Business
Businesses Brace for Currency Chaos in Asia, a Region With a History of Crisis

Tigun Wibisana and Sandra Kok, who personal the SiTigun cafe on Penang Island in Malaysia, are dealing with an excruciating determination that might make or break their enterprise of 14 years: Can they improve costs to cowl rising bills with out driving prospects into the arms of their greater rivals?
The price of the espresso beans that the couple, who’re married, purchase is spiraling as a result of they’re traded globally in U.S. {dollars}, and the Malaysian ringgit has fallen to a 24-year low. Compound that with an inflationary spike in costs for butter and flour, important components for its pastries, and the store’s income have plunged greater than 25 p.c this 12 months.
“Finally we could have to boost costs to outlive, however I don’t have the heart to do it now,” stated Mr. Wibisana, 65, who roasts the beans and makes the baked items.
SiTigun is one among many companies in Asia which are being squeezed by the energy of the greenback, which has soared to report ranges this 12 months. America’s foreign money is used extensively to purchase and promote items around the globe, and its hypervalue is exacerbating the ache of surging costs for power and different imports attributable to the conflict in Ukraine and the pandemic.
All through Asia, from the Vietnamese dong to the Philippine peso, currencies are tumbling to report lows, the kind of widespread foreign money weak spot not seen because the 1997 monetary disaster. That has unnerved companies and policymakers who recall how a string of Asian currencies folded underneath the stress of a powerful greenback.
To reduce the chance of that form of calamity, policymakers are scrambling to stabilize their currencies. The State Financial institution of Vietnam raised rates of interest by a full proportion level final month after Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh implored the central financial institution to behave. The dong had fallen for 9 straight days to a 29-year low.
The identical day Vietnam raised rates of interest, Japan, the place the yen has dropped round 25 p.c in opposition to the greenback this 12 months, introduced it will intervene to strengthen its foreign money for the primary time since 1998. In China, the place the renminbi is buying and selling close to 14-year lows, the central financial institution has taken a collection of measures to gradual the foreign money’s depreciation, together with warning speculators in opposition to making bets on it.
Heightening the alarm, the greenback — powered by essentially the most fast Federal Reserve rate of interest will increase in many years — exhibits no indicators of slowing. It’s up almost 20 p.c in opposition to a gaggle of main currencies from a 12 months in the past.
In Asia, the difficulty dealing with native currencies has resurfaced the collective trauma of 25 years in the past, when pleasure over the area’s dazzling progress turned a disaster seemingly in a single day.
Extra on the Relations Between Asia and the U.S.
The chaos began in Thailand when the nation’s central financial institution ran out of the {dollars} it was utilizing to maintain its personal foreign money steady and again its loans. It rapidly unfold to South Korea, Indonesia and different nations as they struggled to cushion their falling currencies. Speculators who had charged into the area en masse anticipating large returns retreated simply as rapidly.
By the top of 1997, the Worldwide Financial Fund had organized greater than $100 billion price of assist for Thailand, Indonesia and South Korea to stop their monetary programs from collapsing. The subsequent 12 months, the economies of the nations on the coronary heart of the disaster retreated sharply: 13.7 p.c in Indonesia, 9.7 p.c in Thailand, 6.7 p.c in Malaysia and 5.8 p.c in South Korea. Governments struggled with company bankruptcies and political instability.
“It was very insulting, humiliating and devastating, and I feel the area will always remember it,” stated Hoe Ee Khor, chief economist at ASEAN+3 Macroeconomic Analysis Workplace, often known as AMRO, a gaggle that helps the Chiang Mai Initiative, an settlement amongst Asian nations to pool funds to assist each other in a money disaster. “However due to that, they have been decided to by no means let it occur once more, they usually took the painful medication to reform.”
Most economists and monetary market analysts imagine there’s little threat {that a} comparable disaster will unfold throughout the area. At the least not but. Asian economies are essentially stronger than earlier than, they are saying, and the painful classes discovered from the meltdown spurred them to construct monetary programs designed to stop future collapses.
Nations have undergone a number of main adjustments which have made their economies a lot much less inclined to a powerful greenback than they have been within the late Nineties. For one factor, they’ve a lot much less debt borrowed in {dollars}: The scale of native foreign money bond markets in 10 Southeast Asian nations, plus Japan, China and South Korea, is about 123 p.c of their collective gross home product, in contrast with 74 p.c in 2000, in response to AMRO.
Many Asian central banks that used to maintain their trade charges in step with the dollar now enable them to fluctuate with market forces. Whereas meaning extra unstable trade charges, it additionally relieves some pent-up stress that may set off a collapse.
And most Asian nations have extra international foreign money coming in than going out, permitting them to sock away important reserves that they will deploy in an emergency to complement imports or defend their very own foreign money from depreciating.
Consequently, Asia right now is “in a lot better form than every other area on the planet,” stated Sayuri Shira, a professor of economics at Keio College and former member of the Financial institution of Japan’s coverage board.
Nonetheless, the robust greenback is testing the area’s defenses, forcing central banks to make use of their conflict chests to prop up their currencies — primarily by shopping for their very own currencies and promoting {dollars}. India and Thailand have spent greater than 10 p.c of their reserves on interventions this 12 months, spending $75 billion and $27 billion within the international trade markets, in response to estimates from Nomura Holdings.
Corporations are having to adapt as falling currencies blow up their provide chains and put stress on their income.
Suh Jin, an govt at Mirage Furnishings on the outskirts of Seoul, stated the corporate imports $15 million to $20 million price of dwelling furnishings in a mean 12 months. However Mirage Furnishings, which buys most of its merchandise from Vietnam with U.S. {dollars}, has needed to lower its imports by 10 p.c since Might due to the weakening gained, which is buying and selling close to 13-year lows in opposition to the U.S. greenback.
Whereas South Korea was in a position to emerge from the 1997 monetary disaster pretty rapidly, Mr. Suh stated, he’s apprehensive that the corporate could have to put off employees if the robust greenback and excessive inflation persist.
