NIHILISM’
Dr. Jonathan Liss, a neurologist from Columbus, Georgia, who serves on Eisai’s scientific advisory board and has tested Leqembi in clinical trials, said he first warned about nihilism at a November 2022 conference following a presentation of Leqembi’s breakthrough study.
Eisai had asked its scientific advisors how the drug might fare against future rivals. Liss cautioned that rivals were not the enemy; “your enemy is nihilism,’” he recalled. “All of the neurologists around the table started applauding.”
FIRST DRUG PROVEN TO SLOW ALZHEIMER’S WON’T BE AVAILABLE TO MOST PATIENTS FOR SEVERAL MONTHS
Dr. Nathaniel Chin, a geriatrician with the University of Wisconsin’s Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center, said he was the target of negative comments on social media after he urged geriatricians to embrace such treatments in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
Geriatricians, geriatric social workers and nurses objected, arguing that the drug’s statistically significant benefit was not clinically meaningful to patients, especially given the risks, he said.
“I would ask the question, ‘Is it ethical to withhold a medication that is FDA-approved and covered by insurance from someone who knows the risk and is willing to take it?’” Chin said.
Dr. Priya Singhal, executive vice president and head of development at Biogen, acknowledged some apathy among physicians about the treatment but said that infrastructure and lack of access to neurologists have been bigger issues.
Singhal said the companies are working with physician and patient advocacy groups and developing educational programs and materials aimed at diagnosing early-stage patients, managing side effects and understanding the drug’s benefits.
The companies said they intend to increase their salesforce by 30% as they aim for 100,000 patients by 2026.
For the moment, Leqembi is the only Alzheimer’s drug on the market designed to slow the course of the disease. A decision on Lilly’s donanemab has been delayed until the FDA convenes an advisory panel.
Lilly neuroscience president Anne White said in an interview that she sees doctor hesitancy as an issue that the company hopes to address by making clear which patients benefit from such treatments.
In the early stages of Alzheimer’s, many patients are still independent, and to be able to remain so for longer is very meaningful, she said.
‘PEACE AND QUIET’
Lyn Castellano, 64, who founded and ran a St. Louis breast cancer charity for 20 years and trained therapy dogs, started taking Leqembi last September, nearly a year after she found herself struggling with keeping track of appointments and was diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment.
Castellano said the prospect of bleeding in the brain – a possible side effect of the drug – was her biggest concern, but her family believed the drug may offer a chance at slowing the disease.
She is one of more than 140 patients being treated by physicians from Washington University in St. Louis, and has had 13 infusions and two MRIs without incident.
Dr. Suzanne Schindler, an Alzheimer’s researcher who is treating Castellano, said Leqembi “forces clinicians to completely change the way they have practiced medicine for many years.”
She said she is candid about Leqembi’s modest benefit as well as the risks. About 80% of those she believes are good candidates have opted for the treatment, she said.
While Castellano can’t tell if Leqembi is helping, she says the treatment has given her hope, and she doesn’t mind the twice monthly infusions.
“I get to go, sit back in a nice chair, have my dog with me and read a book for a couple hours. It’s about the only place I get some peace and quiet.”
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNine questions about the Trump trial, answered
-

 World6 days ago
World6 days agoIf not Ursula, then who? Seven in the wings for Commission top job
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoHungary won't rule out using veto during EU Council presidency
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoFilm Review: Season of Terror (1969) by Koji Wakamatsu
-

 World7 days ago
World7 days agoCroatians vote in election pitting the PM against the country’s president
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoGroup of EU states should recognise Palestine together, Michel says
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoTrump trial: Jury selection to resume in New York City for 3rd day in former president's trial
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoThe Take: How Iran’s attack on Israel unfolded
