“We concern that the present scenario will last more,” he stated.
The robust greenback has affected even companies that not often use it.
Traditional Japan, a flower importer in Tokyo, had lengthy paid its South East Asian distributors in yen. However sellers hungry for worthwhile {dollars} have begun providing their merchandise elsewhere, making it troublesome to acquire some uncommon flowers, corresponding to orchids.
“Home manufacturing is falling, so we wish to import extra,” stated Kio Nishio, the corporate’s president. However the present scenario has made that troublesome, he stated.
Some firms, in fact, can profit from a powerful greenback, which might carry company backside traces in nations like South Korea which are closely export centered. In Japan, buying and selling firms and main producers like Toyota which have substantial abroad enterprise have gotten a wholesome revenue enhance from belongings and earnings held in {dollars}.
On the SiTigun cafe in Malaysia, the total affect of the weak ringgit won’t be felt till months from now, when the following crop of beans has labored its method by farmers and middlemen to their espresso pots.
“The pandemic has already affected many companies, after which inflation got here as one other problem,” stated Ms. Kok, who manages the store. “However inflation and foreign money hits everybody. How will we survive?”
Liani MK contributed reporting from Penang, Malaysia; Hisako Ueno from Tokyo; and Jin Yu Younger from Seoul.

Business
Hollywood, accusers condemn reversal of Weinstein conviction: 'We know what happened'
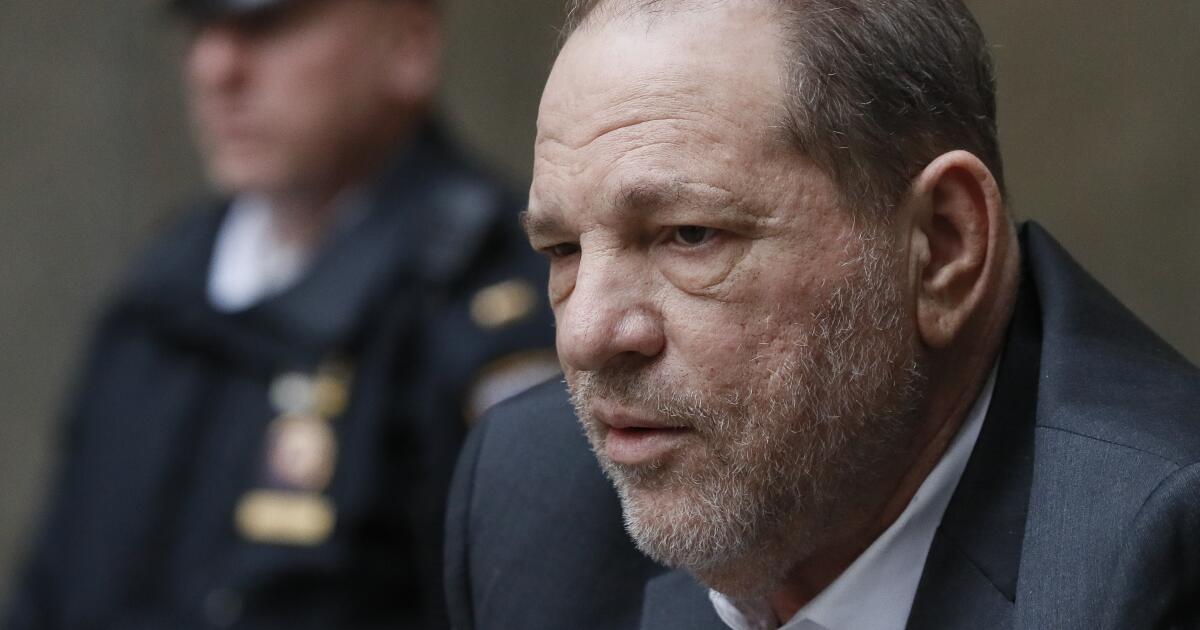

Harvey Weinstein’s accusers and opponents of sexual violence in Hollywood and beyond are speaking out against the reversal of the disgraced movie mogul’s rape conviction in New York.
Ashley Judd, Mira Sorvino and others who have accused the former Hollywood producer of sexual misconduct condemned a New York court of appeals’ decision on Thursday to overturn the verdict.
Weinstein has been serving a 23-year sentence since he was convicted in 2020 of rape and a felony sex crime after allegedly assaulting former production assistant Mimi Haley and once-aspiring actor Jessica Mann.
“This today is an act of institutional betrayal. And our institutions betray survivors of male sexual violence,” Judd said during a news conference at the Millennium Hilton hotel in New York . “I stand shoulder to shoulder with women who have bloody knees because male sexual violence may knock us down, but we get right back up. And together we are in the struggle for freedom from male entitlement to our bodies.”
“This is unfair to survivors,” Judd added on her Instagram story. “We live in our truth. We know what happened.”
Tarana Burke, founder of the #MeToo movement, remarked during the news conference that “moments like this underscore why movements are necessary and … why we keep going.”
“We are devastated for the survivors who are connected to this case and the survivors who have found some solace and catharsis in the original verdict,” Burke said. “We will always stand with resolve and resilience. … This is not a blow to the movement. It is a clarion call, and we are prepared to answer that call.”
The New York appeals court found, in a 4-3 decision, that the judge who presided over Weinstein’s trial prejudiced the case by allowing four women who said Weinstein had assaulted them to serve as witnesses, even though their allegations were not part of the case.
The trial judge also made a mistake, the court determined, in permitting prosecutors to question Weinstein about uncharged and decades-old allegations if he decided to testify.
Weinstein was also convicted of rape in California and the New York ruling will have no practical effect on his imprisonment.
Sorvino wrote on X that she was “horrified” by the news, which surfaced during Sexual Assault Awareness Month.
“Since when don’t courts allow evidence of pattern of prior bad acts to be admitted?” Sorvino said. “He’s a prolific serial predator who raped/harmed 200+women! Disgusted w/justice system [skew toward] predators not victims.”
Weinstein has denied all allegations of sexual assault.
The Silence Breakers — a coalition of 23 women who have accused Weinstein of sexual misconduct that includes actors Judd, Rose McGowan and Rosanna Arquette — issued a statement calling the reversal “disheartening” and “profoundly unjust.”
“This ruling does not diminish the validity of our experiences or our truth; it’s merely a setback,” the Silence Breakers said.
“The man found guilty continues to serve time in a California prison. When survivors everywhere broke their silence in 2017, the world changed. We continue to stand strong and advocate for that change. We will continue to fight for justice for survivors everywhere.”
Anita Hill, chair and president of the Hollywood Commission, said in a statement that Thursday’s reversal evinces “a lack of progress in addressing the power imbalances that allow abuse to occur” and proves that “sexual assault continues to be a pervasive problem.”
“Many survivors do not pursue justice because they believe nothing will be done,” Hill added.
“Today’s decision underscores the urgent need for systemic changes in our institutions — and redoubles our commitment to survivors to push for the policies and systems that will ensure accountability and bring about workplaces free from the behavior that drives the need for these systems in the first place.”
Attorney Douglas Wigdor — who has represented eight Weinstein accusers, including two of the witnesses at the New York criminal trial — denounced Thursday’s decision as “a major step back in holding those accountable for acts of sexual violence.”
“Courts routinely admit evidence of other uncharged acts where they assist juries in understanding issues concerning the intent, modus operandi or scheme of the defendant,” Wigdor said in a statement.
“The jury was instructed on the relevance of this testimony and overturning the verdict is tragic in that it will require the victims to endure yet another trial.”
In a statement provided to The Times, a spokesperson for the Manhattan district attorney’s office said, “We will do everything in our power to retry this case, and remain steadfast in our commitment to survivors of sexual assault.”
Times staff writer Jenny Jarvie contributed to this report.
Business
'The bane of retail.' To prevent theft, many big chains now lock up all kinds of merchandise

Detergent and deodorant, toothpaste, the entire shampoo aisle.
“It’s all locked up,” Corey Potter sighed, describing shelves encased behind security glass at a Target near her Echo Park home. “I hate it.”
Potter recalled once waiting 15 minutes for an employee to unlock a case at another Target location. These days, if she sees several other shoppers waiting for too few frenzied workers, the 30-year-old video editor typically skips items on her list and later does something she doesn’t feel great about: buys more home essentials on Amazon.
“Rather than go to Target and wait,” she said, shrugging, “I’ll just give Daddy Bezos my hard-earned cash.”
Shoplifting is as old as shopping itself. And retailers have long played a game of cat and mouse with thieves, searching for ways to thwart them while still giving paying customers easy access to merchandise.
The true severity and scope of the problem remain an enduring mystery of the free market, as national chains eagerly point to retail theft as a key drag on profits, but are reticent to publicly discuss internal numbers on shrink — the industry term for theft and other types of loss — or specifics of new anti-theft measures. Adding to the murkiness, the issue has become more politicized in recent years as some voters and elected officials in Los Angeles, San Francisco and other city centers clamor for a response to what they see as a worsening problem.
But what is clear to anyone who has shopped at a drug, grocery or home improvement store in L.A. in recent years is that retailers are increasingly resorting to the drastic step of barricading entire swaths of their stores behind lock and key.
Using a tactic once reserved for a few pricey, high-demand items — cold medication, electronics, baby formula and razors to name a few — big chains now routinely lock up almost every type of merchandise. A shopper looking to grab a box of condoms or a $1.99 set of crayons, ointment to remove calluses or a container of instant coffee, now often has no choice but to hit a button to summon a store employee with a key and wait.
Executives focused on their companies’ bottom lines are no happier about taking the drastic step to deter shoplifters. Although they’re in the business of selling as much as possible, they’ve been left to make the seemingly backward calculation that thefts require them to make it harder for paying customers to buy things.
“Locking a product,” a spokesperson for CVS said in an email, “is a measure of last resort.”
Retail theft has become a priority for California leaders in recent years.
In September, Gov. Gavin Newsom sent $267 million to cities and counties to increase arrests and prosecutions of organized retail crimes. A few weeks earlier, L.A. Mayor Karen Bass announced a task force focused on such crimes, following a string of robberies at high-end stores such as Gucci and Yves Saint Laurent that garnered a flurry of media attention and helped further cement a new phrase into the zeitgeist: A smash-and-grab.
In February, California Atty. Gen. Rob Bonta filed criminal charges against a woman he called the ringleader of a retail theft group prosecutors say stole nearly $8 million in beauty products to resell on her Amazon storefront. And last week, the coalition behind a tough-on-crime ballot initiative that would roll back the landmark Proposition 47 by stiffening penalties for some retail thefts in California submitted enough signatures that it appears the measure will go before voters in November.
The initiative was bankrolled largely by big chains, including Walmart, Target and Home Depot.
While the companies work publicly to change California law, they are taciturn about discussing their efforts to stop shoplifters, making it hard to quantify how much more merchandise is now locked up and which stores have embraced the strategy.
Representatives for several of the region’s largest retailers — Target, Vons, Rite Aid and CVS — either didn’t respond to requests to discuss internal deliberations on stemming theft or sent brief statements about their anti-theft measures.
David Johnston, vice president of asset protection and retail operations at the National Retail Federation, said that locking up more merchandise is “an unfortunate necessity” to combat theft and what he characterized as a rise in organized retail crime and violent incidents in stores.
Toothbrushes are among the many products now locked behing security glass at a Target in Pasadena.
(Ryan Fonseca / Los Angeles Times)
Retailers know that the additional supplies and labor needed to lock up more merchandise cut into their bottom line and frustrate customers, Johnston said, but some have decided it’s a necessary trade-off to keep shelves stocked with often-stolen items such as baby formula and medications.
“Right now, the best approach in many instances is putting it behind lock and key,” Johnston said. “These measures are last-ditch efforts.”
Joe Budano, the chief executive of Indyme, a San Diego-based company that makes buttons to beckon sales associates to specific aisles, estimated that frustration over waiting for locked merchandise leads to a 10% to 25% reduction in sales, calling the cages “the bane of retail.”
His company also has developed technology — the Freedom Case, they call it — that allows shoppers to open cases themselves using personal information such as their cellphone number or by scanning their face.
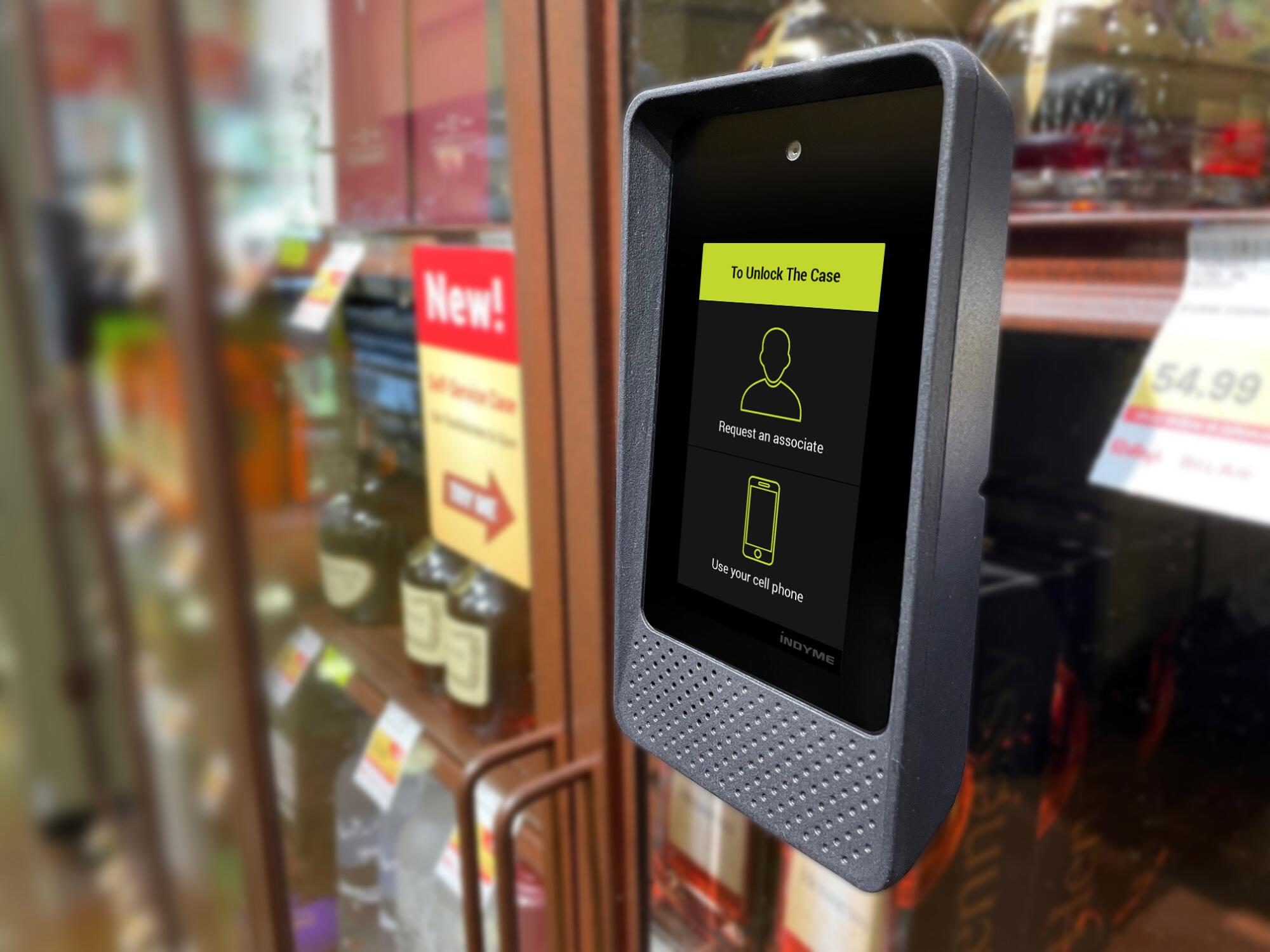

The Freedom Case, technology developed by a San Diego-based company called Indyme, allows shoppers to open locked merchandise themselves using personal information such as their cellphone number.
(Joseph Budano)
More than 40 retailers are testing the Freedom Case in stores, Budano said, including a national chain he declined to name.
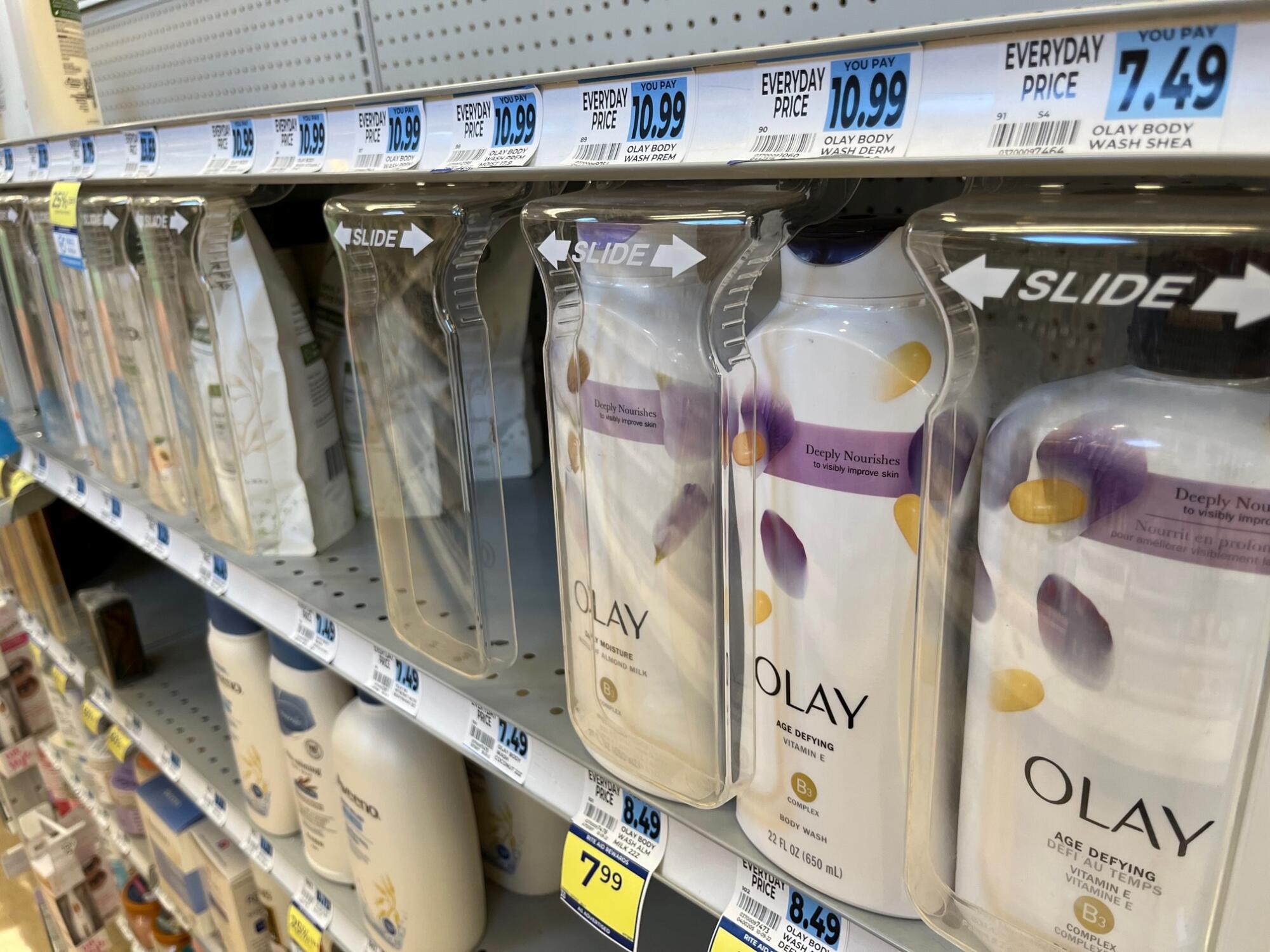
To combat theft, Budano said, companies often scrutinize missing merchandise using individual SKUs, the most granular data possible.
“They know all the way down to which flavor of Oil of Olay is most stolen,” he said. “The pace at which things have gotten locked up tells you the magnitude of the problem.”
But that magnitude — which retail industry groups say has reached “unprecedented” and “epidemic” levels, despite data showing such characterizations are overblown — varies by city.
The Council on Criminal Justice, a nonpartisan research organization, tracked shoplifting trends in 24 cities from 2019 to the middle of 2023 and found that rates were down in more than two-thirds of the cities. New York City and L.A. were the two biggest exceptions, logging increases of 64% and 61%, respectively.
Even in light of the recent surge in L.A., the rate of reported shoplifting incidents in L.A. County in late 2022 was slightly lower than it had been 2014, according to a report from the Public Policy Institute of California, a nonpartisan think tank that analyzed state Department of Justice statistics. During that eight-year period, only three of the state’s 15 most populous counties — all in the San Francisco Bay Area — saw increased rates of shoplifting, a misdemeanor crime defined as stealing goods valued at less than $950.
The report’s author, Magnus Lofstrom, said that rates of reported shoplifting dropped in much of the state, including L.A. County, when stores emptied out during the 2020 shutdowns. But the region saw a steady rise in the summer of 2021, he said, and by late 2022, the most recent data at the time of his report, the rate was at least 10% above the pre-pandemic level.
In recent months, several companies, including the 99 Cents Only chain and Target, have cited theft or shrink as a reason that factored into their decisions to shutter locations.
Charis Kubrin, a professor of criminology at UC Irvine who studies retail theft, said that although some stores lock up lots of merchandise, others cage almost nothing.
“It’s kind of an uneven distribution,” she said. “A mixed bag.”
A Times analysis from 2022 found that stores in higher-income areas locked up fewer items even in places where property crime rates were higher, creating an additional burden for shoppers in certain neighborhoods. And inconsistencies in how locked merchandise is released to customers — sometimes workers hand you items to put in your cart, other times they escort merchandise to the register — raise the same questions of racial profiling that have long plagued retail establishments.
“The owners and employees have wide-scale discretion,” Kubrin noted.

Security devices at Walgreens are designed to slow down shoplifters.
(Hugo Martin / Los Angeles Times)
The scale of merchandise theft, Kubrin added, is sometimes overblown by a retail industry happy to pin its problems, which include market forces such as inflation and a shift to online shopping, on stolen merchandise.
Crime, she acknowledged, is part of the equation. As a consumer, Kubrin distilled her frustration with locked merchandise down to the same word many other shoppers used: “Annoying.”
A man posted on TikTok recently that CVS was treating a bag of Werther’s Original caramel candies like a controlled substance and on Reddit someone said the anti-theft measures should force an entire genre of retailer to rebrand themselves:
“Inconvenience store.”
In interviews with five employees at retail locations across the Southland, workers said rushing to unlock merchandise for often-peeved customers has made their slammed shifts more hectic.
“I apologize a lot and I get yelled at a lot,” said a supervisor at a Vons in Pasadena.
But several workers said they understood their employers’ decisions, noting that around late 2021 or early 2022, they’d noticed an uptick in people putting multiples of a single piece of merchandise into big bags and walking out — boosters, as they call shoplifters they suspect will resell the merchandise.
The criminal complaint filed by Bonta’s office this year included text messages suggesting that the defendants, who prosecutors say targeted beauty retailers Ulta and Sephora, used that method.
“I’m not stealing regular I’m going to start filling up my bag quick,” one defendant wrote. “I want to know stuff I can grab.”
Rogelio Madrigal, a shift supervisor at a CVS in San Pedro, started 16 years ago and has noticed changes through the years.
There was a time, he said, when the main thing they locked up was Sudafed. Eventually, items such as Plan B and razors got added and then, a couple years ago, he noticed more people swiping Tide Pods. Now, he mainly sees people walk out with boxes of diapers and cosmetics.

Laundry detergent items are stored in the Freedom Case.
(Joseph Budano)
“It was happening before,” he said, “but not as bad as now.”
On a recent morning at a Rite Aid in East Hollywood, the lone cashier greeted customers who walked through a doorway lined with security alarm panels.
“Welcome in,” he said.
Many of the aisles were lined with anti-theft mechanisms, including red magnets at the end of metal prongs holding items like eyelash curlers and an individual plastic cage around a $22 box of lice treatment. Some sections, including all the toothpaste and most of the detergent, were locked behind long, clear cages.
A customer steadying himself with a cane peeked through a cage at a bottle of Tide and shrugged, settling instead on a small container of Persil, one of the few non-caged detergents, before walking to the register.
At a nearby Vons, the greeting cards and candy were out on shelves, but an assortment of school supplies, including a ruler for $1.47, was locked up.
In the medication aisle, a woman with a full cart sighed when she realized that one of the last items she needed — a small bottle of Claritin, an allergy medication — was locked up. She pressed the button and an automated refrain that, during busy hours, rings out like the store’s soundtrack played: “Thank you, someone will be with you shortly.”
Less than a minute later, when a worker with a key ring rounded the corner, her eyes widened in surprise.
“That was fast!” she told him.
“We try,” he said.
Business
Questions swirl over the future of TikTok. Who could own it? How will the platform operate?

TikTok on Wednesday faced a formidable threat to its business, with a new law signed by President Biden that could dramatically change the way the popular video app operates.
TikTok, which is owned by Chinese company ByteDance, has faced scrutiny from U.S. government officials over how it handles the data of its users here as well as its ties to China. The new law would require ByteDance, a tech company founded in China in 2012, to sell TikTok or the app will be banned in the U.S.
In a statement, TikTok said it has invested billions of dollars to protect the data of its U.S. users and that a ban would “devastate seven million business and silence 170 million Americans.”
The social media app, which has a large presence in Culver City, is a key platform for influencers, musicians and Hollywood talent.
“This unconstitutional law is a TikTok ban, and we will challenge it in court,” TikTok said in a statement. “We believe the facts and the law are clearly on our side, and we will ultimately prevail.”
Now that Congress has voted to ban TikTok, how soon could a sale occur?
The law requires ByteDance to sell TikTok’s U.S. operations in 180 days or face a ban . If the Biden administration grants an extension, ByteDance could have a year to sell .
This isn’t the first time the app has faced such a threat. The company confronted a similar fate four years ago when the Trump administration banned it in the U.S.
TikTok sued the federal government, arguing that a ban would violate free speech. Ultimately, the order was blocked by two federal courts, which ruled the administration had exceeded its authority.
“It’s obviously a disappointing moment, but it does not need to be a defining one,” TikTok Chief Executive Shou Zi Chew said in a video posted on X on Wednesday. “It’s actually ironic because the freedom of expression on TikTok reflects the same American values that make the United States a beacon of freedom.”
Any sale of TikTok would also need the approval of the Chinese government.
How valuable is TikTok and who might buy it?
The most valuable aspect of TikTok is its algorithm, which surfaces videos that aim to consistently attract the attention of its users in the U.S.
“TikTok’s ability to serve up relevant and entertaining content to its users is unparalleled in the social media world,” Jasmine Enberg, a principal analyst with insights provider Emarketer, said in a statement.
Enberg noted that U.S. users spend 54 minutes on TikTok each day, compared with 35 minutes a day on Instagram’s app.
If ByteDance sells TikTok with its algorithm — which is unlikely — the platform would be worth $100 billion. Without the algorithm, TikTok would have a valuation of $30 billion to $40 billion, said Daniel Ives, a managing director with Wedbush Securities.
The most likely bidders? Computer software giants Microsoft and Oracle, analysts said.
“This would be a major strategic asset that would enable these tech stalwarts to have a massive consumer platform,” Ives said. “Data is gold, and TikTok would be like finding a gold mine for a tech stalwart.”
Microsoft declined to comment. Oracle did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
Microsoft in August 2020 had explored taking control of TikTok in the U.S., Canada, New Zealand and Australia, which would have helped the company expand its presence in social media. But in September 2020 Microsoft said that ByteDance had rejected its offer.
Instead, then-President Trump outlined a framework of a deal in 2020 that involved Oracle and Walmart, in which Oracle would host TikTok’s U.S. user data and TikTok would have a commercial partnership with Walmart. That transaction never materialized.
Other investors have also shown interest. Former Treasury Secretary Steven T. Mnuchin, who heads Liberty Strategic Capital, in March said he is assembling an investor group to bid for TikTok, telling CNBC, “This should be owned by U.S. businesses.”
TikTok will attract interest from other private equity players as well, Ives said.
What about Triller?
Triller, an L.A.-based social media company that attracted a lot of influencers to its app in 2020, had previously attempted to acquire TikTok with Centricus Asset Management.
But that deal was never consummated and Triller experienced its own legal issues. Earlier this month, Hong Kong financial services company AGBA Group Holding Ltd. said it planned to acquire Triller in a reverse merger.
“Triller is reviewing all options at this time to secure its position as the leading social video platform in the U.S.,” Triller Chief Executive Bobby Sarnevesht said in a statement.
Could Google or Meta acquire TikTok?
That’s unlikely. Google, which owns YouTube, and Meta, which owns Instagram and Facebook, are already big leaders in the digital advertising and social media space and could face significant antitrust concerns if they were to attempt to buy TikTok.
Both tech giants also already have their own competing products to TikTok and stand to benefit if the video app were to go away, or if influencers were to encourage their massive audiences to follow them on other platforms.
“The clock is already ticking, and any potential buyer must have deep pockets and a strong stomach,” Enberg of EMarketer said. “While many would want to get their hands on TikTok’s coveted algorithm, most of those who could afford to buy the app wouldn’t be able to clear antitrust hurdles.”
So what would a ban mean for the creator economy in L.A.?
Los Angeles is ground zero for TikTok content creation in the U.S., with huge numbers of full-time creators calling the city home and droves of influencers regularly flying in from around the world to film videos and attend industry events.
Communities and mini economies have formed around TikTok influencers, who employ talent managers, agents, stylists and personal assistants, and start their own businesses related to their fandom.
Many creators have become overnight sensations and near-instant millionaires, banding together to rent mega-mansions and spending lavishly on cars, clothes and products — and encouraging their huge follower bases to do the same.
They have enormous influence on trends and purchasing decisions. Take, for example, Erewhon: After TikTokkers made its Strawberry Glaze Skin Smoothie a thing, thousands of consumers poured into the luxury grocery chain’s stores to buy the $19 pink drink.
“The amount of money creators are spending on travel, on products, on creating brands — there’s just so much that’s tied to this app,” said Michelle York, 40, a lifestyle and beauty creator from Moorpark, Calif.
With 203,000 followers on TikTok, she quit her job as an executive at an insurance and technology firm last month after discovering that she was earning more money from the app. If TikTok is banned, “the blowback I think will be astronomical,” York said. “And also the financial losses.”
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIf not Ursula, then who? Seven in the wings for Commission top job
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoFilm Review: Season of Terror (1969) by Koji Wakamatsu
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoGOP senators demand full trial in Mayorkas impeachment
-
 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: The American Society of Magical Negroes
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoShort Film Review: For the Damaged Right Eye (1968) by Toshio Matsumoto
-
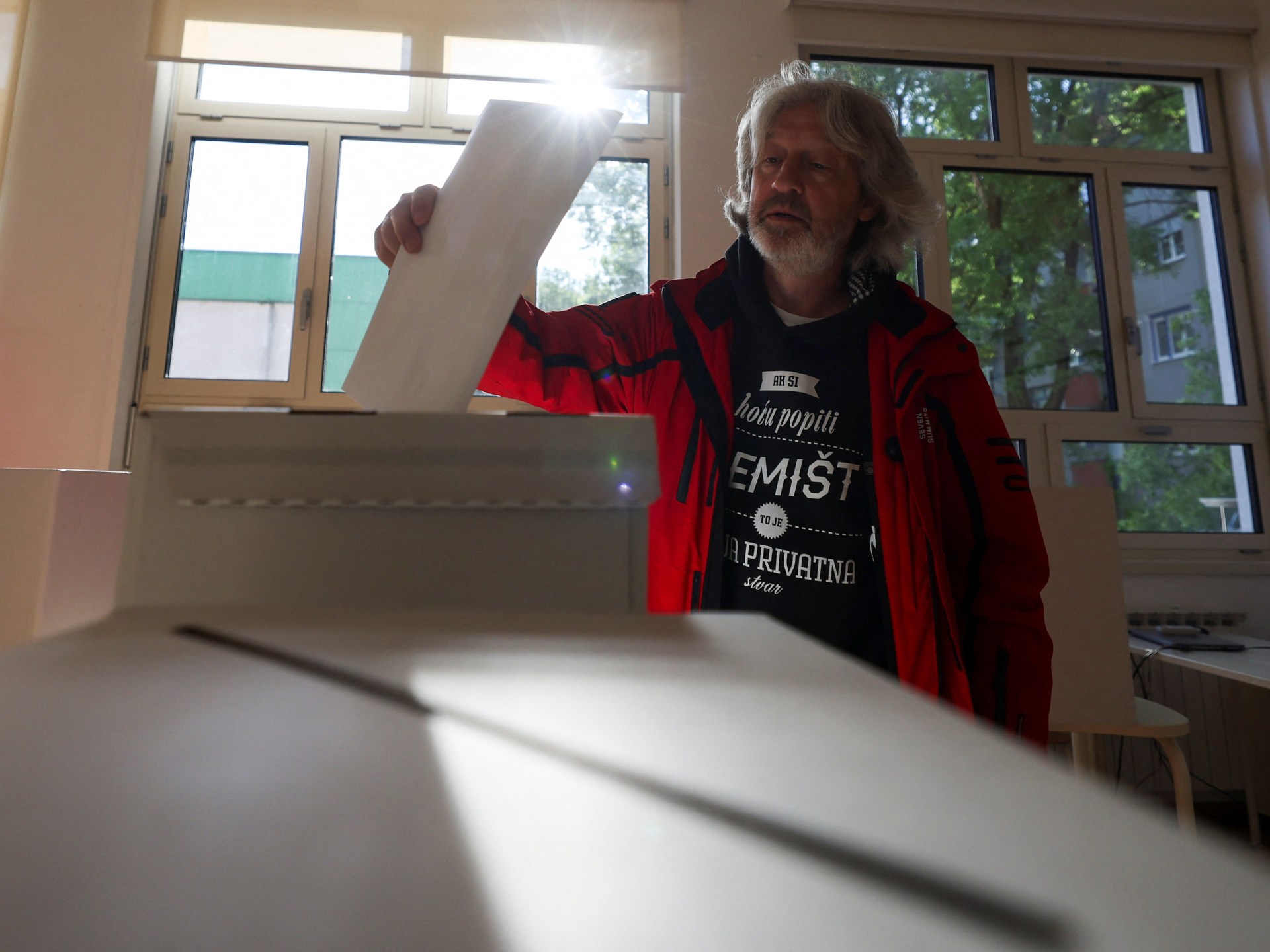

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCroatians vote in election pitting the PM against the country’s president
-
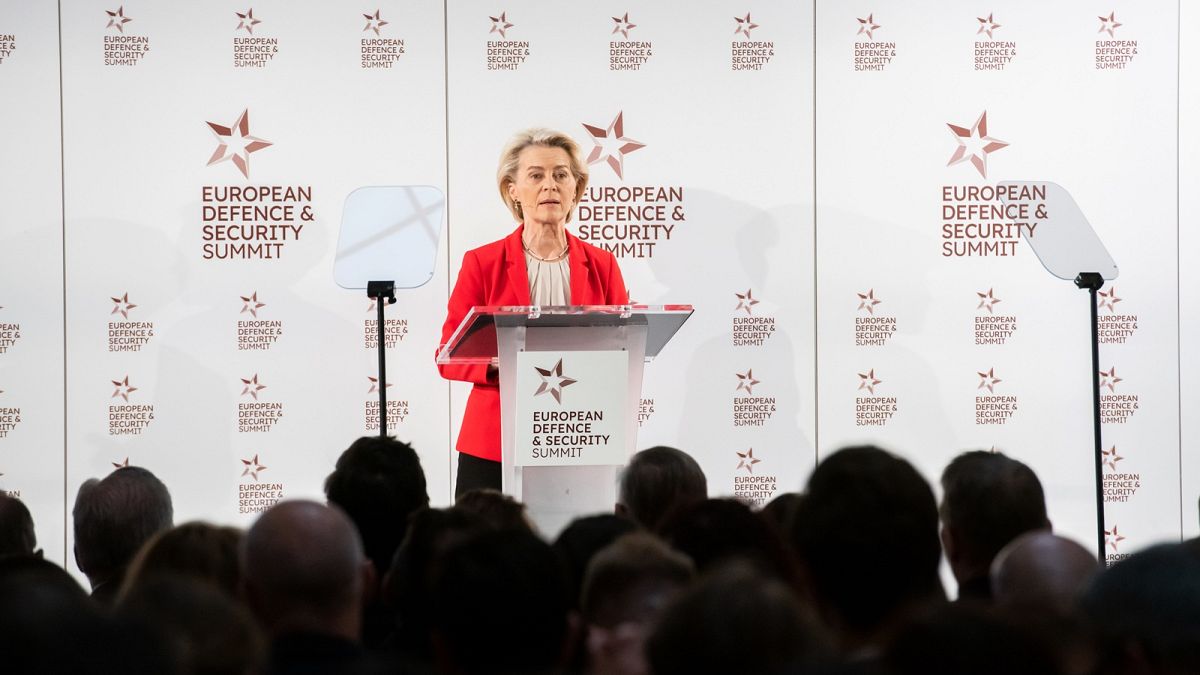

 World1 week ago
World1 week ago'You are a criminal!' Heckler blasts von der Leyen's stance on Israel
-
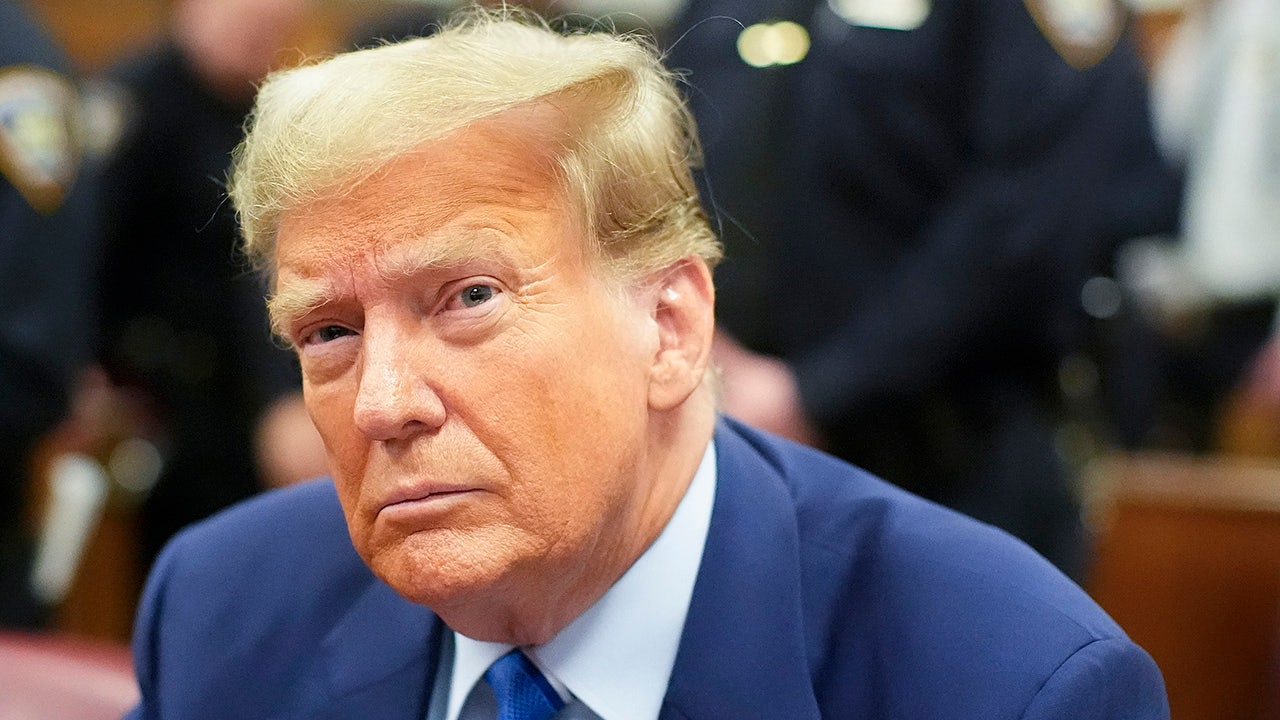

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTrump trial: Jury selection to resume in New York City for 3rd day in former president's trial